Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FLUID MECH - Statical Stability of Floating Bodies
Uploaded by
Jezreel AskenazimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FLUID MECH - Statical Stability of Floating Bodies
Uploaded by
Jezreel AskenazimCopyright:
Available Formats
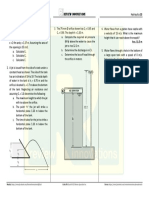
73. A small metal pan of length 1 m, width 20 cm and depth 4 cm floats in water.
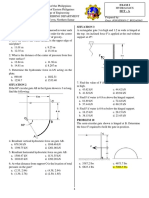
When a uniform load of 15 N/m is applied as shown in Fig. DD, the pan assumes the figure shown. Find the weight of the pan and the magnitude of the righting moment developed. 76. A cylindrical caisson has an outside diameter of 6m and floats in fresh water with its axis vertical. Its lower end is submerged to a depth of 6m below the water surface. Find: a) the initial metacentric height; b) the righting couple when the caisson is tipped through an angle of 10. 77. A rectangular scow 9.15 m wide by 15.25 m long has a draft of 2.44 m in fresh water. Its center of gravity is 4.60 m above the bottom. Determine the height of the scow if, with one side just at the point of submergence, the scow is in unstable position. 78. A rectangular scow 9.15 m wide by 15.25 m long and 4.60 m high has a draft of 2.75m. Its center of gravity, transversely and longitudinally, is at the center of the scow. If the scow is tipped transversely until one end is at the point of submergence, find the righting couple. 79. A rectangular raft 3 m wide and 6 m long has a thickness of 60 cm and is made of solid timbers (sp. Gr. 0.60). If a man weighing 890 N steps on the edge of the raft at the middle of one side, how much will the original water line on that side be depressed below the water surface? 80. The timber shown in Fig. EE is 30 cm square and 6 m long, having a specific gravity of 0.50. A man standing at a point 60 cm from one end causes that end to be just submerged. Find the weight of the man. 81. A submarine of 10,700 KN displacement has its center of gravity 30 cm from its center of volume. What is the righting couple when it is submerged in the sea water and the angle of heel is 5. 82. A log 30 cm in diameter weighs 4900 N/m3. What is its shortest length so that it may float in water with the axis horizontal? 83. A block of wood is 15 cm square and 30 cm long. What is the specific gravity of the wood if the metacenter is at the same point as the center of gravity of the wood when the block is floating in water on its side. Would it be stable floating on its end? Explain. 84. Fig. FF shows a scow equipped with derrick with boom 5.50 m long. What maximum weight could be picked by the boom at its end along the longitudinal side in order that water will not enter the scow? Assume the weight of the boom to be negligible and consider its position to be always horizontal.
You might also like
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 5Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Lesson 5AlejandroGonzagaNo ratings yet
- ES 65 Problem Solving Drill I (12/10/08)Document2 pagesES 65 Problem Solving Drill I (12/10/08)edmark icalina83% (6)
- Vertical forces-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesVertical forces-WPS OfficeJesusa EstradaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- FluidsDocument2 pagesFluidsPatrick AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics10 Neric10Document12 pagesHydraulics10 Neric10jrmmansayonNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 4Document3 pagesActivity Sheet 4Shiebastian ArietaNo ratings yet
- Energy Equation - Flow MeasurementDocument11 pagesEnergy Equation - Flow MeasurementAsa Ka50% (2)
- Seatwork 4Document11 pagesSeatwork 4Emer67% (6)
- Problem Set#8 PDFDocument29 pagesProblem Set#8 PDFMark Genesis VelonzaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Discharge, Engergy and Head, Power and EfficiencyDocument14 pages1.1 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Discharge, Engergy and Head, Power and EfficiencyJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Set 2Document3 pagesHydraulics Set 2cielo_cetd3670100% (1)
- PROBLEMS For Orifice and WeirsDocument1 pagePROBLEMS For Orifice and WeirsIrene Grace Batalao50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- 1S1920 - SW - Fluid Mechanics: Name DateDocument12 pages1S1920 - SW - Fluid Mechanics: Name DateBosz' AceNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1547387158279Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1547387158279menma chanNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lesson 4Document3 pagesFluid Mechanics Lesson 4AlejandroGonzagaNo ratings yet
- BatteryExam MathDocument6 pagesBatteryExam MathjadeNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Exam 2Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Exam 2Jan Jan AnoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems: Palara, Arman S. (Inc) SPL Ce 5BDocument23 pagesExercise Problems: Palara, Arman S. (Inc) SPL Ce 5BKristel LenonNo ratings yet
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- 115Document10 pages115Memo LyNo ratings yet
- Ce Board Strength ReviewerDocument1 pageCe Board Strength ReviewerZherrinore RasayNo ratings yet
- No Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set ADocument4 pagesNo Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set AAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics ReviewerDocument146 pagesHydraulics ReviewerKarl Anne DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ri Engineering Econ 2 CompressDocument1 pageRi Engineering Econ 2 CompressMel Macairy NavarroNo ratings yet
- NCESQ 2018 QuestionsDocument3 pagesNCESQ 2018 QuestionsMelanio VillaverdeNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowDocument14 pages4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Lesson - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Lesson - Water HammerEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- Ce ReferenceDocument1 pageCe ReferenceOwen Francis Arles MaongatNo ratings yet
- EVAL 4 pt.1 - XPERTZ CE REVIEWDocument22 pagesEVAL 4 pt.1 - XPERTZ CE REVIEWSteven ValerioNo ratings yet
- Ce Reviewer MathDocument16 pagesCe Reviewer MathfuturecivilengineerNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Trigonometry and Surveying: Excel - Ri Ce Review Specialist, IncDocument4 pagesPart 1 - Trigonometry and Surveying: Excel - Ri Ce Review Specialist, IncKurapika Freccs ZoldyickNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument18 pagesHydraulicsJeff MagliaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - FLUIDSDocument7 pagesExperiment 5 - FLUIDSJoeNo ratings yet
- Exam in Fluids1Document4 pagesExam in Fluids1Prince Winderic Gaza AclanNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Document8 pagesCollege of Engineering, Computer Studies and Architecture: Problem Sets in Hydraulics (HYDL01E)Ria LauronNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - FluidsDocument9 pagesExperiment 8 - FluidsJL CleofeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1Kenn Fabre100% (2)
- Ce140 PS 3 PDFDocument1 pageCe140 PS 3 PDFAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- Fluids MechanicsDocument5 pagesFluids MechanicsKhale Kyrzhal RamirezNo ratings yet
- Final Quiz Problems To Be MadeDocument16 pagesFinal Quiz Problems To Be MadeRyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Review 1Document8 pagesReview 1Lyka Jane Pesigan100% (1)
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1eduardwhocares100% (1)
- Strength of Materials-Moving LoadsDocument48 pagesStrength of Materials-Moving Loadscmrayos100% (3)
- Assignment in HydaraulicsDocument9 pagesAssignment in HydaraulicsJhona PancitoNo ratings yet
- HYDRO VesselsDocument5 pagesHYDRO VesselsMarvinPatricioNarca0% (1)
- S1 FM Buyyancy T+answersDocument18 pagesS1 FM Buyyancy T+answersprabathiyaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Problem SetDocument2 pagesHydraulics Problem SetHo BiNo ratings yet
- Assgn 3Document2 pagesAssgn 3shishirNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3BDocument6 pagesTutorial 3Bnexowa9068No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Review ProblemsDocument9 pagesHydraulics Review ProblemsrojethtrinidadNo ratings yet
- CECA 2 Problem Set No. 03Document11 pagesCECA 2 Problem Set No. 03carldomingoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Problem SetDocument4 pagesFluid Problem SetJupissa Espinosa100% (1)
- Flid Mechanics AssignmentDocument2 pagesFlid Mechanics AssignmentAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- A Classic Guide to Building Punts and Canoes - Including Construction Your Own Canvas Canoes and Building a Sailing BoatFrom EverandA Classic Guide to Building Punts and Canoes - Including Construction Your Own Canvas Canoes and Building a Sailing BoatRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Itemize Cost Breakdown & Bill Quantities: /lot /lot /lot /lot /lotDocument4 pagesItemize Cost Breakdown & Bill Quantities: /lot /lot /lot /lot /lotJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Sample Memo No. 1Document1 pageSample Memo No. 1Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Slab Bottom BarsDocument1 pageSlab Bottom BarsJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- PerspectiveDocument1 pagePerspectiveJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- 12Mm Bars Spaced at 100Mm, Bars From Slab Top Bars Extended, Hook at The EndDocument1 page12Mm Bars Spaced at 100Mm, Bars From Slab Top Bars Extended, Hook at The EndJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- 10Mm Temp. Bars Spaced at 300MmDocument1 page10Mm Temp. Bars Spaced at 300MmJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Benliro Residence ModelDocument1 pageBenliro Residence ModelJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Support Detail For Precast Moulding at 2F Hallway-Layout2Document1 pageSupport Detail For Precast Moulding at 2F Hallway-Layout2Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- LabelsDocument1 pageLabelsJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Bink's SakeDocument2 pagesBink's SakeJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Support Detail For Precast Moulding at 2F Hallway-Layout1Document1 pageSupport Detail For Precast Moulding at 2F Hallway-Layout1Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Angelina TrussesDocument1 pageAngelina TrussesJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Hydrologic StudiesDocument39 pagesGroup 1 Hydrologic StudiesJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Mathematics and Surveying May 2013Document7 pagesMathematics and Surveying May 2013Jezreel Askenazim100% (1)
- Salutatory AddressDocument4 pagesSalutatory AddressJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Math Magic: Example 1 Example 2Document1 pageMath Magic: Example 1 Example 2Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- Math Magic: Example 1 Example 2Document1 pageMath Magic: Example 1 Example 2Jezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument1 pageQuestionnaireJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument1 pageQuestionnaireJezreel AskenazimNo ratings yet