0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views38 pagesAnatomy Objectives
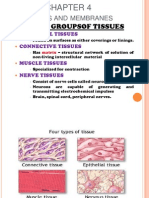
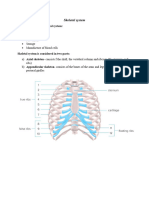
This document outlines the objectives and key concepts related to human body orientation, the integumentary system, muscle mechanics, and musculoskeletal anatomy. It includes details on the structural organization of anatomy, anatomical positions, muscle types, bone functions, and joint movements. Additionally, it covers the anatomy of skin, muscle tissue properties, and the functions of various types of cartilage and bones.
Uploaded by
pr2fx9fs7zCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views38 pagesAnatomy Objectives
This document outlines the objectives and key concepts related to human body orientation, the integumentary system, muscle mechanics, and musculoskeletal anatomy. It includes details on the structural organization of anatomy, anatomical positions, muscle types, bone functions, and joint movements. Additionally, it covers the anatomy of skin, muscle tissue properties, and the functions of various types of cartilage and bones.
Uploaded by
pr2fx9fs7zCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd