Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ischemic Heart Disease Case Study
Uploaded by
nur syafiqah kamaruzamanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ischemic Heart Disease Case Study
Uploaded by
nur syafiqah kamaruzamanCopyright:
Available Formats
Ischemic Heart Disease
29(2/2005)
1686
Preface
Ischemic heart disease is very interesting and
challenging case to do beside heart is on of the most
important organ.
I decided to choose this case is because heart disease is
common case and it is advantage if the medical
management is known.
In preparing the case study, I find out more about the
ischemic heart disease in detail which include definition,
etiology, pathophysiology, complication, treatment,
investigation, medication and extra information about
ischemic heart disease.
Learning objective
Learn about the anatomy and physiology of the
cardiovascular system
State the definition of the ischemic heart disease
State the predisposinng factor
Explain the pathophysiology of the ischemic heart
disease
Sate the clinical manifestation of the ischemic heart
disease
List up the complication of the ischemic heart disease
Explain all the investigation given to the patient with
ischemic heart disease
Carry out the nursing care plan for patient with
ischemic heart disease
List the medication given to patient with ischemic
hear disease
Provide health education for patient about self care
at home
Introduction
Admission
Name: Mr. S
Registered number: 93***
Date of birth: **-**-****
Age/Sex: 57 years old/Male
Marital status: Married
I/c No.: 4909********
Race/Religion: Chinese/Buddhist
Occupation: Laboratory supervisor
Consultant: Dr. T
Date of admission: 6
th
June 2006
Reason of admission: complained of
chest pain (on & off) & S.O.B 2/52
Diagnosis: Ischemic Heart Disease
Medical history: Diabetes Melitus,
hypertension
Surgical history: angiography and PTCA
on 30
th
March 2006
Family history: Nil
Allergies: Nil
Current medication: Imdur, dormicum,
betaloc, plavix, cardiprin,
Condition of admission
Vital sign
Temperature: 36
o
C
Pulse: 47bpm
Respiration: 20bpm
Blood pressure:
112/68mmHg
Weight: 50kg
Height: 161cm
Mode of admission: walk
in
Level of consciousness:
conscious
Mental status: orientated
Emotional status: calm
Skin Condition: dry
Activity daily living
Breathing
He has difficulty in breathing when he is walking in
long distance
Cough
Mr. S does not has any cough
Smoke
Mr. S does not smoking
Eating/drinking
Mr. S does not having problem in eating.
He does not take cold water, seafood
He likes to eat red meat especially mutton and durian.
He used to has supper with fried mee frequently
His favourite drink is coffee
Elimination-bowel
He has his bowel movement daily.
He does not has problem in passing motion
Elimination-bladder
He does not has problem in passing urine
He used to get up at night to pass urine twice, noturia
Sleeping
He does not has any problem in sleeping
Mobility
Mr. S is able to ambulate
Personal Hygiene
He able to has self hygiene
Safe environment
Siderails is needed to promote safety
Physical examination
Orientation
During the admission on Mr. S, a orientation was
given according to the checklist as below:
1. Ward
Room no./bed no.
Television
Call bell
Bed chair
2. Staff
Unit manager
Staff nurse/assistant nurse
Care assistance
Student nurse
Ward clerk
3. Routine
doctors rounds
Nurses rounds
Meal times
4. Hospital policies
Visiting hours
Companion
Property/valueable
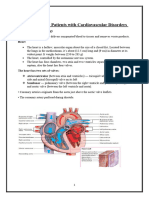
Anatomy
Location of the heart
The heart is a hollow, cone-shaped, muscular
organ lying obliquely in the thoracic cavity.
The upper border (base) lies just below the
second rib.
The lower border (apex) is directed downward,
forward, and to the left, and lies on the
diaphragm at the level of the fifth intercostal
space in the left midclavicular line.
Layers of the heart
Pericardium
Pericardium is a strong, non-distensible sac which loosely encloses
the heart and attaches to the large blood vessels at the base of the
heart and to the diaphragm at the apex.
The walls of the heart composed of three layers of tissue:
1. epicardium outer layer of the heart
visceral layer of the pericardium
2. myocardium middle layer of the tissue
composed of the invonluntary striated muscle fibres
which interlace, branch and anastomose
responsible for the hearts contractile force
3. Endocardium thin layer of endothelial cells lining the inferior
surface of the hearts chambers which covers the
heart
create a smooth surface, reducing friction between
moving blood and the walls of heart
Anatomy of the heart
Anatomy of the heart
Circulation of the heart
DEFINITION
Definition
Coronary artery disease or ischemic heart
disease affect three major coronary arteries
(right coronary artery, left anterior descending
artery and left circumflex artery) that provide
oxygen and nutrient to myocardium.
When blood flow through these major vessel
becomes partially or completely blocked,
ischemia and infarction of the myocardium may
result. Ischemia occurs when the balance
between oxygen supply and demand becomes
disproportionate.
(Medical Surgical Nursing, Page 2149)
Etiology
Etiology
1. Decrease aortic pressure
2. Increased intravascular pressure and
myocardial infarction
3. Coronary artery stenosis
Atherosclerosis
Fixed coronary stenosis
Acute plague change(rupture,hemmorhage)
Coronary artery thrombosis
Vasoconstricion
4. Aortic valve stenosis
5. Aortic regurgitation
6. Increased right artrial pressure
What is atherosclerosis
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is caused
by atherosclerosis (the thickening and
hardening of the inside walls of arteries).
Some hardening of the arteries occurs
normally as a person grows older.
Atherosclerosis
1) In atherosclerosis, plaque
deposits build up in the
arteries. Plaque is made up of
fat, cholesterol, calcium, and
other substances from the
blood. Plaque buildup in the
arteries often begins in
childhood. Over time, plaque
buildup in the coronary arteries
can:
Narrow the arteries. This
reduces the amount of blood
and oxygen that reaches the
heart muscle.
Completely block the arteries.
This stops the flow of blood to
the heart muscle.
Cause blood clots to form. This
can block the arteries that
supply blood to the heart
muscle.
Risk factor
Modified risk factor
Hyperlipidemia
Hypertension
Diabetes Melitus
Physical activity
Cigarette smoking
Obesity
High alcohol intake
Personality characterics
Pathophysiology
ageing
hypertension
Diabetes melitus
atherosclerosis
hyperlipidemia
Inflammatory process
T-lymphocytes & monocytes(become macrophages)ingest the lipids & die
Degeneration of smooth muscle cells(vessel)
Fibrous capis form(over fatty core(called plague/atheromas
Disturbance
Insuffiency of oxygen & nutrient demand to myocardium
Myocardila ischemia
Narrow & obstruct blood flow
Clinical manifestation
Breathlessness, shortness of breath or dyspnea.
Lack of oxygen supply to myocardium because of the
narrowing of the right coronary artery.
Chest pain
The volume of oxygenation blood deliver to the
myocardium is lesser due to the occlusion artery cause
the workload of heart increase lead angina attack.
Palpitation
The workload of heart is increasing and pump harder to
meet the oxygen demand.
Fatigue
It is because patient use accessory muscle to help in
increase breathing process to inhale more oxygen
Syncope
The symptom of syncope is happen in a sudden,
transient loss of consciousness due to
inadequate cerebral blood flow
Diaphoresis
Anxiety
Mr. S is always anxiety during chest pain.
Patient might be fear an anxious during the
chest pain as they are afraid of dying
Nausea and vomiting
Lightheadedness
Pallor
Complication
complication
Myocardial infarction
Congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Myocardial rupture
Cardiogenic shock
Dysrhythimias
Acute heart failure (pulmonary oedema)
Pericardial effusion and cardiac
tamponade
Investigation
Investigation
List of investigation
done:
Diagnostic test:
Chest x-ray
Electocardiogram
Angiography
Stress test
Laboratory test:
1. Haematology-value of
haemoglobin
2. Total white blood count
and WBC differential
count
3. Random blood sugar
(RBS)
4. Urea electrolyte (BUSE)
5. Lipid profile
6. Blood coagulant test
Result of Chest x-ray
Report:
Heart size normal
Lung fields clear
No hilar abnormality seen
Electrocardiogram
Result of the
electrocardiogram
ST segment depression of 0.6mm in lead
I, II and V5 V6. According to the
Result of blood test
[Total white blood count & WBC differential count]
Examination Result/unit Normal range
Total white blood
count
White blood cell
7.8/uL
4.3-10.5
WBC differential
count
Neutrophil
Lymphocyte
Eosinophil
Monocyte
Basophil
66.7%
20.6%
6.1%
4.7%
1.1%
40-75
20-45
0-6
1-11
0-2
Result of random blood
sugar
Examination Result/unit Normal range
Glucose 6.2mmolL
111mg/dL
3.9-6.1
70-110
Angiography
Selective coronary angiography is the only
method currently available for accurately
delineating human coronary anatomy as well
as for locating and quantitating obstruction
in large-caliber coronary arteries.
Occlusion coronary arteries of
Mr. S
Result of angioraphy
Report:
Left Main Stem, LMS: Normal
Left anterior descending artery, CAD: Normal
First Diagonal of the CAD: 90%Tight stenosis (done
PTCA with balloon)
Left circumflex artery, LCX: 90% Tight stenosis
(done PTCA with stent)
Right coronary artery, RCA: 60%-70% distal stenous
mild stenous with posterior
descending artery, PDA
Result of stress test
Summary of the treadmill stress test
Total of exercise time: 06:23
Maximum heart rate:144bpm 87% of maximum
predicted 164bpm
Maximum ST level :-2.90mm in lead III in Stage3
is 6:23
Reason for termination: Fatigue,chest discomfort
Conclusion: Positive stress test
Phase &
time
Position time Speed
(km/h)
Grade
(%)
B/P
(mmHg)
HR
(bpm)
Workload RPP
(100)
VE
(1min)
ST
levelII
(mm)
Comment
Pretest supine 00:39 0.00 0.00 130/70 100 1.0 130 0 -0.99
standing 00.31 1.60 0.00 100 1.0 0 -0.95
Warm
up
00.31 1.60 0.00 97 1.1 0 -0.70
Exercise Stage 1 03.00 2.70 12.00 170/80 127 4.6 215 0 -1.65
Stage 2 03.01 4.00 12.00 200/80 147 7.2 284 0 -2.70
Stage 3 00.23 5.50 14.00 147 7.5 0 -2.90 6.10
chest
pain
Recovery 06.13 0.00 0.00 180/80 93 1.0 167 0 -1.75
Example of the stress test
Result of lipid profile
Examination Result/unit Normal range
Total cholesterol 7.4mmol/L
2.87mg/dL
<5.20
<200
Triglycerides 1.64mmol/dL
144mg/dL
<2.28
<200
HDL cholesterol 2.43mmol/L
94mg/dL
>1.42
>55
LDL cholesterol 4.9mmol/L
165mg/dL
<3.40
<130
LDL
cholesterol/HDL
cholesterol
3.1 Up to 4.0
Result of the blood test
aPartial thromboplastin time & aPTT control
Examination Result/unit Normal range
aPartial
thromboplastin
time
>180 sec
(prolonged)
30-40
aPTT control 33.0sec 28-36
Result of blood studies
(Activated clotting time, ACT)
Date/time Examination Result/unit Normal range
6/6/06 at
10.00p.m
Activated
clotting time,
ACT
337sec <160
6/6/06 at
12.00p.m
Activated
clotting time,
ACT
159sec <160
Treatment
Invasive procerdure,
Percutaneuos Transluminal
Coronary Artery (PTCA)
PTCA is an invasive procedure where
narrow coronary artery that are block by
the plague on the arterial wall is dilate by
balloon or stent. This procedure is carried
out in the cardiac catheterization
laboratory.
A preparation will be done before send
patient for PTCA
Pre-PTCA, checklist
1. Patient name,M.R.N
2. Consent
3. Patients height/weight
taken
4. Allergy to contrast
5. Allergy to
drugs/elastroplast
6. Present medication
7. Pre-medication
8. Last meal or drink
taken
9. Fever
1. Asthma
2. Chest x-ray
accompanying patient
3. ECG records
accompanying patient
4. HB,B.U.S.E,RBS
5. VRDL/HEPATITS
B/AIDS
6. Dentures removed
7. Shaving done
8. Patient passed urine
9. Nittoderm in place on
the right chest
10. Venofix inserted
11. others
Invasive procerdure,
Percutaneuos Transluminal
Coronary Artery (PTCA)
Balloon is deflated
Angiography
Diagnose the
occlusion coronary
artery by
introduced using
femoral artery
Atheroma are
verified
A balloon
catheter are
inserted into the
distal of the RCA
Balloon
inflated to
expand the
stent
Catheter id
removed, stent
is hold to open
the artery
Coronary stent
The patient might return to ward with a large peripheral
vascular access sheath in place. The sheath are
removed after blood studied (e.g activated clotting time)
indicate that the clotting time is within an acceptable
range.
The patient must remain flat in the bed and keep the
affected leg straight until the sheath are removed and
then for few hours to maintain hemostasis.
After hemostasis is achieved, patient usually can be
weaned from intravenous medications, resumed self-
care, ambulate unassist within 1 to 12 hours in the
procedure
The nurses teachers the patient to monitor the site for
bleeding or development of hard lump that is larger than
a walnut.
Post-PTCA
Medication
Aspirin, aspirin 100mg,glycine 45mg
Group name: Anticoagulant drug
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: Continue at home
Route: Oral
Dosage: 150mg
Frequency: BD
Indication: Transient
ischemic attacks, secondary prevention
of MI, vascular occlusion and deep vein
thrombosis
Plavix, Clopidrogel hydrogen sulfate
Group name: Anticoagulant drug
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: Continue at home
Route: oral
Dosage: 75mg
Frequency: BD
Indication:
Prevention of atherothrombotic events
Herbresser, Diltiazem hydrochloride
Group name: Calcium antagonist
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: 6th June 2006
Route: Oral
Dosage: 30mg
Frequency: BD
Indication: Mild and
moderate hypertension, angina
pectoris,variant angina pectoris
Lipitor, Astrovastatin Calcium
Group name: Antihyperlipidaemicagent
Date on: 6th June2006
Date off: Continue at home
Route: Oral
Dosage: 10mg
Frequency: Daily
Indication: Reduction of
elevated total and LDL cholesterol
Imdur, Isosorbide-5-mononitrate
Group name: Antianginal
Date on: 6th June2006
Date off: Continue at home
Route: oral
Dosage: 30mg
Frequency: Daily
Indication: Prophylactic
treatment of angina pectoris
Diamicron, Gliclazide
Date: 6th June2006
Date off : 6th June2006
Route: oral
Dose: 40mg
Frequency: BD
Indication: Type II diabetes
Nitroderm, Nitroglycerin
Group name: Antianginal
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: 6th June 2006
Route: topical
Dose: 10 mg
Frequency: stat
Indication:
Prevention of the angina pectoris
Ativan, Lorazepam
Group name: Sedative
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: 8th June 2006
Route: oral
Dose: 0.5mg
Frequency: daily
Indication:
Management of anxiety disorders or
anxiety associated with depressive
symptoms
Valium, Benzodiazepine
Group name: Antianxiety
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: 6th June 2006
Route: oral
Dose: 5mg
Frequency: stat
Indication:
preoperatively as a relaxation
Heparin, Heparin Leo
Group name: Anticoagulant agent
Date on: 7th June 2006
Date off: 7th June 2006
Dosage: 1000u per hour in 8hours
Frequency: Stat
Indication:
Deep-vein thrombosis, prevention of
DVT/PE
Controloc, Pantoprazole sodium
sesquihydrate
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: 6th June 2006
Route: oral
Dose: 40mg
Frequency: stat
Indication:
long term management and prevention of
relapse of reflux oesophagus,
Glyceryl Trinitrate DBL, Glyceryl Trinitrate
Group: Antianginal drug
Date on: 6th June 2006
Date off: continue at home
Dosage: 25mg
Route: Sublingual
Frequency: Stat
Indication:
Control of hypertension treatment of
angina pectoris unresponsive to
recommended doses of organic
nitrates
Nursing care plan
1. Alteration in emotional status: anxiety related to invasive
procedure, Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
2 .Potential of bleeding associated with arterial puncture after
invasive procedure after invasive procedure, PTCA
3. Potential of chest pain related to decrease myocardial
oxygenation and ischemia (angina attack)
4. Alteration in sleeping pattern discomfort relate to new
hospital environment
5.Knowledge deficit related to home care management of
Ischemic heart disease
1
Date on: 6thJune 2006
Time: 12.00 noon
Problem identified:
Alteration emotion status: Anxiety related to invasive
procedure, Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Artery,
PTCA
Supporting data:
Patient verbalized that he worry about the severity of his
disease and chance to recover
Patient appear fear, and anxious when he was inform
the PTCA will be done on 4.00pm
Expected outcome:
Patient will has manageable level of his anxiety and
become more relaxed, less anxious, fear and ready to go
for PTCA within 1 hour of the nursing interventions given
Nursing interventions:
1) Assess patient general condition: level of
the anxiety (facial expression) and his
undestanding regarding to the invasive
procedure, PTCA
Rationale: to act as baseline data and to
plan an appropriate nursing intervention
Implementation: I assess his point of
view towards the PTCA, he replied that
although he had done PTCA once on
March, he still anxious because he
confuse about it
2) Provide conducive environment to rest,
expression of fears
Rationale: determine his feeling and
problem regarding the PTCA. Rest and
expression of fears may promote
relaxation at the same time.
Implementation: I encourage him to rest
and express feeling his own feeling about
his real problem and I explain it is
important to my knowledge to help him
answer
3) Encourage patient to ask questions and
do not avoid questions
Rationale: enable patient feel free to ask
questions and promote confidence in
patient to staff nurse by not avoiding
questions
Implementation: I encourage Mr. S to ask
any questions he feel confuse and I try to
answer it and some of the question, I get
answer from Staff nurse N
4)Reinforce doctors explaination regarding to the PTCA
in clearly and accurate way, plus give him a phamplet
about the PTCA. Then evaluate his understanding
beside obtain his consent on behalf of the doctor after
Dr. T had given the explaination to him
Rationale: Increase of his knowledge of the PTCA
may enable patient to sign the consent confidently
Implementation: I explain to the patient about PTCA
briefly and clear plus given him a phamplet regarding
the PTCA. I evaluate the understanding of the
explaination I given and he signed the consent under
the observation by the Staff nurse A
5) Inform the reason of asking for allergy to
contrast, drugs or elastroplast before the
PTCA
Rationale: enable Mr. S to know the
reasons allergies being assess
Implementation: I explain to the patient
that if he allergy to certain matter, it will
affect the progress of the PTCA since the
dye contain iodine
6) Provide explaination that the staff nurse
obtained the when he taken his last meal
or drink is because prevent aspiration of
food into lung if the patient collapse
Rationale: allay his anxiety since he might
curious because he is order to nil by
mouth
Implementation: I tell Mr. S that he need
to fasting to prevent aspiration of food into
lung
7) Assess his reaction when he being assess for
having fever or asthma and comfort him by
briefly explaination that fever indicate infection
whereas asthma may cause patient to have
difficulty in breathing so that the health
personnel will take precaution
Rationale: evaluate his anxiety status for being
assess having fever or asthma
Implementation: I observe his reaction: facial
expression when the staff is assess his
temperature and asthma. He look confuse but
he just answer he has asthma since 4 year ago.
I tell the patient is it an precaution for the PTCA
8)Reinforce that assess and obtain
VRDL/HEPATITIS B /AIDS test is act for
precaution to the health personnel care
and enable them to perform it in excel
Rationale: enable not to angry or worry
that the tests being investigate to promote
co-operative environment between nurse-
patient
Implementation: I tell him the tests is
assess for precaution and future
references
9)Assure the patient dentures is removed
and it is because the dentures might
cause complication; obstruction of airway
Rationale: allay patient curiosity and
reinforce the explaination so that patient
can be co-operate well
Implementation: Mr. S asked me that
purpose for the dentures need to be take
out. I answer the dentures may cause
obstruction of airway during the procedure
10) Provide information that the nitroderm in
place on the right chest
Rationale: enable patient to know the
patchess purpose so that he would not
confuse
Implementation: I tell him not to worry
about the patches being stick on the right
chest, its just for precaution
Date: 6th June 2006
Time: 1.00p.m
Evaluation: Patients anxiety status is reduced,
calm and ready to do the PTCA after one of
nursing intervention given.
Supporting data:
Patient verbalized that he is more confident to face the
PTCA
He thank you me for me giving him a briefly view of the
PTCA for the second time
Initiated by: STN Low,1686
Date: 6thJune 2006
Time: 7.40p.m
Problem identified:
Potential of bleeding associated with arterial puncture
after invasive procedure after invasive procedure, PTCA
Supporting data:
Patient is administer with intravenous heparin from
12.00a.m until 5.00a.m
Patient has done the PTCA
Expected outcomes:
Patient will has intact and dry at the arterial puncture as
it monitor during the nursing intervention given within 8
hours
Nursing interventions:
1) Assess patient general condition: facial
expression e.g pale, fatigue and his complaint is
taking seriously
Rationale: Fatigue and pale is a signs of
prolonged bleeding or large volume of blood is
loss from the large artery, femoral artery. Beside
patients complaint is important to be pay
attention to detect any abnormalities
Implementation: I assess patients facial
expression and ask for his concern, he looked
pinkish, tired and he has no complaint
2) Monitor vital sign and oxygen saturation
hourly
Rationale: Act as baseline data and the
changes in blood pressure indicate pain
or decrease of blood volume
Implementation: I monitor hourly in first
4 hours for once with the observation by
the staff nurse in-charge and the
following of the monitoring I do not do as
my shift is end on that day
3) Monitor the puncture site hourly and record the
color, movement, sensation, warm or cold in the
circulation chart
Rationale: Potential of bleeding may occur
after PTCA since large artery being punctured
by determine the circulation in the right groin is
intact as the sign and symptom of the bleeding
is mentioned as above
Implementation: The monitoring of the groin
is done by the staff nurse in-charge and I
observe once. The patient groin appeared
pinkish, able to move a bit of the right leg,
sensation is felt and it felt warm
4) Obtain the coagulant studies as order by
doctor e.g Activated coagulant test,ACT
Rationale: help to determine the
tendency to bleed
Implementation: The staff nurse in-
charge obtain the patients blood for ACT
twice an the 1st result is prolong and the
2nd result is in acceptable range
5) Inspect all the body fluid for presence of
the blood e.g urine, sputum, stool,
vomitus
Rationale: Internal bleeding may be
manifested in urine, sputum and
gastrointestinal drainage
Implementation: I inspect all the body
fluid which belonged to Mr. S frequently
and I inform him if he notices the
presence of blood the body fluid to report
to the nurses immediately
6) Avoid intramuscular injection
Rationale: Intramuscular injection may
have potential to cause bleeding since
the needle being inject to the muscle
Implementation: All the staff nurse have
ensure the injection not given through
muscle
7)Keep and ensure intravenous line on the
other hand which not giving the heparin is
patent
Rationale: A patent intravenous line may
be needed during complication occur such
as active bleeding
Implementation: I ensure the intravenous
line is patent and tell him the importance
of keeping the line is intact
8) Ensure one pint of whole blood is
reserved
Rationale: patient may has risk of
bleeding, thus the blood transfusion may
be treat at once
Implementation: The staff nurse ensure
one pint whole blood is reserved and
prepare it if blood transfusion is needed
9) Advise the patient to lie flat on the bed
for 6 hours and provide explanation
Rationale: If patient sit up the groin is
flex and the femoral sheath apply
pressure is decrease plus the high
pressure from the femoral artery may
have tendency to bleed
Implementation: I tell him lie on the bed
flat for 6 hours to prevent the puncture
site from bleeding
10)Ensure the other anticoagulant drug is
not administer to patient
Rationale: Assure the risk of bleeding
increase as the prevention of blood
clotting is enhance
Implementation: the staff nurse assure
that there are no others anticoagulant
drug is given as ordered as doctor
Date: 8th June 2006
Time: 8.00a.m
Evaluation:
The potential of bleeding is monitor and no
bleeding occur during the nursing intervention
given and during hospitalization
Supporting data:
The arterial puncture site is intact
Patient appeared pinkish and not fatigue but
complain a little pain at the groin when moving
Initiated by: STN Low,1686
Nursing care plan 3
Date: 6th June 2006
Time: 12noon
Problem identified:
Potential of chest pain related to decrease myocardial
oxygenation and ischemia (angina
Attack)
Supporting data:
Patient having is diagnose has single vessel disease-
40% of mild stenosis of RCA from previous angiogram
Patient verbalized he experienced chest pain on and off
last 2 last 2 weeks
Expected outcome:
Patient will has absent of chest pain after 1 day of the
nursing interventions given and hospitalization
Nursing interventions:
1)Assess the characteristic of the chest pain such as
quality, location, severity of pain (scale pain:0-absent of
pain till 10-severe pain), time onset and duration,
determine it occurs at rest or during exertion, strong
emotion, or during exposure to temperature extreme
Rationale: to obtain as baseline data, symptoms and
causes associated with angina usually precipitated by
exertion or emotion and can occur on during the day and
night or both
Implementation: I interviewed the patient and his wife
regarding the characteristic of pain. They described to
me that his chest pain occur is like squeezing around the
area of the chest and he chosen 6-7 rate of rate of the
scale pain. The duration is lasting not more than 30
minute and it occur during the minimal exertion and rest.
2) Provide patient to rest in bed in calm,
quiet environment, avoid stressful
situations
Rationale: to reduce oxygen
consumption and excessive used of
energy to have balance between oxygen
supply and demand by resting. Stressful
environment may not promote relaxation.
Implementation: I advised rest in bed if
he having chest pain and will ensure the
environment is quiet and suitable for him
to rest
3) Monitor vital sign and oxygen saturation
by pulse oxymeter 4 hourly
Rationale: Detect any abnormalities
especially dyrhsthimas and high blood
pressure
Implementation: I monitor vital sign and
oxygen saturation 4 hourly.
4) Provide assistance aids to complete his
ADL e.g bath
Rationale: reduced used of excessive
energy that will increase workload of the
heart
Implementation: I offer my help to
assist him to bath in the bathroom
5) Provide certain equipment which enable
patient to complete his ADL on bed e.g
urinal
Rationale: reduce metabolic rate to
decrease energy to complete ADL on
bed. Hence myocardial oxygenation may
be adequately supply to the heart
Implementation: I offer a urinal to Mr. S
and tell him to pass urine in it
6) Inform patient to report to health
personnel care immediately sign and
symptom of chest pain occur e.g Short of
breath, palpitation, syncope
Rationale: to be notified and further
treatment is given immediately.
Implementation: I tell the patient to report
to nurse if about sign and symptom of
chest pain occur
10) Administer medication as prescribed by
doctor e.g Sublingual gylceryl trinitrate,
GTN
Rationale: Enable chest pain can be
treated immediately by dilate the narrow
vessel and increase cardiac output
Implementation: I did not administer
medication as prescribe because patient
not complaining of chest discomfort
7) Do the nurses round frequently and
assess patients general condition
complain at the sane time
Rationale: Enable detectation of any
abnormalities especially chest pain and
assessing patients general condition and
complaint as well
Implementation: Always do the ward
round to the patient frequently on my free
time and assess his complaint.
8) Restrict visitors and inform the visiting
time such as 12 noon-2 pm; 4 pm-9 pm
Rationale: Enable patient to have rest
and reduce over-emotional status such as
happy.
Implementation: I tell the patient to let
the amount visitor reduce to one or two
and inform the visitor about the
visiting time.
Date: 6th June 2006
Time: 1 p.m
Evaluation: Patient verbalized he did not experience chest
pain or sign and symptom of chest discomfort after 1
hour the nursing intervention given and during
hospitalization.
Supporting data:
Patient verbalized that no sign and symptom of chest
pain
Patients vital sign is in normal range as below:
T
O
: 36.7OC
P : 70 bpm
R : 20 bpm
BP : 100/60 mmHg
Initiated by: STN Low,1686
Date: 6th June2006
Time: 12.00 noon
Problem identified:
Alteration in sleeping pattern discomfort relate to new
hospital environment
Supporting data:
He complain of chest pain occur on and off at night
since last two weeks
He seem fatigue, weak
Expected outcomes:
Patient will have undisturbance of sleep at night within 1
day of nursing interventions
Nursing interventions:
1) Assess patient general condition:
lethargic signs e.g fatigue, weak, dizziness
Rationale: determine sleeping pattern
level to act as baseline data and plan
appropriated nursing intervention
Implementation: I interview the Mr. S
about is problem in sleeping disturbance
and assess sign of lack of sleep
2) Provide warm drink at night, 2 hours
earlier before he sleep
Rationale: warm drink to induce the
patient to have good sleep and given 2
hours earlier is to prevent patient wake
up to pass urine
Implementation: I provide a cup of
warm Milo to Mr. S 2 hours before he
sleep and ask him to pass urine before
sleep
3) Provide conducive environment which is
quiet, calm and peaceful
Rationale: enable patient to have good
rest because the noisy environment may
produce stressful feeling
Implementation: I ensure the
environment is quiet, peaceful and calm
as all the patients in the six bedded room
are sleeping as well
4) Advise the patient not to having nap
during the day or a short period of nap
may be acceptable since patient might
feel tired
Rationale: Having nap produce excessive
rest and might change the habit to sleep
very late at night
Implementation: I advise the patient may
have short period of nap or not to do so if
he able to manage and admit this one of
the reason he having difficulty in sleeping
5) Encourage patient to express his feeling
according to his problem
Rationale: Express feeling of problem
help to relieve stress and might promote a
very peaceful sleep
Implementation: I encourage Mr. S to
voice out his problem and he said he
always have chest pain at home during
sleeping, he also anxious about the effect
of PTCA since he done the PTCA is
purposely to live longer to take care of his
family
6) Teach patient to use diversional therapy
or relaxation therapy
Rationale: promote relaxation and divert
patient problem to others matters so that
patient able to sleep well
Implementation: I teach patient about the
relaxation therapy such as listening to the
peaceful songs while patient go to bed
7) Allow one companion to stay in the
hospital at night with the patient e.g family
member
Rationale: Allay patient anxiety and
promote comfort as family member is with
patient
Implementation: I tell Mr. S may has one
companion is allow to accompany him at
night so that he can feel more comfortable
8) Administer medication as ordered by
doctor to enable he sleep well e.g ativan
0.5mg daily
Rationale: Ativan assist in relieve
depression and promote relaxation
Implementation: The staff nurse
administer ativan as prescribed by doctor
and follow the 5R, right patient, right drug,
right route, right dose, right time and tell
him it help to induce sleeping
Date: 8th June2006
Time: 12 noon
Evaluation:
Patients sleeping pattern has improved within 1
day after the nursing intervention given and
during hospitalization.
Supporting data:
Patient verbalised he is able to sleep well
Initated by: STN Low
Date : 8th June 2006
Time: 9.00a.m
Problem identified:
Knowledge deficit related to home care management of
Ischemic heart disease
Support data:
Mr. S ask me about method of prevention as he
discharge
Mr. S seem to ask me a lot of question about his disease
He seem anxious of home care as he go home
Expected outcome:
Patients knowledge about home care will be improved
within 1 hour as the nursing interventions given
Nursing intervention:
1) Assess patients general condition: facial
expression and patients complaint
Rationale: Obtain general information fro
patient due to his problem of home care
deficit
Implementation: I assess patients
general condition: Facial expression, ask
for his concern. He complain he is worry
about the name care at home.
2) Assess patients level of knowledge or
understanding of his disease and method
of care should be taken
Rationale: Determine patients
knowledge of his disease and step of
care for himself at home
Implementation: I assess his education
level by ask for his occupation,
knowledge of medical term or any
information in ischemic heart disease
3)Inform the sources or causes, sign and
symptom of his chest pain such as
palpitation and short of breath, fatigue
Rationale: enable patient to has
awareness over the cause of chest
discomfort so that he can avoid these
sources
Implementation: I inform the patient that
the cause that triggers the chest pain e.g
exertion activity and it normally will occur
fatigue and short of breath as symptoms
4) Reinforce patient to has low cholesterol diet,
low salt diet, high fiber, low oily food and soft
diet
Rationale: Low cholesterol and low oily may
help to reduce of restore of plague in the
occlusion vessels. Low salt reduce water
retention, thus maintain B/P value. High fiber
help to stimulate bowel movement and soft diet
is enable the food eaten to be digested easily.
Implementation: I reinforce the patient to
have control over the diet r.g low cholesterol,
low oily, low salt, and high fiber and soft diet
5) Encourage patient to do regularly
exercise start with gradually exercise
Rationale: Gradually exercise is an
effective may burn the fat being store
and enable heart workload increase
slowly in acceptable range
Implementation: I always encourage the
patient to do gradual exercise by
walking for short distance and gradually
increase to jogging if persist
6) Advise patient to have rest between the
stressful activity e.g exercise or even
after meal
Rationale: reduce oxygen demand in
stressful environment to prevent chest
pain occur because cardiac workload
increase
Implementation: I advise Mr. S to rest
as he feel stress or tired to relive chest
discomfort
7) Advise patient to change his eating habit
by changing not to take supper
especially oily food and reduce eating of
red meat e.g mutton as well as consume
caffeine drink
Rationale: reduce the risk factor of
increase atherosclerosis by modify the
eating unhealthy habit
Implementation: I advise him to change
his unhealthy eating habit: not to take
supper, can has 1/2 of mutton and do not
consume coffee
8)Maintain the level of blood glucose by
reduce low sugar diet, take medication
prescribed by doctor
Rationale: to monitor the glucose in blood
to reduce risk of complication occur from
ischemic heart disease such as
myocardial infarction
Implementation: I reinforce patient to
maintain the level of blood glucose by
taken right mediaction and reduce sugar
intake, fruit e.g durian
9)Advise patient ot do self-administer mediaction
as orderd by doctor e.g Lipitor, Aspirin, Herbresser
,Imdur
Rationale: Lipitor user to maintain cholesterol
level whereas aspirin is assist in prevent blood
clot formation in the coronary artery stent.
Hebresser may reduce hypertension and
angina pain as well as Imdur. Overall patients
condition is controlled by these medication
Implementation: I advise patient to take the
medication on time, to maintain his severity of
his disease become worse.
Date: 8th June 2006
Time: 10.00a.m
Evaluation: Patients has improving his knowledge
regarding to the home care deficit in management of the
ischemic hear disease after 1 hour the nursing
intervention given.
Supporting data:
Patient verbalized that he is more confident to take care
of himself at home
Patient appreciated my lessons on him and he even
wish to try the steps as soon as possible.
Initiated by: STN Low,1686
On 8th June2006, I have teach Mr. S about
the health education in the morning before
he proceed his discharged. I given the
health education as stated below:
Diet
Medication
Exercise
Risk factor
Life style
Date:8
th
June 2006
Time:12noon
TTA:
Aspirin 150mg, BD
Plavix 1/1 BD
Lipitor 1omg daily
Imdur 90mg daily
Herbresser 30mg
daily
Diamicron 40mg daily
Date: 20
th
June 2006
Dr. S has seen Mr. S. Doctor evaluate his
condition that it is now improving of recovery.
Dr. S also stated the patient his is showing a
good sign after post PTCA and no complication
of the PTCA is identified.
Dr. S also had assess his blood pressure and
the result is 110/80 mmHg
TTA: Zocor 40mg, Daily
Aspirin 150 mg, BD
Plavix 1/1, BD
Herbresser 30mg, Daily
Imdur 30mg, Daily
Mr. S was admitted to JSH for PTCA. Actually, he has
developed chest pain on and off after 2 years ago. Then
he felt chest pain is became severe and intolerance.
Hence a few investigation was done when he admitted
on 30/O6/06. An angiogram is performed, the findings
are single vessel disease of right coronary artery 40%
mild stenosis, 90% thigh stenosis of left circumflex artery
and thigh 90% of the first diagonal of left anterior
descending artery. He had done a PTCA on 3O/6/O6
However he still experience chest pain after the PTCA,
thus he decreased to do second PTCA to dilate the
narrow distal of the right coronary artery.
During his admission, he came from Dr. Ts clinic to the
ward, he looked fatigue. He complained of chest pain on
and off since two weeks ago. He had normal Dr. T had
decided to perform the PTCA on4.00p.m
Value of haemodynamic accept his heart rate was
bradycardia, 47beats per minute. Dr. T seen had him
and decided to perform the PTCA on 4.00 pm. Doctor
also had prescribed the drugs for him as below:
Aspirin 150mg, BD
Plavix 1/1, BD
Lipitor 10mg, Daily
Ativan 0.5mg Daily
After the PTCA was completed, the patient
was sent to the High Dependcence Unit,
HDU on 7.40p.m for close monitoring. He
came out from the cardiac catheterization
laboratory with femoral dressing is dry and
intact. Close observation is and potential
of bleeding was monitored beside assess
for complication
1)C. Smeltzer S. ,Bare B.July 2003(tenth edition) Brunner and
Suddarths Medical Surgical Nursing, Coronary Artery Disease
2) Wange A,Grant A 2001 (ninth edition)Ross and Wilson, anatomy and
Physiology In health and Illness, Cardiovascular System
3) Ignatavicius D.D, Bayne M.V, Medical Surgical Nursing Coronary
Artery Disease)
4) Walsh W. 2006 (Sixth Edition)Watsons Clinical Nursing and
Related Sciences, Disorders of myocardial blood supply
5) Lemone P, Burke K, (Third edition), Medical Surgical Nursing,
Coronary Heart Disease
6) Skidmore-roth L., (2004), Mosbys Nursing Drug Reference
(102nd Edition 2005), MIMS
8) Martin E.A, (2005), Dictionary Nursing Malaysian Edition
9) http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/nhlb/contact/index.htm
10) www.heart.com
11) www.heartonline.com
12) www.healthcentral.com
Thank You
You might also like
- Psychiatric Case StudyDocument32 pagesPsychiatric Case Studyrachael85% (33)
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument35 pagesAcute Myocardial Infarctionvirnzrobz80% (10)
- 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know NowDocument29 pages50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know Nowtandz100% (19)
- Meet The Profesor 2021Document398 pagesMeet The Profesor 2021Raúl AssadNo ratings yet
- Phys Ed FinalDocument12 pagesPhys Ed Finalmellisa samooNo ratings yet
- MCQingeneralsurgeryforundergraduates PDFDocument259 pagesMCQingeneralsurgeryforundergraduates PDFNAVANEETHAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- PamphletDocument2 pagesPamphletapi-25931970033% (3)
- Ami Case Study 4aDocument53 pagesAmi Case Study 4aHannah ChiuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Cardiovascular PathologiesDocument65 pagesNursing Care for Cardiovascular Pathologiesyayah coletteNo ratings yet
- Ami Case StudyDocument53 pagesAmi Case StudyRose Ann CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack: Understanding Myocardial InfarctionDocument21 pagesHeart Attack: Understanding Myocardial InfarctionJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented byDocument76 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented bySoma Al-mutairiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology GuideDocument15 pagesCardiovascular Pathology Guidejaniceli0207No ratings yet
- Cardiac Function Tests ExplainedDocument8 pagesCardiac Function Tests ExplainedJosiah BimabamNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Case Analysis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis (MIDocument76 pagesMyocardial Infarction Case Analysis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis (MIIpeNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment # 3: Circulatory SystemJefferNo ratings yet
- Cardio ReviewerDocument21 pagesCardio ReviewerJean Rynne Barrameda BongaisNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument42 pagesMyocardial Infarctionarif mahammad bhuniyaNo ratings yet
- CV DisorderdsDocument59 pagesCV DisorderdsMustafa Al KhattarıNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2Document76 pagesMed Surg 2sham gowliNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction "Heart Attacks"Document16 pagesMyocardial Infarction "Heart Attacks"Camzii Borland100% (1)
- Cardiac FunctionCardiacDocument18 pagesCardiac FunctionCardiacMary Jean Hernani100% (1)
- CHD Sahil ThesisDocument78 pagesCHD Sahil Thesismanwanim18No ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular SystemDocument43 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E: Nursing Care of The Client: Cardiovascular Systemsarah morleyNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis (39Document5 pagesCoronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis (39Rapunzel LeanneNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Cronary Heart Diseas (CHD)Document7 pagesBiology Project Cronary Heart Diseas (CHD)احمد المغربي50% (2)
- Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyDocument35 pagesHypertrophic CardiomyopathyfawalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular Systemtheglobalnursing75% (4)
- Ischemic Cardiac Conditions Cardiac Muscle Dysfunction: Dr. Afaq Ahmad PT Cardiopulmonary Physical TherapyDocument19 pagesIschemic Cardiac Conditions Cardiac Muscle Dysfunction: Dr. Afaq Ahmad PT Cardiopulmonary Physical TherapyHUSNAIN TECH AND FUNNo ratings yet
- Cad - Coronary Artery Disease & Myocardial InfarctionDocument6 pagesCad - Coronary Artery Disease & Myocardial Infarctionmaulikmd21No ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology 2Document145 pagesClinical Pathology 2daniyfondoNo ratings yet
- Presentation B. INGGRIS FIKS BUK PUPUTDocument52 pagesPresentation B. INGGRIS FIKS BUK PUPUTRosy OktaridaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument83 pagesCardiovascular DisordersUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 3 F2018Document34 pagesCardiology 3 F2018TkNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DentDocument92 pagesCardiovascular DentVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- CMS 251 Unit 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument114 pagesCMS 251 Unit 1 Cardiovascular SystemAmon RicoNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument20 pagesAngina PectorisJyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of the HeartDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of the HeartLyka Milo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease PWDocument13 pagesIschemic Heart Disease PWEunica RamosNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction: Understanding Heart AttacksDocument17 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Understanding Heart AttacksAbram Nathaniel BunoanNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING 5 جامعة القدس دوسية PDFDocument77 pagesMEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING 5 جامعة القدس دوسية PDFAbdallah AlwawiNo ratings yet
- General Nursing Science 1 2020 PDFDocument95 pagesGeneral Nursing Science 1 2020 PDFRicardo DomingosNo ratings yet
- MYOCARDITIS: THE INFLAMMATION OF THE HEART MUSCLEDocument52 pagesMYOCARDITIS: THE INFLAMMATION OF THE HEART MUSCLE7337man100% (1)
- ACS Guide for PhysiotherapistsDocument48 pagesACS Guide for PhysiotherapistsLJie ChanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesThe Circulatory SystemEduardson PHNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Ischemia: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MDDocument37 pagesMyocardial Ischemia: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MDHaleema SultanNo ratings yet
- Segundo CorteDocument4 pagesSegundo CorteNicolasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular2006 Lecture NotesDocument31 pagesCardiovascular2006 Lecture NotescystanarisaNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfacDocument34 pagesMyocardial InfacWindelyn GamaroNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Disorderhxqf25mbvvNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SGD CaseDocument3 pagesCardiovascular System SGD CaseZH TVNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular LectureDocument10 pagesCardiovascular LectureJaysonPangilinanAbanNo ratings yet
- Cardio Disease - Full Document - LightGBMDocument29 pagesCardio Disease - Full Document - LightGBMThe MindNo ratings yet
- Heart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathDocument6 pagesHeart Muscle Shortness of Breath Tired Swelling of The Legs Heart Failure Irregular Heart Beat Fainting Sudden Cardiac DeathSachin DwivediNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: Indri Kartika Sari - Indri - Sari@student - Sgu.ac - IdDocument27 pagesAtherosclerosis: Indri Kartika Sari - Indri - Sari@student - Sgu.ac - IdMaruli PandjaitanNo ratings yet
- Joy B. Johnson Department of PharmacologyDocument55 pagesJoy B. Johnson Department of Pharmacologymatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- Left Chest Pain and ST Elevation in Mr. HeriDocument7 pagesLeft Chest Pain and ST Elevation in Mr. HeriRara Puspita BamesNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology 2Document12 pagesMedical Terminology 2azzazy040No ratings yet
- Reverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)From EverandReverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Natural Treatments for Heart Diseases: Through Medicinal Alkaline Herbs, Diets, & Aerobic Physiotherapy that Boost Natural Immunity; Detoxification & Prevent Infections, Inflammation & Cardiac ArrestFrom EverandNatural Treatments for Heart Diseases: Through Medicinal Alkaline Herbs, Diets, & Aerobic Physiotherapy that Boost Natural Immunity; Detoxification & Prevent Infections, Inflammation & Cardiac ArrestNo ratings yet
- Assignment Madam ZazaDocument5 pagesAssignment Madam Zazanur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Sedation and Weaning Protocols Combined Lancet 2008 PDFDocument9 pagesSedation and Weaning Protocols Combined Lancet 2008 PDFnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Reflective Practice: Implication For NursesDocument6 pagesReflective Practice: Implication For NursesIOSRjournal100% (2)
- The Eff Ectiveness of Supported Employment For People With Severe Mental Illness: A Randomised Controlled TrialDocument7 pagesThe Eff Ectiveness of Supported Employment For People With Severe Mental Illness: A Randomised Controlled Trialnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- ACLS Study Guide for IU Health ClassDocument18 pagesACLS Study Guide for IU Health ClassZarah Jane Rull NateNo ratings yet
- Group 402Document28 pagesGroup 402nur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- The Eff Ectiveness of Supported Employment For People With Severe Mental Illness: A Randomised Controlled TrialDocument7 pagesThe Eff Ectiveness of Supported Employment For People With Severe Mental Illness: A Randomised Controlled Trialnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Bond 2004 Systematic ReviewDocument15 pagesBond 2004 Systematic Reviewnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- (Roche-Dialysis Expert Workshop) Optimizing The Treatment of Renal Anemia. 100412Document28 pages(Roche-Dialysis Expert Workshop) Optimizing The Treatment of Renal Anemia. 100412nur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Group 402Document28 pagesGroup 402nur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- CRE Soup of InfectionDocument27 pagesCRE Soup of Infectionnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Essential Airway SkillsDocument21 pagesEssential Airway SkillsNia WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Matrix No: I674 Group: 29 (2 / 2005)Document150 pagesBronchitis: Matrix No: I674 Group: 29 (2 / 2005)nur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- StyeDocument21 pagesStyenur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Colles FractureDocument89 pagesColles Fracturenur syafiqah kamaruzaman100% (1)
- Peritonitis and Other GIT ComplicationsDocument80 pagesPeritonitis and Other GIT Complicationsnur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox PresentationDocument14 pagesChicken Pox Presentationnur syafiqah kamaruzaman100% (3)
- P129Document4 pagesP129AshwinNo ratings yet
- Hi Per TensyDocument81 pagesHi Per TensysyahidNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 1 Heart N BloodDocument30 pagesBio Unit 1 Heart N BloodsechosNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument7 pagesThesis On Coronary Artery Diseasesherielliottbillings100% (1)
- Cholesterol Special Report - by Dr. MercolaDocument17 pagesCholesterol Special Report - by Dr. Mercola4webusers administrator100% (3)
- Nutrients and Phytochemicals in White VegetablesDocument9 pagesNutrients and Phytochemicals in White VegetablesGarv JainNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesAtherosclerosis PathophysiologyHuman ResourcesNo ratings yet
- ABG analysis for respiratory failure therapy effectivenessDocument25 pagesABG analysis for respiratory failure therapy effectivenessHan Nah0% (1)
- Diamicron MR Factsheet - FINALDocument5 pagesDiamicron MR Factsheet - FINALRoxana Potur100% (1)
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument6 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEMJanelleNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis 1Document11 pagesCase Analysis 1Eloisa DanoNo ratings yet
- Onion Phytochemical and Health PropertiesDocument24 pagesOnion Phytochemical and Health PropertiesPépé DiopNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease PHD ThesisDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Disease PHD Thesisafknawjof100% (2)
- Case PresentationDocument24 pagesCase Presentationnaega hoshii'hhNo ratings yet
- Quantum Resonance Magnetic Analyzer - Arnulfo Yu Laniba TestDocument87 pagesQuantum Resonance Magnetic Analyzer - Arnulfo Yu Laniba TestArnulfo Yu Laniba100% (3)
- Prebeta-1 HDL and Coronary Heart Disease: ReviewDocument5 pagesPrebeta-1 HDL and Coronary Heart Disease: ReviewrafaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation on Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument18 pagesCase Presentation on Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseMaria Vanessa Lopez - BSN Level 3 A100% (1)
- Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Dyslipidemia: Gerald T. Gau, MD, and R. Scott Wright, MD, FACC, FAHA, FESCDocument42 pagesPathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Dyslipidemia: Gerald T. Gau, MD, and R. Scott Wright, MD, FACC, FAHA, FESCCalvin LitraNo ratings yet
- 31 Health Benefits of Diatomaceous EarthDocument4 pages31 Health Benefits of Diatomaceous Earthpigoto100% (4)
- Cardiac Biomarkers Expert Advice For CliniciansDocument255 pagesCardiac Biomarkers Expert Advice For CliniciansS Ram KishoreNo ratings yet
- EM2020 ProceedingsDocument555 pagesEM2020 ProceedingsAnaPaulaFranceschettoNo ratings yet
- 2000 Bookmatter TextbookOfAngiologyDocument19 pages2000 Bookmatter TextbookOfAngiologydavidmarkovic032No ratings yet
- Results NDocument1 pageResults NBea Carla Asuncion CunananNo ratings yet
- Answering Unit 1 - Biology (Ed Excel)Document42 pagesAnswering Unit 1 - Biology (Ed Excel)SharmilaJerome100% (5)
- Heart DiseasesDocument73 pagesHeart DiseasesturbomurboNo ratings yet
- DietandCVDriskfactorsinBotswana Kwape PhDthesis2012 (1) (001-025)Document25 pagesDietandCVDriskfactorsinBotswana Kwape PhDthesis2012 (1) (001-025)Indri Reskiawanti GalibNo ratings yet