Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Bio Stuff Term 2
Uploaded by
Eagan ChanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Bio Stuff Term 2
Uploaded by
Eagan ChanCopyright:
Available Formats
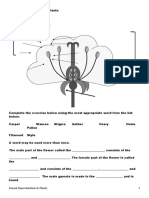
Important things to remember for tomorrow: Plant reproduction
Features of self pollination 1. Flowers are bisexual with the anthers and stigmas maturing at the same time 2. The stigma is situated directly below the anthers 3. Some flowers never open (cleistogamous flowers) Pros and cons of self-pollination Only one parent plant is required Off springs inherits beneficial genes from parent plant Does not depend on external factors (insect or wind) Higher probability (anther closer to stigma) Less pollen and energy is wasted Off springs genes are similar less varieties and less adapted to changes Off springs may become weaker, smaller and less resistant to diseases Features of cross-pollination 1. Flowers are of same gender, if bisexual: stigma and anther positioned far apart, stigma above anthers 2. Anthers and stigma maturing at different times 3. Having structural features (Stigma and Anthers positioned such that pollen grains are deposited from insect to stigma and will drop on insect) 4. Having substances which prevents pollen penetration or growth of pollen tube of the same plant Pros and cons of self pollination Off spring may inherit beneficial qualities from both parents More varieties, greater genetic variation, increasing chance of surviving change in environment thus less likely to destroy all varieties of same species. More viable seeds, can last longer before germination Two parents plants required Dependent on external factors (wind or insect) Lower probability (one plant to another) More pollen and energy wasted
Insect pollination Flowers large, brightly colored and scented to attract insects Nectar present to attract insects Stigma small, contact and does not protrude out Sticky so that pollen grains are not easily displaced Stamens are not pendulous and does not protrude out Nectar guides are present to guide insects towards nectar Pollen grains are heavy, large and sticky with rough surfaces to cling on insects bodies The eye
Wind pollination Flower small, dull and not scented Nectar absent Stigma large and feathery, protruding out to provide a large surface area to trap pollen Long pendulous filaments and protruding anthers that sway easily so that pollen grains are shaken out of anthers Nectar guides absent Pollen more abundant due to high wasted Pollen dry, smooth and light to be easily blown about by the wind
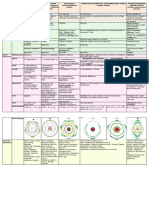
High light intensity falls on fovea of the retina Low light intensity falls on fovea of the retina A nerve impulse is initiated at the photoreceptors and transmitted along the sensory neuron through the optic nerve towards the brain The brain processes the nerve impulse and initiates another nerve impulse which is transmitted along the motor neuron back to the eye At the receptors which is the iris, the nerve impulse causes The circular muscles to contract The circular muscles to relax The radical muscles to relax The radical muscles to contract The pupil constricts The pupil dilates To let less light into the eye To let more light into the eye 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sudden blindness Rods are sensitive to low light intensity because they contain visual purple In high light intensity settings, the visual purple is bleached Nerve impulses cannot be sent to the brain from rods, so the person cannot see Visual purple must be reformed so the person can see It takes awhile for it to form again
Light rays from distal object is parallel Light rays from near object is divergent The ciliary muscles relax The ciliary muscles contract Pulling on the suspensory ligaments Relaxing the pull on the suspensory ligaments Suspensory ligaments taut Suspensory ligaments slackens Pulling on the edge of the lens Relaxing pull on the edge of the lens The lens becomes thinner and more convex The lens becomes thicker and less convex Increasing the focal length Decreasing the focal length Light rays from object are sharply focused on fovea of the retina Photoreceptors are stimulated Nerve impulses produced are transmitted by the optic nerve to the brain The brain interprets the impulses and the person sees the object The nervous system
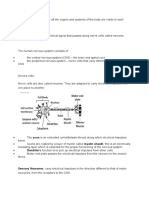
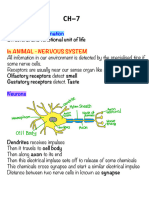
Nerve fibers that transmit impulses towards the cell body are called dendrons The axon is the long fibre that transmit impulses away from the cell body The terminal branches of both axons and dendrons are called dendrites The nerve fibers are enclosed by the myelin sheath A thin membrane, the neurilemma, in turn, surrounds this. Nerve impulse is forced to jump from node to node along the length of the axon, which greatly increases the speed of conduction Impulses transmitted from the axon to Dendron across a minute space are called the synapse. It is done through chemical means through the release of neurotransmitters.
Grey matter Consists mainly of the cell bodies of the neurons. It forms the outer layers of the brain and the central parts of the spinal cord. White matter consists mainly of the nerve fibers. It forms the central part of the brain and the outer layers of the spinal cord. The mixed spinal nerve that is made up of a sensory neuron and a motor neuron. If it is injured, Nerve impulses cannot be transmitted along the sensory neuron towards the brain. Thus, the person cannot feel. Nerve impulses cannot be transmitted along the motor neuron towards the effectors. Thus, the person cannot move. The dorsal root is made up of sensory neurons. If it is injured, Nerve impulses cannot be transmitted along the sensory neuron towards the brain. Thus, the person cannot feel. But he can move, as the motor neuron is not affected. The ventral root is made up of motor neurons. If is injured, He can still feel as nerve impulses can still be transmitted along the sensory neuron to the brain. Nerve impulses cannot be transmitted along the motor neuron towards the effector. Thus, the person cannot move. Light rays from the bottle falls onto the fovea of the retina. Photoreceptors are stimulated Nerve impulses are initiated at the photoreceptors And transmitted along the sensory neuron in the optic nerve towards the brain. The brain interprets the nerve impulse And initiates another nerve impulse which is then transmitted along the motor neuron back to the effectors The muscles contact and Heat stimulates the receptors in the skin. Never impulses are initiated and transmitted along the sensory neuron to the spinal cord. Here, impulses are transmitted along a synapse to the relay neuron and then across the synapse to the motor neuron. Nerve impulses leave the spinal cord along the motor neuron to the effector The muscle contract and
The endocrine system Are produced by endocrine glands; Are transported by the blood to target organs; Alter the activity of one or more target organs; Destroyed by the liver; Excreted by the kidneys. The pituitary gland plays an important role as a controller. It secretes a number of hormones, which controls the functions of several other endocrine glands. Master gland. Also secretes anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas secretes insulin and glucagon Decreased blood glucose concentration by: Increasing the permeability of cell membranes to glucose. Increasing the rate of glucose uptake by cells. Stimulates the liver and muscle cells to convert glucose to glycogen for storage. Increasing oxidation of glucose during tissue respiration. Glucose cannot be stored or utilized by tissue cells. Blood glucose concentration rises. Some glucose is subsequently lost in urine. This gives rise to a disease called diabetes mellitus. Muscle cells have no reserves of glycogen; the body grows weak and continuously loses weight. The body oxidizes fats instead of glucose to produce energy. Results in the production of poisonous substances called ketones that are excreted in urine (ketonuria). Death may occur. Abnormal decrease in blood glucose concentration. Low blood glucose concentration results in a condition called shock. Coma and death may occur. Increases blood glucose levels by speeding up the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver and muscles for respiration Increases metabolic rate, more energy in the form of ATP is released in tissue respiration Increases the rate of heartbeat and causes a rise in blood pressure so that oxygen and glucose are carried faster to the muscles Increases the rate and depth of ventilation Constricts arterioles in skin, causing paleness, thus channeling more blood to the muscles Increases the rate of blood coagulation Causes pupils to dilate to enhance vision Contracts hair muscles, producing goose bumps
You might also like
- Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesCoordination and ResponseDewan Anisha IslamNo ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 14 Coordination and Response - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument8 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 14 Coordination and Response - CAIE Biology IGCSEAmnaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument45 pagesNervous SystemKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- IrritabilityDocument30 pagesIrritabilityAnnesley RobanNo ratings yet
- Coordination 22-23Document14 pagesCoordination 22-23hiNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues QuestionsDocument8 pagesCells Tissues QuestionsMeily ZoelNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 14 Coordination and Response - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument134 pagesFlashcards - Topic 14 Coordination and Response - CAIE Biology IGCSEGopika KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument7 pagesCoordination and ResponseMemona KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2 ReactionsDocument43 pages2 ReactionsTrixie Anne CordovaNo ratings yet
- Form 3 History BookDocument21 pagesForm 3 History BookDISHONNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument11 pagesSummary NotessamNo ratings yet
- Detailed NotesDocument11 pagesDetailed NotesSukhraj SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Bio Class 10Document15 pagesChapter 7 Bio Class 10Aysha KhanNo ratings yet
- Coordination And: ResponseDocument29 pagesCoordination And: ResponseSolángé MirembeNo ratings yet
- Sensation and PerceptionDocument9 pagesSensation and PerceptionMaryam El-GuindyNo ratings yet
- D) COORDINATIONDocument10 pagesD) COORDINATIONamarashah182No ratings yet
- Contro Coordination 1Document7 pagesContro Coordination 1hithendrak.sNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document8 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 pagesControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniNo ratings yet
- Biology - B9 - Summary 1 - IGCSEDocument16 pagesBiology - B9 - Summary 1 - IGCSE《Akari - San》 AMV ; 3No ratings yet
- Notes-Control & Coordination - BIO PPTDocument6 pagesNotes-Control & Coordination - BIO PPTkareebs03No ratings yet
- Biology 12Document11 pagesBiology 12Akili ArmaniNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response IGCSE NotesDocument11 pagesCoordination and Response IGCSE NotesDrRemyaranjith Menon100% (1)
- Coordination (Word)Document5 pagesCoordination (Word)Technical NihalNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Irritability, Sensitivity and CoordinationDocument94 pagesGrade 11 Irritability, Sensitivity and CoordinationAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Control and CordinateDocument12 pagesControl and CordinateHarsh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Coordination - Human Bio HB10Document5 pagesCoordination - Human Bio HB10Zah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesControl and CoordinationkkNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination and Response Noteskavya.gulatiNo ratings yet
- 4A Notes Coordination and ResponseDocument15 pages4A Notes Coordination and ResponsenatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- GCSE OCR GATEWAYBiology - YOUR SENSES AND NERVOUS SYSTEM (Includes About Eyes)Document16 pagesGCSE OCR GATEWAYBiology - YOUR SENSES AND NERVOUS SYSTEM (Includes About Eyes)m4a1_attiyaNo ratings yet
- Psychology E ProjectDocument46 pagesPsychology E ProjectShrutiNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Class NotesDocument13 pagesControl and Coordination Class NotesTripura Neelima100% (2)
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Azzem JenalNo ratings yet
- Control & CoordinationDocument71 pagesControl & CoordinationPrabhnoor kaurNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?Document22 pagesControl and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?So TemptedNo ratings yet
- Biology HandoutDocument9 pagesBiology Handouttashema rhodenNo ratings yet
- Kep InggrisDocument18 pagesKep InggrisArif RimbunNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Is The Way All The Organs and Systems of The Body Are Made To WorkDocument11 pagesCo-Ordination Is The Way All The Organs and Systems of The Body Are Made To WorkIshita ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Biology Handout Coordination and HormoneDocument5 pagesBiology Handout Coordination and HormoneCorry SepviaNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 Bio Notes Class 10 Control Coordination Part 1Document7 pagesCh-7 Bio Notes Class 10 Control Coordination Part 1khushi.kashyap0468No ratings yet
- Control Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Document16 pagesControl Coordination (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Bio NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Y3 Bio Notes Unit 2Document38 pagesY3 Bio Notes Unit 2SANJAY SHIVANINo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Document1 pageCoordination and Response - IGCSE Biology Notes (2020)Misheel BatzorigNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response Pt. 2Document22 pagesCoordination & Response Pt. 2Yagna LallNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 (Coordination and Response)Document13 pagesUnit 9 (Coordination and Response)《Akari - San》 AMV ; 3No ratings yet
- Lesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument6 pagesLesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMNatoya RichardsNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response - HandoutDocument7 pagesCoordination and Response - HandoutWaniya NadeemNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System and Sense OrgansDocument75 pagesThe Nervous System and Sense OrgansMik MiczNo ratings yet
- CoordinationDocument75 pagesCoordinationThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Coordination Igcse BiologyDocument108 pagesCoordination Igcse BiologyEllie HousenNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Presented By: S. Harry 13/12/20Document16 pagesThe Nervous System: Presented By: S. Harry 13/12/20Errol WebsterNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologySha WnNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument19 pagesHeredityJhenn MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Control Coordination NotesDocument6 pagesControl Coordination NotesRaman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination and ResponseDocument11 pagesNervous Coordination and ResponseJashya NoorNo ratings yet
- Flora of Presidency of MadrasDocument1,679 pagesFlora of Presidency of MadrasAnantha Krishna K SNo ratings yet
- Qaurter 2 Module 6Document32 pagesQaurter 2 Module 6Roden GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Herbs - D&D 5eDocument17 pagesHerbs - D&D 5eSébastien Roche100% (2)
- Instant Download Biopsychology 10th Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEDocument25 pagesInstant Download Biopsychology 10th Edition Ebook PDF PDF FREEcarole.price742100% (47)
- Exercise Chapter 4 F1Document5 pagesExercise Chapter 4 F1Nadwah HasNo ratings yet
- Gardening in Kerala Suitable PlantsDocument25 pagesGardening in Kerala Suitable PlantsAkshay SNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsDocument45 pagesO Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsHamzu GamingNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants WorksheetDocument6 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants WorksheetKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Useful Plants of Bas-Congo Province DR CDocument321 pagesUseful Plants of Bas-Congo Province DR CSergio JituNo ratings yet
- The Book of Crochet Flower - Vol 2Document99 pagesThe Book of Crochet Flower - Vol 2Chrestella Chairis100% (3)
- Athena Feed Schedules USADocument2 pagesAthena Feed Schedules USAFo'Folk SitNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument7 pagesContentSoh CwNo ratings yet
- AraucariaDocument8 pagesAraucariaImran Sajid ShahidNo ratings yet
- Adventures For Little Inventors OverviewDocument2 pagesAdventures For Little Inventors OverviewChukwuka Egbuiwe100% (1)
- Botany of Desire: The Apple by Michael PollanDocument2 pagesBotany of Desire: The Apple by Michael Pollanadnan joharNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument8 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproducesushantNo ratings yet
- Bearing Habits of Fruit CropsDocument38 pagesBearing Habits of Fruit CropsFlori rs R nagar, Hyd100% (5)
- Plants ClassificationDocument11 pagesPlants ClassificationLeslie GandaNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Picture TalkDocument24 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Picture TalkRobe Jane Harap92% (26)
- Science Reading Article 28 - The Importance of BeesDocument2 pagesScience Reading Article 28 - The Importance of Beesapi-547683285100% (1)
- UN VAGANZA Bahasa Inggris IX SMPDocument10 pagesUN VAGANZA Bahasa Inggris IX SMPGazza ayuNo ratings yet
- Devansh Jain Investigatory Project BiologyDocument25 pagesDevansh Jain Investigatory Project BiologyAKSHAY JAIN100% (1)
- © Ncert Not To Be Published: Structural Organisation in Plants and AnimalsDocument21 pages© Ncert Not To Be Published: Structural Organisation in Plants and AnimalsVijay VallipiNo ratings yet
- Dragon Fruit Plant CareDocument72 pagesDragon Fruit Plant CareLiza Cabalquinto Lorejo100% (2)
- BFTH-Plant Families PDFDocument8 pagesBFTH-Plant Families PDFYekitaSNo ratings yet
- Notes Science Modes in Reproduction PLANTSDocument3 pagesNotes Science Modes in Reproduction PLANTSmary-ann escalaNo ratings yet
- Plant Families NEETDocument2 pagesPlant Families NEETPratyush Raj Saran100% (1)
- Fig Growing in The SouthDocument28 pagesFig Growing in The SouthHector Quezada100% (1)
- Evolutionary Mechanisms and Speciation Lab WorksheetDocument4 pagesEvolutionary Mechanisms and Speciation Lab WorksheetAlton KatzNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy ThesisDocument6 pagesPlant Anatomy Thesisbcreq2m5100% (2)