Professional Documents
Culture Documents
192 Khushboo Rathore
Uploaded by
birla_sOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
192 Khushboo Rathore
Uploaded by
birla_sCopyright:
Available Formats
Design and Implementation of 256K-bits Novel 9T SRAM Memory for Enhanced Data Stability and Reduced Leakage Power
Delegates Name Academic Supervisors Industrial Supervisors Khushboo Rathore VSD (FT-2007)
P. Chandramohan and Prakash Reddy Khushboo Rathore
khushboo.eng@gmail.com Ph. No:0 92431 13071
Keywords: Low Leakage Power 8Kb SRAM, Layout Design, SNM, Data Stability Abstract:
As the operating voltage scales down with the technology, the stability concern for SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) cells has moved to the focus center. Moreover, memories have always been the bottlenecks for high speed and low power designs. The 9T SRAM with inherent data stability and capability of reducing the leakage power is adopted to meet the stringent requirements of the low power designs. The circuit techniques used to reduce the power dissipation and delay of these components have been explored and optimum power consumption is obtained. The building blocks of an SRAM, the row decoders, control block and the IO blocks are designed and proper sizing is done using logical efforts method and mathematical equations. The architecture of the SRAM is planned and a 32-bit data bus is selected. The key to data stability is the isolation between the bitlines and the data node in the 9T SRAM cell. The transistor at the tail of the 9T memcell is implemented with multiplying factor of 2 to reduce the leakage power compared to that of the conventional 6T SRAM cell. The division of read and write sections provide reduction in the leakage power. To reduce the overall power dissipation of the chip, the special hierarchical technique has been adopted for implementation of the 10:1024 row decoder. Finally, a 256Kb prototype 9T SRAM has been designed and implemented. The leakage power of the 9T memcell is 0.02261nW which is nearly 30% less than the conventional 6T SRAM cell. The mask design of the constituent memory blocks is done using Virtuoso tool, the DRC and LVS verified through Hercules/Calibre. The complete 256Kb SRAM memory comprises of 2.4 million transistors. The design is simulated at a clock speed of 3.33GHz. The read access time is found to be 0.85ns while the write access time is found to be 1.246ns at pre-layout simulations. The total leakage power dissipation is 20.579mW at pre-layout simulations. The SNM for 9T cell is 9.75% more than conventional 6T SRAM cell, with leakage power reduced to half.
Comparison of pre and post-layout simulation for 256Kb SRAM memory
Block diagram for the 256Kb SRAM
Low power 256Kb SRAM full chip layout Book of Abstracts 192
Waveform for read/write access time April 2009
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Knowledge Paper XDocument28 pagesKnowledge Paper XLaurențiu Cătălin NeagoeNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination FormatDocument7 pagesMental Status Examination FormatMala Rasaily100% (3)
- Narrative Report of Landfill VisitDocument3 pagesNarrative Report of Landfill VisitNestor Jan Kenneth P BorromeoNo ratings yet
- James M. Buchanan - Why I, Too, Am Not A Conservative PDFDocument121 pagesJames M. Buchanan - Why I, Too, Am Not A Conservative PDFHeitor Berbigier Bandas100% (2)
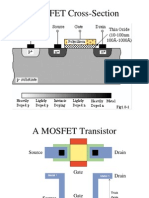
- Mosfet 01Document56 pagesMosfet 01Edward Allan MangubatNo ratings yet
- Avelino Vs Cuenco (Case Digest)Document8 pagesAvelino Vs Cuenco (Case Digest)Christopher Dale WeigelNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001Document501 pagesPRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001vamcodong71% (7)
- Holy Week Labyrinth GuideDocument4 pagesHoly Week Labyrinth GuideEileen Campbell-Reed100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Portfolio Theory: Prepared By: Wael Shams EL-DinDocument21 pagesChapter 7 Portfolio Theory: Prepared By: Wael Shams EL-DinmaheraldamatiNo ratings yet
- A Rite of SpringDocument10 pagesA Rite of SpringLucius Gregory MeredithNo ratings yet
- Goethe Zertifikat b1 HorenDocument2 pagesGoethe Zertifikat b1 HorenLevent75% (4)
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Logic CircuitsDocument61 pagesDynamic Logic Circuitsbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Spectral Multidimensional Scaling: Signi FicanceDocument6 pagesSpectral Multidimensional Scaling: Signi Ficancebirla_sNo ratings yet
- Tvlsi Kuang IeeexploreDocument13 pagesTvlsi Kuang Ieeexplorebirla_sNo ratings yet
- CompDocument11 pagesCompBommanayakanahalli subramanya saiNo ratings yet
- Specifying Simulation Output: Using Output Statements Selecting Simulation Parameters Displaying Simulation ResultsDocument58 pagesSpecifying Simulation Output: Using Output Statements Selecting Simulation Parameters Displaying Simulation ResultsChristopher PattersonNo ratings yet
- LayoutDocument64 pagesLayoutrahul_varmakNo ratings yet
- Synopsys VCS Is A Popular and Commonly Used EDA Tool in The Logical Chip Design ProcessDocument1 pageSynopsys VCS Is A Popular and Commonly Used EDA Tool in The Logical Chip Design Processbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diode Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Diode Characteristics: Objectivebirla_sNo ratings yet
- Verilog ProblemsDocument3 pagesVerilog Problemsbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Combinational Circuit 2Document55 pagesCombinational Circuit 2birla_sNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diode Characteristics: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 Diode Characteristics: Objectivebirla_sNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument35 pagesCircuitsbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Few SlidesDocument14 pagesFew Slidesbirla_sNo ratings yet
- VCS TutorialDocument11 pagesVCS TutorialSenthil KumaranNo ratings yet
- VLSI EngineeringDocument1 pageVLSI Engineeringbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Combinational Circuit 2Document55 pagesCombinational Circuit 2birla_sNo ratings yet
- Partitioning 1Document41 pagesPartitioning 1birla_sNo ratings yet
- Opamp ProjectDocument10 pagesOpamp Projectbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Few SlidesDocument14 pagesFew Slidesbirla_sNo ratings yet
- 3 The TTL NAND GateDocument7 pages3 The TTL NAND Gateanupamj4u0% (1)
- SRAM Dynamic Stability: Theory, Variability and Analysis: Wei Dong Peng Li Garng M. HuangDocument8 pagesSRAM Dynamic Stability: Theory, Variability and Analysis: Wei Dong Peng Li Garng M. Huangbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Opamp ProjectDocument10 pagesOpamp Projectbirla_sNo ratings yet
- Opamp ProjectDocument10 pagesOpamp Projectbirla_sNo ratings yet
- 1161 Article+Text 5225 1 4 20220712Document9 pages1161 Article+Text 5225 1 4 20220712Warman FatraNo ratings yet
- Band Theory and Bloch Theorem in Solid State PhysicsDocument8 pagesBand Theory and Bloch Theorem in Solid State PhysicsVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- Lab Practice # 01 An Introduction To MatlabDocument10 pagesLab Practice # 01 An Introduction To MatlabGhulam Abbas LashariNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing Communication PlanDocument5 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communication Planprojectwork185No ratings yet
- Actor analysis explores decision-making in environmental governanceDocument48 pagesActor analysis explores decision-making in environmental governancerizkyNo ratings yet
- Course Code Part Sem Paper Code Paper NameDocument3 pagesCourse Code Part Sem Paper Code Paper Nameshiv mishraNo ratings yet
- Group ActDocument3 pagesGroup ActRey Visitacion MolinaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 and Flu Vaccination Walgreens Immunization ServicesDocument1 pageCOVID-19 and Flu Vaccination Walgreens Immunization ServicesAitana MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- RRT LH: Gt'R:Ut (TLDocument75 pagesRRT LH: Gt'R:Ut (TLkl equipmentNo ratings yet
- LUMIX G Camera DMC-G85HDocument9 pagesLUMIX G Camera DMC-G85HnimodisNo ratings yet
- The Life of The Last Pharaoh of EgyptDocument16 pagesThe Life of The Last Pharaoh of EgyptShanelle BarrilNo ratings yet
- Strawberry GenerationDocument2 pagesStrawberry GenerationImat12No ratings yet
- Advanced Guide To Digital MarketingDocument43 pagesAdvanced Guide To Digital MarketingArpan KarNo ratings yet
- ADWEA Approved Vendor List - 18.4.2013Document297 pagesADWEA Approved Vendor List - 18.4.2013Anonymous kjvaeVJNNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 RespirationDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Respirationlock_jaw30No ratings yet
- DissertationDocument15 pagesDissertationNicole BradyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22A - Sound WavesDocument24 pagesChapter 22A - Sound Wavesqwivy.comNo ratings yet
- Bee WareDocument49 pagesBee WareJayNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone R Salmonella Typhi 02Document8 pagesCeftriaxone R Salmonella Typhi 02docsumitraiNo ratings yet