Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Cell
Uploaded by
Mirko Miguel Quispe ChumbesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Cell
Uploaded by
Mirko Miguel Quispe ChumbesCopyright:
Available Formats
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
The Cell
The body can be studied from its simplest to its most complex level, beginning with the cell, the basic unit of living organisms. Cells carry out metabolism, the sum of all the physical and chemical activities that occur in the body. Providing the energy for metabolic reactions is the chemical ATP (adenosine triphosphate), commonly described as the energy compound of the cell. The main categories of organic compounds in the body are: Proteins, which include the enzymes, some hormones, and structural materials Carbohydrates, which include sugars and starches. The main carbohydrate is the sugar glucose, which circulates in the blood to provide energy for the cells. Lipids, which include fats. Some hormones are derived from lipids, and adipose (fat) tissue is designed to store lipids. Within the cytoplasm that fills the cell are subunits called organelles, each with a specific function. The main cell structures are named and described in Display 4-1.
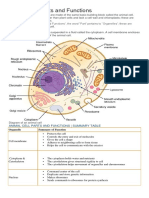
FIGURE 4-1. Diagram of typical animal cell showing the main organelles. (Reprinted with permission from Cohen BJ, Wood DL. Memmiers The Human Body in Health and Disease. 9 th Ed. Philadelphia> Lippincott Williams &^Wilkins, 2000.)
All body functions derive from the activities of billions of specialized cells. The nucleus is the control region of the cell. It contains the chromosomes, which carry genetic information. (Fig. 4-2).
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Each human cell, except for the sex cells, contains 46 chromosomes. The chromosomes are composed of complex organic substance, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which is organized into separate units called genes. Genes control the formation of enzymes, the catalysis needed for metabolic reactions. To help manufacture enzymes, the cells use a compound called RNA (ribonucleic acid) which is chemically related to DNA. When a body cell divides, by the process of mitosis, the chromosomes are doubled and the equally distributed to the two daughter cells. Sex cells (egg and Sperm) divide by another process (meiosis) that halves the chromosomes in preparation for fertilization. CELL STRUCTURES NAME Plasma membrane DESCRIPTION outer layer of the cell; composed mainly of lipids and proteins colloidal suspension that fills cell large, dark-staining body near the center of the cell, composed of dna and proteins small body in the nucleus, composed of RNA, DNA, and protein network of membranes in the cytoplasm small bodies attached to the ER; composed of RNA and protein large organelles with folded membranes inside layers of membranes small sacs of digestive enzymes rod-shaped bodies (usually two) near the nucleus short , hairlike projections from the cell long, whiplike extension from the cell FUNTION limits the cell, regulates what enters and leaves the cell holds cell contents contains the chromosomes with the genes (the hereditary material that directs all cell activities) needed for protein manufacture used for storage and transport; holds ribosomes. manufacture proteins convert energy from nutrients into atp put together special substances within the cell digest substances within the cell help separate the chromosomes in cell division create movement around the cell moves the cell
Cytoplasm Nucleus
Nucleolus Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ribosomes Mitochondria Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Centrioles Cilia Flagellum TISSUES
Cells are organized into four basic types of tissues that perform specific functions. (Fig. 4-4) Epithelial tissue covers and protects body structures and lines organs, vessels, and cavities. Connective tissue supports and binds body structures; it contains fibers and other nonliving material between the cells. Included are adipose tissue (fat) cartilage, bone, and blood 2 I CICLO
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Muscle tissue contracts to produce movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal or voluntary muscle moves the skeleton. Cardiac muscle forms the heart. It functions without conscious control and is described as involuntary. Smooth, or visceral, muscle forms the walls of the abdominal organs; it is also involuntary.
Nervous tissue makes up the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It coordinates and controls body responses by the transmission of electrical impulses.
The simplest tissues are membranes. Mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick fluid that lubricates surfaces and protects underlying tissue. Serous membranes, which secrete a thin, watery fluid, line body cavities and cover organs.
FIGURE 4-4.
ORGANS AND ORGAN SYSTEMS Tissues are arranged into organs, which serve specific functions (Fig. 4-5). The organs, in turn, are grouped into systems. Each of the body systems is discussed in Part 3. Bear in mind, however, that the body functions as a whole-no system is independent of the others. They work together to maintain the bodys state of internal stability, termed homeostasis.
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO WORDS PARTS PERTAINING TO CELLS, TISSUES, AND ORGANS ROOT morph/o cyt/o, -cyte nucle/o kay/o hist/o, histi/o fibr/o reticul/o aden/o papill/o myx/o muc/o somat/o, -some MEANING form cell nucleus nucleus tissue fiber network gland nipple mucus mucus, mucous membrane body EXAMPLE polymorphic cytogenesis nuclear karyotype histologist fibrosis reticulum adenoma papilliform myxadenitis mucorrhea somatik
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
DEFINITION OF EXAMPLE having many forms the formation of cells pertaining to a nucleus picture of chromosomes of a cell organized according to size specialist in the study of tissue abnormal formation of fibrous tissue a network tumor (oma) of a gland resembling a nipple inflammation of gland that secretes mucus increased flow (-rhea ) of mucus pertaining to the body
Karyotype
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Karyomegaly is enlargement (-megaly) of the ______________________ Adenitis is inflammation (-itis) of a ______________________ A papilla is a projection that resembles a(n) ______________________ A fibril is a small ______________________ Histogenesis is the formation (-genesis) of ______________________ A myxoma is a tumor of tissue that secrets ______________________ The term reticular means resembling or pertaining to a(n) ______________________ A dimorphic organism has two ______________________ The term mucosa is used to describe a membrane that secretes ____________________
10. Nucleoplasm is the material that fills the ______________________ 11. Somatotropin, also called growth hormone, has a general stimulating effect on the __________________
USE THE SUFFIX LOGY TO BUILD A WORD WITH EACH OF THE FOLLOWING MEANINGS: 12. The study of cells ______________________ 13. The study of tissues ______________________ 14. The study of form ______________________
Laboratory Study of Tissues Biopsy is the removal and examination of living tissue to determine a diagnosis. The term is also applied to the specimen itself. Biopsy comes from the Greek word bios, meaning "life," plus opsis, meaning "vision." Together they mean the visualization of living tissue. Some other terms that apply to cells and tissues come from Latin. In vivo means "in the living body," as contrasted with in vitro, which literally means "in glass" and refers to procedures and experiments done in the laboratory, as compared with studies done in living organisms. In situ means "in its original place," and is used to refer to tumors that have not spread. In toto means "whole" or "completely," as in referring to a structure or organ removed totally from the body. Postmortem literally means "after death," as in referring to an autopsy performed to determine the cause of death.
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO Roots for Cell Activity ROOT blast/o, blast gen phag/o phil plas trop troph/o MEANING immature cell, productive cell, embryonic cell origin, formation eat, ingest attract, absorb formation, molding, development act on, affect feeding, growth, nourishment EXAMPLE leukoblast
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
DEFINITION OF EXAMPLE an immature white blood cell the science of genes and heredity cell that ingests waste and foreign matter attracting acid stain overdevelopment of an organ or tissue affecting rate or timing wasting away (lack of nourishment)
genetics phagocyte fag-osit acidophilic hyperplasia chronotropic atrophy
The roots in Table 4-2 are often combined with a simple noun suffix (-in, -y, or -ia) or an adjective suffix (-ic) and used as word endings. Such combined forms that routinely appear as word endings will simply be described and used as suffixes in this book. Examples from the above list are -trophy, -plasia, -tropin, -philic, -genic.
EXERCISE Match the following terms and write the appropriate letter to the left of each number: ___ 1. erythroblast ___ 2. hypertrophy ___ 3. phagocytosis ___ 4. karyogenesis ___ 5. autotroph ___ 6. somatotropic ___ 7. chromophilic ___ 8. neoplasia ___ 9. aplasia ___ 10. gonadotropin a. organism capable of manufacturing its own food b. formation of a nucleus c. increased growth of tissue d. ingestion of waste by a cell e. immature red blood cell f. attracting color g. acting on the body h. substance that acts on the sex glands i. new formation of tissue j. lack of development
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO Identify and define the root in each of the following words: Root 11. esophagus 12. normoblast 13. dystrophy 14. aplastic 15. regenerate
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Meaning of Root
_______ _______ _______ _______ _______
____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________
SUFFIXES AND ROOTS FOR BODY CHEMISTRY WORD PART SUFFIXES -ase -ose ROOTS hydr/o gluc/o glyc/o water, glucose sugar, glucose fluid hydrophilic glucosuria hyperglycemia attracting water a presence of glucose in the urine (-ur/o) high blood sugar enzyme sugar lipase lactose enzyme that digests fat (lipid) milk sugar MEANING EXAMPLE DEFINITION OF EXAMPLE
sacchar/o
sugar
polysaccharide
compound containing many sugars
amyl/o
starch
amyloid
resembling starch
lip/o adip/o steat/o prote/o
lipid, fat fat fatty protein
lipogenesis adipocyte steatorrhea protease
formation of fat
cell that stores fat discharge (-rhea) of fatty stools enzyme that digests protein
Fill in the blanks: 1. Amylase is an enzyme that digests ______________________________. 2. The ending -ose indicates that maltose is a(n) ______________________________. 3. Glucogenesis is the formation of ________________________. 4. Hydrotherapy is treatment using ______________________________. E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA 7 I CICLO
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
5. Liposuction is the surgical removal of ______________________________. 6. Adipose tissue stores ______________________________.
Identify and define the root in each of the following words: Root 7. glucolytic 8. asteatosis 9. normoglycemia 10. lipoma Meaning of Root
_______ _______ _______ _______
____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________
SUPPLEMENTARY TERMS amino acids anabolism The nitrogen-containing compounds that make up proteins. The type of metabolism in which body substances are made; the building phase of metabolism. The type of metabolism in which substances are broken down for energy and simple compounds. A fibrous protein found in connective tissue. The outer region of an organ. A complex sugar compound stored in liver and muscles; broken down into glucose when needed for energy. Between parts, such as the spaces between cells in a tissue. The inner region of an organ; marrow (root medull/o).
catabolism collagen cortex glycogen
interstitial medulla
parenchyma The functional tissue of an organ. parietal soma Pertaining to a wall; describes a membrane that lines a body cavity. The body. Used as the suffix -some to mean a small body, as in ribosome, lvsosome, chromosome. An immature cell that has the capacity to develop into any of a variety of different cell types. A precursor cell. Pertaining to the internal organs; describes a membrane on the surface of an organ.
stem cell
visceral
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Match the following terms and write the appropriate letter to the left of each number: ___ 1. Ribosomes ___ 2. ATP ___ 3. homeostasis ___ 4. NA ___ 5. Cartilage a. genetic material b. state of internal stability c. organelles that contain RNA d. a type of connective tissue e. energy compound of the cells
___ 6. cytoplasm ___ 7. Metabolism ___ 8. mitochondria ___ 9. erythroblast ___ 10. Mitosis
a. organelles that produce ATP b. immature red blood cell c. material that fills the cell d. cell division e. all the activities of the cell
___ 11. megakaryocyte ___ 12. reticulocyte ___ 13. Chromosome ___ 14. adenoid ___ 15. Fibroma
a. resembling a gland b. fibrous tumor c. cell with a very large nucleus d d. cell that contains a network e. structure that contains genes
___ 16. Fibroplasias ___ 17. Amorphous ___ 18. Papillary ___ 19. atrophy ___ 20. Basophilic
a. Without form b. wasting of tissue c. attracting basic stain d. formation of fibrous tissue e. like or resembling a nipple
___ 21. hyperplasia ___ 22. hypoglycemia ___ 23. amylase ___ 24. mucoid ___ 25. lipase
a. resembling mucus b. low blood sugar c. enzyme that digests fat d. overdevelopment of an organ or tissue e. enzyme that digests starch
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO ___ 26. proteolytic ___ 27. nucleosome ___ 28. somatotropic ___ 29. adipocyte ___ 30. somatopsychic
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES a. pertaining to the body and the mind b. destroying or dissolving protein c. cell that contains fat d. small body in the nucleus e. acting on the body
SUPPLEMENTARY TERMS ___ 31.catabolism ___ 32.collagen ___ 33.amino acid ___ 34.anabolism ___ 35.cortex a. building phase of metabolism b. outer region of an organ c. building block of protein d. fibrous protein in connective tissue e. breakdown phase of metabolism
Fill in the blanks: 36. The four basic tissue types are ________________________________________________ 37. The simple sugar that is the main energy source for metabolism is ___________________ 38. The control center of the cell is the ____________________________________________ 39. The number of chromosomes in each human cell aside from the sex cells is____________ 40. An organic compound that speeds the rate of metabolic reactions is a (n) _____________ 41. Karyomegaly (kar-e-o-MEG-a-le) is enlargement (-megaly) of the ____________________ 42. A cytotoxic substance is damaging or poisonous to ________________________________ 43. The term hydration refers to the relative amount of _______________________________ 44. Adiposuria (ad-i-po-SU-re-a) is the presence in the urine of _________________________ 45. A myxocyte is found in tissue that secretes ______________________________________
Word building. Write a word for each of the following definitions: 46. The study of form and structure ________________________________________ 47. The study of tissues ______________________________________________ 48. The formation of cells (use -genesis as an ending) ________________________ 49. An enzyme that digests proteins _______________________________________
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
10
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Case Studies
Hematology Laboratory Studies J.E. had a blood test as required for preoperative anesthesia assessment in preparation for scheduled plastic surgery on her breasts. The report read as follows: Complete blood count (CBC) and differential Red blood cell count (RBC)4.5 million/ul Hemoglobin (Hgb) 1 2.6 g/dL Hematocrit (Hct) 38% White blood cell count (WBC)8,500/uL Neutrophils58% Lymphocytes34% Monocytes6% Eosinophils2% Basophils0.5% Platelet count200,000/uL Prothrombin time (PT)11.5 seconds Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)65 seconds Blood glucose84 mg/dL The surgeon reviewed these results and concluded that they were within normal limits (WNL). Pathology Laboratory Tests R.C., the manager of the clinical and pathology laboratory, received several surgical specimens taken from a 26-year-old female patient with a 4-week history of nonspecific pelvic pain. The specimens included several small containers of pink-tinged cloudy fluid labeled pelvic lavage (washing) for cytology, which R.C. took to the cytology laboratory to be made into slides and checked microscopically for abnormal cells. R.C. also received a tissue specimen labeled uterine myoma, a wedge biopsy of right ovar- ian neoplasm, and four jars cach labeled pelvic lymph nodes. She took all of the tissue specimens to the pathology laboratory for gross and microscopic evaluation. A test tube half-filled with a cloudy gel and a cotton-tipped applicator labeled swab of pelvic fluid for culture and sensitivity and Gram stain was taken to the microbiology laboratory to be streaked on a culture plate and incubated to look for growth. Any organisms that grew out would be Gram-stained and tested for sensitivity to antibiotics that might be used in treatment. The laboratory form was accompanied by a surgeon's note staling that the patient's preoperative diagnosis was cervical dysplasia with atypical cells and a positive urine leukocyte esterase, indicating a urinary tract infection. R.C. placed a copy of the laboratory forms and surgeon's note on the desk of the pathologist who was involved in carcinogenesis (cancer) research.
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
11
I CICLO
INGLS BSICO CASE STUDY QUESTIONS
MIRKO QUISPE CHUMBES
Multiple choice: Select the best answer and write the letter of your choice to the left of each number. 1. J.E.'S blood test results were within normal limits. She could be described as being in a state of: a. Normosmosis b. dysplasia c. homeostasis d. Hematophiiia e. myogenesis 2. The suffix in glucose indicates that this compound is a: a. cervix b. enzyme c. protein 3. The suffix in esterase indicates that this compound is a: a. sugar b. carbohydrate c. cell
d. sugar
e. fat
d. enzyme
e. Lipid
4. The root gen in carcinogenesis refers to a cancers: a. Origin b. Treatment c. Location d. laboratory result
e. severity
Identify and give the meaning of the prefixes in each of the following words: Prefix Meaning of Prefix 5. monocytes _______ _________________________ 6. prothombin 7. neoplasm 8. atypical 9. leukocyte _______ _______ _______ _______ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________
Find words in the case studies for the following: 10. Three words that contain a root that means attract, absorb: _______________________ _______________________ _______________________
11. Three words with a root that means formation, molding, development: _______________________ _______________________ _______________________
12. Four words with a root that means cell:
_______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________
E.A.P. MEDICINA HUMANA
12
I CICLO
You might also like
- Hse Risk Assessment - 006 Ra - Hdpe Duct LayingDocument7 pagesHse Risk Assessment - 006 Ra - Hdpe Duct Layingbinunalukandam83% (12)
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Webster 2018 Life Science ReviewDocument88 pagesWebster 2018 Life Science Reviewapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Tung DocumentreviewDocument8 pagesTung DocumentreviewRodrigo Bittencourt100% (3)
- Head To Toe Patient AssessmentDocument2 pagesHead To Toe Patient AssessmentJaypee Nuñez100% (2)
- AOTA Statement On Role of OT in NICUDocument9 pagesAOTA Statement On Role of OT in NICUMapi RuizNo ratings yet
- Cairo: Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation, 6th EditionDocument7 pagesCairo: Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation, 6th EditionLesly Peinado Torres100% (1)
- Slide 2:: Transcript: Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument3 pagesSlide 2:: Transcript: Introduction To Human AnatomyClarkStewartFaylogaErmilaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: Cells, Tissues, Organs & SystemsDocument16 pagesThe Human Body: Cells, Tissues, Organs & SystemsNguyễn Thị HiênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Human Cells Journey: Organ Syste MDocument7 pagesHuman Cells Journey: Organ Syste MArina CucuruzaNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissueDocument14 pagesCells and TissueEla NavalesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument136 pagesCellsJake Paulo BelardoNo ratings yet
- Acfrogc3gyc9hecinc9o Mzkfwkgitusaxej6csoi Anypznx2yrc0x Ie4yg Gmmtxrliza1ll8kexew2j8pgzbfy97ga0ltqn B0kqfgvie5 Cwfk7vrzhgqo59afizbbd5ollwwdttbdt52 VDocument147 pagesAcfrogc3gyc9hecinc9o Mzkfwkgitusaxej6csoi Anypznx2yrc0x Ie4yg Gmmtxrliza1ll8kexew2j8pgzbfy97ga0ltqn B0kqfgvie5 Cwfk7vrzhgqo59afizbbd5ollwwdttbdt52 VKazi Al MasumNo ratings yet
- Histology MicroanatomyDocument17 pagesHistology MicroanatomyNu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Biosci 107 Cellular Processes and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesCells and Tissues: Biosci 107 Cellular Processes and Developmentjyip947No ratings yet
- 1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pages1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONOlamide KoleNo ratings yet
- HO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFDocument10 pagesHO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion On TissueDocument2 pagesClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- (W2) Intro To H A P PDocument3 pages(W2) Intro To H A P PFRANCES DEANNE ALABADONo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapeDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: Cells: Size & ShapePedro SuyuNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKanaga ValliNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellDocument20 pagesImmunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellJoia De LeonNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument18 pagesCELLshivanshkansal099No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDocument12 pagesCells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Document22 pagesSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Histology, CellDocument12 pagesHistology, CelljuamiakaNo ratings yet
- Course 2 Irregular Plurals and Word FormationDocument6 pagesCourse 2 Irregular Plurals and Word FormationVladut FagarasNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3. ContentsDocument7 pagesBiology Unit 3. ContentsThanusri Vasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Body Chemistry: Processes That Characterise LifeLeo OrtegaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesDocument11 pagesLECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Cells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryDocument8 pagesCells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryjamielNo ratings yet
- Module 1 RAWDocument25 pagesModule 1 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsDocument18 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems FunctionsHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Types of CellsDocument6 pagesCell Theory and Types of CellsLance Afraim MortelNo ratings yet
- لكجر ٢ بايو نضريDocument10 pagesلكجر ٢ بايو نضري5wfkcyrxqzNo ratings yet
- General Biology ModuleDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology ModuleKimberly C. Javier100% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Document11 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Pradeep KhanthNo ratings yet
- Gambar Jaringan HewanDocument10 pagesGambar Jaringan HewanHimawan SandhiNo ratings yet
- Cell Types, Modification, and the Cell CycleDocument79 pagesCell Types, Modification, and the Cell CycleAron CabreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET FOR CELL MODULEDocument7 pagesACTIVITY SHEET FOR CELL MODULEAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Weeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportDocument8 pagesWeeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportShana AquinoNo ratings yet
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionDocument27 pages10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىNo ratings yet
- Basic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Document228 pagesBasic A&p Booklet Short Version 3Hilary Christopher100% (1)
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGYDocument64 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGYJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNo ratings yet
- Biological Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument5 pagesBiological Tissue Types and Functionsrjohn 7No ratings yet
- Histology Hand OutsDocument3 pagesHistology Hand OutsRemigio T. Arguilles Jr.No ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Biology Cytology IntroductionDocument5 pagesMedical Biology Cytology IntroductiondhdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Document170 pagesANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Jewell Nivera CarpioNo ratings yet
- cellDocument4 pagescellgitansh2010gauravNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Organelles & Functions in 40 CharactersDocument14 pagesAnimal Cell Organelles & Functions in 40 CharactersAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review TissueDocument4 pagesChapter Review TissueGeorge IvyNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument52 pagesCell Physiologyhafsah sidi abdullahi100% (4)
- Cell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeDocument33 pagesCell and Tissue: Mathew Jeffrey MikeKristine JoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells ExplainedDocument4 pagesProkaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells ExplainedGeramie TamayoNo ratings yet
- Module-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesModule-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- List of Mandatory Documents: Document Checklist For Medical Treatment Visa Forms Can Be Downloaded atDocument2 pagesList of Mandatory Documents: Document Checklist For Medical Treatment Visa Forms Can Be Downloaded atAdegokeNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Gases, Liquefied Petroleum Gas: IdentificationDocument4 pagesPetroleum Gases, Liquefied Petroleum Gas: IdentificationdigecaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of The Efficacy of Cedarwood Oil, Coconut Oil and Dish Wash Liquid As Alternatives To Xylene As Deparaffinizing AgentsDocument98 pagesA Comparative Study of The Efficacy of Cedarwood Oil, Coconut Oil and Dish Wash Liquid As Alternatives To Xylene As Deparaffinizing AgentszzzzNo ratings yet
- 8 RA 4688 (Clinical Laboratory Law)Document32 pages8 RA 4688 (Clinical Laboratory Law)AIRRA CLAIRE ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- 1992 2007 Kpds Ilgisiz Cumle Sorulari Seyfihocacom - Pdf.pdfsifreDocument24 pages1992 2007 Kpds Ilgisiz Cumle Sorulari Seyfihocacom - Pdf.pdfsifreozgurekinsuNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Surge - Rapid Fat Loss ProgramDocument5 pagesMetabolic Surge - Rapid Fat Loss ProgramTamer Luka100% (2)
- Chapt01 The Sudy of ChangeDocument34 pagesChapt01 The Sudy of ChangeIkhsan Abdul HanifNo ratings yet
- (Bio 024) Lab Activity 12 - BloodDocument9 pages(Bio 024) Lab Activity 12 - Bloodelaq dr100% (1)
- Hsmi Hudco TrainingDocument20 pagesHsmi Hudco TrainingThomas PeguNo ratings yet
- Cricket Academy Head Coach RoleDocument4 pagesCricket Academy Head Coach Roletauseef1716No ratings yet
- BCS Class of DrugsDocument45 pagesBCS Class of DrugsLionO50% (2)
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1kunalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Environmental Impact of Madukkarai Limestone Mine, CoimbatoreDocument11 pagesA Study On Environmental Impact of Madukkarai Limestone Mine, CoimbatoreRamasamyNagarajan100% (1)
- Asq 3 42 MDocument8 pagesAsq 3 42 MMohammed AlsuwaidiNo ratings yet
- Pesticide ApplicationDocument5 pagesPesticide ApplicationPrashant GurjarNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Lumbar Central Neuraxial Block 2016Document8 pagesUltrasound-Guided Lumbar Central Neuraxial Block 2016drkis20100% (1)
- SpitzDocument30 pagesSpitzprabhatNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Omd553-Telehealth TechnologyDocument53 pagesUnit 1-Omd553-Telehealth TechnologyjgjeslinNo ratings yet
- Umftgm 2017 MarissiensisDocument148 pagesUmftgm 2017 MarissiensisAdriana VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PDFDocument87 pagesWater Treatment PDFJubin KumarNo ratings yet
- Annexure I: Block / Building Fire Safety Audit-Check List Fire Safety Audit ChecklistDocument5 pagesAnnexure I: Block / Building Fire Safety Audit-Check List Fire Safety Audit ChecklistGaurav Singh67% (3)
- 5324623-1EN Rev 02 9900 Elite Service Manual SupplementDocument225 pages5324623-1EN Rev 02 9900 Elite Service Manual SupplementJonathan Woodward86% (7)
- Hazards of Nitrogen AsphyxiationDocument10 pagesHazards of Nitrogen AsphyxiationRaja Senthil NathanNo ratings yet
- Que No4 & 5-With Clues and Without CluesDocument4 pagesQue No4 & 5-With Clues and Without CluesMir Yamin Uddin ZidanNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Hydrabadi Mix Ball On Nutritional Status Among Malnourished Under Five Year Children at Selected Anganwadi in Barabanki, Uttar PradeshDocument15 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Hydrabadi Mix Ball On Nutritional Status Among Malnourished Under Five Year Children at Selected Anganwadi in Barabanki, Uttar PradeshEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet