G 10 1 3D Coordinate Systems
We're going to extend our knowledge of how math works in 2D and extend it to 3D
Points Planes and Axes
Z
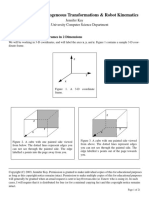
Our new 3D loordinate system adds the z axis and looks like this
C this is often referred to as IR
There are multiple ways you can draw 123 but it HAS to obey the
right hand rule Hold your right hand out have your 4 fingers
point in the positive x axis curl them towards the positive
y axis your thumb needs to point in the positive Z axis
The 3 coordinate axis 11123 creates 3 different coordinate planes
the xz plane created by the x axis andZ axis and squishingthey axis
lou can also see that the 3 planes splitup 1123 into 8 octants in IR we had 4 quadrants The
first octant is the one inthe positive x y and z points Points in 1123 are now writen in x y z
Wecan also do whatisusually referred to as dropping a perpendicularwhere we ignore one axis at a time
so P XY Z would look at lx Y o lx O Z and o Y Z Themoreformal vocabulary is called
ooking at the projection of point P on the xy plane for ix y o and so on and soforth for the
ther projections
example Plotthepoint example Graph thepoints that correspondto all possible
3im 1e projections of P 3,2 4 whatshapedoesthis make
coordinates ofpointP
Z
xample Whatsurfale in IR is represented example whatsurfale in1123 is represented
bythe equation z 3 bythe equation y y
y y
x x
�Distance
thedistance between 2 points in R is calculated using the same distant e formula for R2
except with the added z component
The Distance Formula in 3D
The distance between points P lx Y Z and Palka Y Z written IP Pal is
example Find the distance between P 12 1171 and Q 1 3,5
Equation of a sphere
An equation of a sphere with center C1h k l and radius r is
when the center of the lirae is at 10.0.01 the equation is
example Graph the region in IR is represented by the followinginequalities
I Ex y 2214 and Z E o
This is a filled in with
thathas a cutout
at the center cut on the xy plane
and onlyfocused onthe and
centered at