Quiz (Closed book quiz): Name:
1. Calculate the output voltage (V0) of the circuit Fig.1. Vs= 10V, RS=12, RL=8
Fig.1
Solution
Add some marker A, B, I in the circuit
Rtotal=R S + R L =12+ 8=20
V s 10
I= = =0.5 A
R total 20
V o =V AB=I∗R L =0.5∗8=4(V )
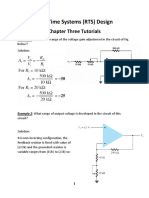
2. Calculate the output current (i0) of the circuit Fig.2. is= 1A, RS=12, RL=8
Fig.2
Solution
� R S∗R L 12∗8
Rtotal=R S /¿ R L= = =4.8
R S + R L 12+ 8
V AB=I S∗Rtotal=1∗4. 8=4 .8 (V )
V AB 4. 8
I 0= = =0 .6 ( A)
RL 8
3. Given a circuit shown in Fig.3. Determine the potential at points: VA, VB, VE, VF and VAB
Fig.3
Solution
The potential at a point is the voltage between that point to the ground. In the circuit, there is no
ground. Therefore, we cannot determine the potential at points: VA, VB, VE, VF
We only know the voltage VAB=5V
4. Given a circuit shown in Fig.4. Determine the potential at points: VA, VB, VE, VF and VAB
Fig.4
Solution
�The potential at a point is the voltage between that point to the ground. In the circuit, there is no
ground.
VE=0 (V); VF=0 (V); VA =0 (V); VB= -5 (V)
VAB=5 (V)
5. Given a circuit shown in Fig.5. Calculate the potential at point: VA, VB, VC, VF, VE, VD, iS1, iS2
and VBE
Fig 5
Solution
As shown in Fig.5, C connects to ground => VC=0, A also connects to ground => VA=0.
However, the difference voltage between A and C is 15 V => the circuit is wrong. We cannot
determine the potential at point: VA, VB, VC, VF, VE, VD, iS1, iS2
6. A small-signal circuit model for a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is shown in Fig.6.
Determine the voltage vo, if vS=5sin(100πt)V, Rs = 5 k, r = 2.5 k, gm = 40 mA/V, ro =
100 k, and RL = 5 k.
Fig 6
Solution
v S∗r ❑ v S∗2.5 v S
v be= = =
RS + r❑ 5+2.5 3
� v 0=−gm v be∗(r 0 /¿ R L )
100∗5
(r 0 /¿ R L )= =4.76( K )
100+5
(mA /V )∗v S
−gm v be =−40 =66.67 sin ( 100 πt ) (mA)
3
Finally
v 0=−gm v be∗(r 0 /¿ R L )= 66.67 sin ( 100 πt ) ( mA )∗4.76 ( K ) =317 sin ( 100 πt ) (V )