Decision Support and Expert Systems
Chapter 10 Oz (5th ed)
�Decision Making in Business
Organizations success depends on quality of
managers decisions
When decisions involve large amounts of data and
complex processing, a DSS is a valuable tool
When decision making involves many uncertainties
and/or lots of alternatives a DSS is needed
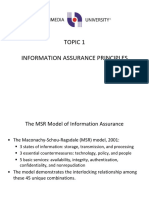
�Simons Stages of Decision Making
Intelligence - the individual collects information to
identify problems occurring
Design - the individual conceives of possible alternative
solutions to the problem
Choice - the individual selects among the various
solution alternatives
Implementation - the individual puts the decision into
effect and reports on the progress of the solution
�The Decision Making Process Is Not Linear
Is there a problem?
Intelligence
What are the alternatives?
Design
Which should you choose?
Choice
Is the choice working?
Implementation
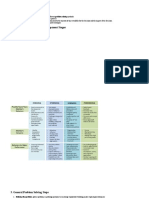
�Typical Activities in the Stages of
Decision-Making
�Structured and
Unstructured Problems
Figure 12.2 Business problems vary from structured to
unstructured. Many fall between the two extremes and are
considered semistructured.
6
�Types of Decisions
Structured decisions are repetitive, routine, and involve
a definite procedure for handling
Unstructured decisions are nonroutine decisions in
which the decision maker must provide judgment,
evaluation, and insights; there is no agreed-upon
procedure for making the decision
Semistructured decisions are ones where only part of the
problem has a clear-cut answer provided by an
acceptable procedure
�Example of a Structured and
Semistructured Problem
Structured problem: How much will I earn after two
years if I invest $100,000 in municipal bonds that pay 4
percent per annum tax free?
Semistructured problem: If I invest $100,000 in stock
XYZ and sell the stock in two years, how much money
will I make?
How are these problems different?
�Examples of Structured and
Semistructured Problems
�A Definition of a DSS
A DSS is a computer system that combines data,
sophisticated analytical models, and user-friendly
software to support semi-structured and unstructured
decision making.
Examples
Some DSS are very sophisticated and built by
experts to improve firm performance (e.g., in
trucking, models are developed to minimize total
mileage and maximize truck loads while
maintaining satisfactory delivery times)
Other DSS are built for individual managers to
assist in daily decision making tasks (e.g., Mrs.
Fields Cookies provides managers with a DSS that
assists in decisions related to which cookies to make,10
how many to make based on prior sales)
�Characteristics of a DSS
DSS offer users flexibility, adaptability, and a quick
response (usually interactive)
DSS allow users to initiate and control the input and
output
DSS operate with little or no assistance from
professional programmers (e.g., personal and CDSS)
DSS provide support for decisions and problems whose
solutions cannot be specified in advance
DSS use sophisticated analysis and modeling tools
11
�How a DSS Can Improve Managerial
Decision Making
In the intelligence phase
produce more timely data
increase the use of quantitative data
make more data available
In the design phase
generate more alternatives
generate more accurate alternatives
In the choice phase
make faster decisions
sometimes rank the choices
12
�Components of a DSS
Data management module
consists of current or historical data and possibly
some external data; data warehouse
Capabilities to manipulate the data
Model management module
collection of mathematical models (statistical
models, linear programming, forecasting, sensitivity
analysis models) available for the user
May also include OLAP or datamining tools
Dialog management module
Interface between user and other modules
Displays the analysis of results
13
�Typical Features of Commercial DSS
Easy to use graphical user interface (Windows like)
Drill down capacity
On-demand financial analysis (ratios or indicators)
Access to external (outside the firm) databases
Statistical analysis tools
Tools to navigate in a database or data warehouse
Ability to perform ad hoc queries or what-if analysis
Ability to solve diverse business problems
14
�Web Sites With DSS Products
Examples of DSS software
http://cdss.state.co.us/
http://www.vanguardsw.com
DecisionScript enables you to build Web-based DSS or CDSS
DecisionPro can be downloaded for free 15-day trial
Examples of EIS
http://visualmining.com
Look at dashboards and specific examples
http://www.meditech.com/productbriefs/pages/ProductBriefsCSES
S.htm
Drill down, customized views, individualized reporting
15
�Types of DSS (one way of classifying)
Model-driven DSS are primarily standalone systems
that use some type of quantitative model to perform
what-if or other types of analysis.
Data-driven DSS are systems that analyze large pools
of data that are (usually) stored in a data warehouse;
these systems permit managers to extract useful
relationships that exist in the data (datamining).
Web-based DSS exist for both types (customer decision
support systems; Vanguard;, Rainbird irrigation
systems), Home Depot (deck projects)
16
�Other Types of DSS
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Customer DSS (CDSS)
17
�Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
A GIS is a DSS for decision aid for map-related
decisions
Typical GIS contains
Database of quantitative and qualitative data
Database of maps
Program to display information on maps
Applications of GIS
Identifying the best site to locate a branch office
Targeting pockets of potential customers
Repositioning promotions and advertising
Tracking the spread of disease or crime
18
�Web Sites for GIS
HUD environmental maps
http://198.102.62.140/emaps/SearchFrame.asp
A major GIS vendor
http://maps.esri.com
An example of how a state can use a GIS
http://www.state.ma.us/mgis/muniapps.htm
An example of how Charlotte, NC uses a GIS
http://meckcama.co.mecklenburg.nc.us/relookup/ /
http://gischamber.co.mecklenburg.nc.us/website/chamber/Defa
ult.aspx
An example from San Francisco, CA
http://www.sfgov.org/site/gis_index.asp
Use APN #8719003 in SFprospector; demographic and
business report for Mission Bay South location
An example from York County, SC
http://www.yorkcountygov.com
19
�Customer DSS (CDSS)
A CDSS is a special type of DSS designed to support
the buying decisions of an existing or potential
customer. Most current CDSS are Web based
Support exists for both the individual consumer (B2C)
and businesses (B2B)
Complexity of products and sophistication of the buyer
often determine the nature of a CDSS
20
�Examples of CDSS
BusinessWeek (www.businessweek.com/bschools)
PriceGrabber ( www.pricegrabber.com)
BankRate (http://www.bankrate.com/)
HomeDepot (http://www.homedepot.com)
Design tools and calculators for various projects
Automobile tires (http://www.tirerack.com)
Assistance for choosing tires for an automobile
Vanguard (Vanguard - Investing for retirement Determine how much to save#early#early)
Retirement planning tool
21
�Manager and Consumer Decision Making
Managers DecisionMaking Process
Customers Purchasing Decision
Process
Need recognition
Intelligence
Information search
Design
Choice
Implementation
Evaluation
Purchase
After purchase evaluation
Description
Customers must recognize they have a need
Customers must search for a product or service
that satisfies this need
Customers use decision heuristics to evaluate and
compare goods and services
The customer must place an order, pay for it, and
arrange for collection delivery, or maybe
installation
Customers evaluate purchases with a view to
future decision-making. Customer support
and maintenance may be important
22
�The Electronic Spreadsheet: A DSS Tool
Most widely used tool for decision support because
it is widely accessible to both experienced and
inexperienced users
Features of spreadsheets that support DSS
construction
Preprogrammed functions enable the use of
many mathematical models
Built in IF-THEN function
Ability to use Visual Basic for Applications
Charts, pivot tables, what-if tables, scenario
management
23
�Ethical and Societal Issues
Decisions by Machines
To what extent should businesses use computer-based
decisions that can affect individuals.
Mortgage companies, credit card companies,
employers, banks, etc.
Distinctions between US and European approaches
Pros for automated decisions efficiency (cost, time,
speed)
Cons injustices due to errors, awareness, and finality
of decision
24
�Model Types
A model is an abstraction of an object or activity
(entity)
Model types
Physical models like a scale model of a building
Narrative models provide spoken or written
descriptions
Graphic models that use lines, symbols and shapes
(ER diagram)
Mathematical models employ equations and(or)
inequalities
25
�Mathematical Models
A system of mathematical expressions usually
equations that describe relationships between variables
in order to better understand or describe a real world
situation or process.
Mathematical models usually contain input and output
variables. Input variables are variables that are
systematically varied (plugged into the equations). The
results from the equations are the output variables.
Types of models
Dynamic versus static
Stochastic (probabilistic) versus deterministic
Linear versus nonlinear
26
�Sample Models by Functional Area
Accounting
breakeven analysis
tax computations
depreciation methods
Finance
cash flow
return on investment
after-tax yield
Marketing
product demand
forecast
pricing strategies
Sales performance
Production
product-mix
inventory level (EOQ)
quality control
production schedule
27
�Uses of Models
Description
Understanding
Prediction
Simulation
Optimization
Models typically do more than one of the above
28