0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views36 pagesControl Plan
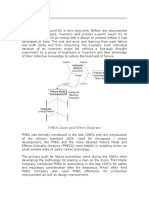
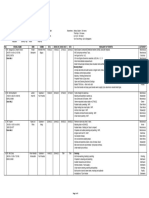
The document outlines the importance of Control Plans and their linkages with FMEA and other quality processes to enhance product quality and reduce variation. It details the types of Control Plans, common mistakes in their development, and the necessary components for effective implementation. Emphasis is placed on continuous improvement, team collaboration, and ensuring that Control Plans are updated and utilized effectively in manufacturing practices.
Uploaded by
FlorinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views36 pagesControl Plan
The document outlines the importance of Control Plans and their linkages with FMEA and other quality processes to enhance product quality and reduce variation. It details the types of Control Plans, common mistakes in their development, and the necessary components for effective implementation. Emphasis is placed on continuous improvement, team collaboration, and ensuring that Control Plans are updated and utilized effectively in manufacturing practices.
Uploaded by
FlorinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd