Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Ecosystem
Uploaded by
rizaabduljaleel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views18 pagesThis document defines key terms related to ecosystems, including habitat, community, environment, biotic and abiotic factors. It describes an ecosystem as a community of living things and abiotic factors in a particular place. Trophic levels within ecosystems are explained, with producers (autotrophs like plants and algae) at the bottom level, followed by primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. Food chains show the transfer of energy between organisms as one eats another. Food webs illustrate how multiple food chains interconnect within an ecosystem. Relationships between organisms, such as mutualism, commensalism, predation, parasitism and competition, are also outlined.
Original Description:
ppt
Original Title
Introduction to Ecosystem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key terms related to ecosystems, including habitat, community, environment, biotic and abiotic factors. It describes an ecosystem as a community of living things and abiotic factors in a particular place. Trophic levels within ecosystems are explained, with producers (autotrophs like plants and algae) at the bottom level, followed by primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. Food chains show the transfer of energy between organisms as one eats another. Food webs illustrate how multiple food chains interconnect within an ecosystem. Relationships between organisms, such as mutualism, commensalism, predation, parasitism and competition, are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views18 pagesIntroduction To Ecosystem
Uploaded by
rizaabduljaleelThis document defines key terms related to ecosystems, including habitat, community, environment, biotic and abiotic factors. It describes an ecosystem as a community of living things and abiotic factors in a particular place. Trophic levels within ecosystems are explained, with producers (autotrophs like plants and algae) at the bottom level, followed by primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. Food chains show the transfer of energy between organisms as one eats another. Food webs illustrate how multiple food chains interconnect within an ecosystem. Relationships between organisms, such as mutualism, commensalism, predation, parasitism and competition, are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
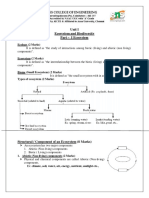
Introduction to ecosystem
Habitat- the place where a plant, animal or
microorganism lives
Community-all the plants, animals and
microorganisms that live in a habitat
Environment-the surroundings of a living
thing. It includes all living things, rocks, soil
and weather conditions
Abiotic factors- factors due to the nonliving
part of an environment eg: air, water rocks
and soil
Ecosystem
Biotic factors- factors of an environment due
to living things such as producers, consumers
Ecosystem- the community of living things
and the abiotic factors found in a particular
place such as forest or a pond
Bio diversity- a term used to describe the
number and variety of species in an
ecosystem
Herbivore an animal that only eats plants
Carnivore-an animal that only eats other
animals
Omnivore- an animal that eats both plants
and animals
Predator- an animal that feeds or preys on
another animal
Trophic levels
Producers[ autotrophs]- they are typically plants
or algae. They make their own food through
photosynthesis. they are also called as a primary
producers
Consumer- an animal that eats plants , other
animals or both
Primary consumer- an animal that eats
plants[this may be herbivore or an omnivore]
Secondary consumer an animal that eats
primary consumers[this may be a carnivore or an
omnivore]
Tertiary consumer
Tropic levels
Food chain
Food chain-a description[often a diagram]of the
way some organisms in a habitat are linked to
each other through feeding. A food chain begins
with a producer and is followed by one or more
consumers
Eg: food chain in the ocean
Algae larvae of crustaceans smaller fish
Bigger fish seals killer whale
The trophic level of an organism is the position
it occupies in a food chain
Food web-a description of how a number of food
chains in a habitat are linked together to show
how food and energy pass through the habitat.
Eg: panda eats bamboo shoots and also eats fish
so that means there are two f food chains i.e.
bamboo panda
water plants snails fish panda
Ecology- it is the scientific study of the biotic and
abiotic factors of an ecosystem and their
relationship.
Different types of relations
among organism
This relationship are useful for ensuring food
and space for living.
These relations are two types
Positive interaction-mutualism and
commensalism
Negative interaction- predation, parasitism
and competition
Positive interaction
Mutualism
Commensalism
Two organisms are
benefited
Butterfly and
flowering plants
One is benefited
and the other is
neither benefited
nor harmed
Vanda and mango
tree
Positive interaction
Positive interaction
Positive interaction
Negative interaction
predation-one is benefited and the other is
harmed
eg: Eagle and chicken
parasitism-one is benefited and the other is
harmed
eg: mango tree and loranthus
competition- both organisms suffer at first.
but the organism which wins is benefited
Predation
competition
You might also like
- Oeap b2 THB Answerkey All UnitsDocument82 pagesOeap b2 THB Answerkey All UnitsAntonio Grgurinović91% (22)
- Holdren, John P. Man As A Global Ecological Force.Document27 pagesHoldren, John P. Man As A Global Ecological Force.Keith KnightNo ratings yet
- FIONA ZHENG - Ecology Lab - Predator Prey InteractionsDocument6 pagesFIONA ZHENG - Ecology Lab - Predator Prey InteractionsFiona ZhengNo ratings yet
- 9780199138760Document16 pages9780199138760eibsource0% (1)
- 5 E Approach Based Lesson Plan - Chapter - 1 - Food - Where Does It Come From? - NCERT - CBSE - CLASS 6th - ScienceDocument27 pages5 E Approach Based Lesson Plan - Chapter - 1 - Food - Where Does It Come From? - NCERT - CBSE - CLASS 6th - ScienceLesson Planner DP100% (4)
- Topic 2 NotesDocument18 pagesTopic 2 Notesapi-293573854No ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifeJoy AlojadoNo ratings yet
- 6 Cell OrganellesDocument4 pages6 Cell OrganellesAnna Mae Dollente100% (1)
- Spaced Learning Session 1 Life ProcessesDocument37 pagesSpaced Learning Session 1 Life Processesapi-210088695No ratings yet
- Spaced Learning Session 2 Exchange Cell Division and OrganisationDocument41 pagesSpaced Learning Session 2 Exchange Cell Division and Organisationapi-210088695No ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant TissuesDocument5 pagesAnimal and Plant TissuesShajara Anglacer AnacanNo ratings yet
- Biome Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesBiome Lesson Planapi-252165886No ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: Submitted ToDocument57 pagesKingdom Protista: Submitted ToAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Lab 10 Porifera & CnidariaDocument25 pagesLab 10 Porifera & Cnidariadraykid100% (1)
- BiosphereDocument27 pagesBiosphereJamaika Sofia LetimNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument11 pagesPlant TissuesRudra Patel100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajNo ratings yet
- 4 Animal KingdomDocument33 pages4 Animal KingdomS SNo ratings yet
- Activity 02 The Cell CityDocument4 pagesActivity 02 The Cell Citybernard0% (1)
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument7 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetKenneth ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion LabDocument8 pagesDiffusion LabGioVanna GVNo ratings yet
- Q2 Bio 1Document12 pagesQ2 Bio 1Nathalie SerafinNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneDocument2 pagesCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaNo ratings yet
- Energy FlowDocument40 pagesEnergy FlowHeather ClarchickNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument8 pagesCell Structure and FunctionTshibambeNo ratings yet
- The Frog and Its External AnatomyDocument1 pageThe Frog and Its External AnatomyDylan Francesca G YuloNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells PuzzleDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal Cells PuzzleLisa Ellis0% (1)
- Powerpoint Patterns EvolutionDocument22 pagesPowerpoint Patterns Evolutionapi-289539870No ratings yet
- CH01 BiologyDocument36 pagesCH01 BiologysugisweNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues 2Document43 pagesPlant Tissues 2Francis MacasioNo ratings yet
- A2 4 3 1 Introduction To PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesA2 4 3 1 Introduction To PhotosynthesisDebbieJonesNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 - Cell Cycle & Cell Division PDFDocument3 pagesActivity 7 - Cell Cycle & Cell Division PDFKiro ZeroNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemCXT EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Cell BiologyReyvan FaltadoNo ratings yet
- Ecology Lec - Lesson #7 - Ecosystem EcologyDocument103 pagesEcology Lec - Lesson #7 - Ecosystem EcologyJocelyn QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- MicrotubulesDocument39 pagesMicrotubulesAdnan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Bio MoleculesDocument79 pagesStructure and Function of Bio MoleculesHanumat Singh50% (2)
- Evol RelationshipsDocument15 pagesEvol RelationshipsCarla BanzuelaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document72 pagesCH 02Handugan Quinlog NoelNo ratings yet
- Homework 7Document62 pagesHomework 7body fayezNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and AnimalsDocument7 pagesWORKSHEET 11.1 Locomotion and Support in Humans and AnimalsSakinah RahimNo ratings yet
- Cell DifferentiationDocument16 pagesCell DifferentiationHarika KeshavNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportDocument21 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 CHP 2Document14 pagesModul 1 CHP 2Fendy HamidNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument44 pagesCharacteristics of Living ThingsCrizlene AdiaNo ratings yet
- Ecological SuccessionDocument16 pagesEcological Successionncl12142No ratings yet
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- L9 & 10 - Water ResourcesDocument59 pagesL9 & 10 - Water ResourcesappleNo ratings yet
- DJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFDocument43 pagesDJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFNick_989893No ratings yet
- Cynel賢人kenDocument34 pagesCynel賢人kenAnonymous wYyVjWTVibNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- ProkaryoticDocument8 pagesProkaryoticFraulin Leslie Sablas IrisariNo ratings yet
- Biology QuizDocument36 pagesBiology QuizNikko CarilloNo ratings yet
- Samuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarreroDocument15 pagesSamuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarrerosamuelNo ratings yet
- Organelle, Descrpition and FunctionDocument2 pagesOrganelle, Descrpition and Functionjahajaha_svensson609No ratings yet
- Edenton Mission College, Inc.: PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageEdenton Mission College, Inc.: PhotosynthesisLae DeeNo ratings yet
- History of Life On EarthDocument23 pagesHistory of Life On Earthmj100% (1)
- 1.1 Cell TheoryDocument1 page1.1 Cell TheoryLucca PiaggioNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes 2.3Document2 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes 2.3gelgabanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell HyperdocDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Cell Hyperdocapi-458056701No ratings yet
- Environmental Change and ExtinctionDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Change and ExtinctionkavinthecornerstoneNo ratings yet
- Principles and Concept of EcosystemDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Concept of EcosystemJay Bianca Abera Alistado100% (1)
- "Household" and Logos "Knowledge" WhichDocument3 pages"Household" and Logos "Knowledge" WhichJessalyn DaneNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 InteractionsDocument18 pagesMODULE 5 Interactionsflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PPT 735Document100 pagesEcosystem PPT 735Pauldavid SelsonNo ratings yet
- Esdm Mod 2Document102 pagesEsdm Mod 2sanjithr619No ratings yet
- Ecosystem Evs Unit 1-1 PDFDocument9 pagesEcosystem Evs Unit 1-1 PDFajithNo ratings yet
- General Science Class-Iii: Animals and Their FoodDocument15 pagesGeneral Science Class-Iii: Animals and Their FoodAyushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- CT2 QP - Grade 6 Answer KeyDocument3 pagesCT2 QP - Grade 6 Answer KeyshamshadNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Ncert Book Biology Organisms and Populations Chapter 13 MergedDocument70 pagesCbse Class 12 Ncert Book Biology Organisms and Populations Chapter 13 MergedvarshilNo ratings yet
- TTTV 4 Plant InsectsDocument54 pagesTTTV 4 Plant InsectsNhật TriềuNo ratings yet
- Tropentag 2012 PDFDocument528 pagesTropentag 2012 PDFilyasNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and Food Webs DFDocument2 pagesFood Chains and Food Webs DFBHADUIWAKNo ratings yet
- About These Lesson Plans and ResourcesDocument8 pagesAbout These Lesson Plans and ResourcesAhmer TariqNo ratings yet
- Mayank EvsDocument10 pagesMayank EvsMayank RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Species & PopulationsDocument63 pages2.1 Species & PopulationsProsper NimleyNo ratings yet
- A Carnivorous PlantDocument11 pagesA Carnivorous Plantyj100% (1)
- Food Chains and Food Webs - Part 1Document19 pagesFood Chains and Food Webs - Part 1Naseeb AliNo ratings yet
- 8563Document31 pages8563mhnkmr9100% (1)
- Sains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Document10 pagesSains SPM Chapter 3 Form 5Sensei J-dai89% (18)
- ZOO223 Learner GuideDocument16 pagesZOO223 Learner GuidevictorNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology ProjectManogya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adaptation For Grade 10Document5 pagesAdaptation For Grade 10BB 07No ratings yet
- 1.2 - Ecology and Ecosystem: Deciduous and Taiga (Boreal) (Links To An External Site.) Forests 3. FreshwaterDocument6 pages1.2 - Ecology and Ecosystem: Deciduous and Taiga (Boreal) (Links To An External Site.) Forests 3. FreshwatercarlNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan On Food ChainDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan On Food ChainMarino Alboleras MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15.1 EcologyDocument18 pagesChapter 15.1 Ecologysriniketan dasNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 01Document11 pagesExp SC 6 - Chapter 01megamind publicationNo ratings yet