0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views15 pagesYear 9 Algebra: Equations & Solutions
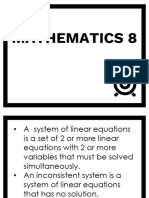
Chapter 4 covers various algebraic concepts including expressions, expansions, indices, fractions, and solving equations. It provides detailed examples on solving simultaneous linear equations using both elimination and substitution methods. The chapter is designed for Year 9 students to enhance their understanding of algebra.
Uploaded by
AMMA'S KITCHENCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views15 pagesYear 9 Algebra: Equations & Solutions
Chapter 4 covers various algebraic concepts including expressions, expansions, indices, fractions, and solving equations. It provides detailed examples on solving simultaneous linear equations using both elimination and substitution methods. The chapter is designed for Year 9 students to enhance their understanding of algebra.
Uploaded by
AMMA'S KITCHENCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd