0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesWinter 2023
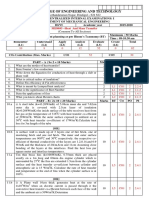
The document outlines the examination details for the Heat Transfer course (BTMC501) at Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, including instructions, exam date, and question structure. It consists of five questions, each requiring students to attempt any two, covering topics such as heat conduction, convection, heat exchangers, and radiation. The exam is scheduled for January 1, 2024, with a total of 60 marks available.
Uploaded by
Rajnandini NagaraleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesWinter 2023
The document outlines the examination details for the Heat Transfer course (BTMC501) at Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, including instructions, exam date, and question structure. It consists of five questions, each requiring students to attempt any two, covering topics such as heat conduction, convection, heat exchangers, and radiation. The exam is scheduled for January 1, 2024, with a total of 60 marks available.
Uploaded by
Rajnandini NagaraleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd