0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views9 pagesEC Lecture 05
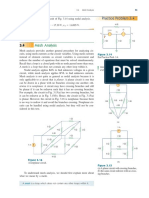
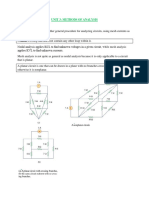
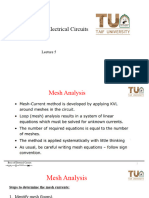
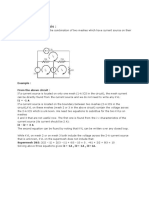
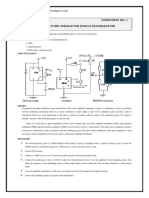
The document provides a detailed explanation of mesh analysis in electrical circuits, outlining the steps to determine mesh currents using Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Ohm's Law. It includes examples of applying mesh analysis to circuits with both independent and dependent current sources, as well as homework exercises for practice. Key points emphasize the flexibility in current direction and the concept of supermesh when current sources are involved between two meshes.
Uploaded by
joy112833Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views9 pagesEC Lecture 05
The document provides a detailed explanation of mesh analysis in electrical circuits, outlining the steps to determine mesh currents using Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Ohm's Law. It includes examples of applying mesh analysis to circuits with both independent and dependent current sources, as well as homework exercises for practice. Key points emphasize the flexibility in current direction and the concept of supermesh when current sources are involved between two meshes.
Uploaded by
joy112833Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd