Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B3.2.3 Irrigation Techniques Sprinkler Irrigation: - Dependent On Wind, Temperature, Humidity
B3.2.3 Irrigation Techniques Sprinkler Irrigation: - Dependent On Wind, Temperature, Humidity
Uploaded by
Adaad AsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B3.2.3 Irrigation Techniques Sprinkler Irrigation: - Dependent On Wind, Temperature, Humidity
B3.2.3 Irrigation Techniques Sprinkler Irrigation: - Dependent On Wind, Temperature, Humidity
Uploaded by
Adaad AsCopyright:
Available Formats
B3.2.
3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation
Uniform application by artificial rain
Good application efficiencies (0.7 0.8)
dependent on wind, temperature, humidity
Fairly terrain independent (but design must
take terrain into account)
Can have a low labour content
But
High(ish) investment cost
High maintenance cost due to pumping
Can be complex to run
1
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Criteria
(from Cornish)
Must permit cost recovery within one to two
years (and double investment in a short time)
Must be suitable for use on small and irregular
shaped plots
Must require only simple maintenance and
tools
Have a low risk of component failure
Be simple to operate
Be durable and reliable able to withstand
rough and frequent handling without serious
damage
2
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
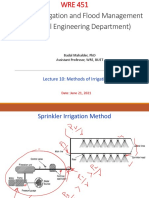
Sprinkler irrigation: System layout
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Drag hose system
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Sprinkler
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Spray pattern
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Spray pattern
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Spray pattern:
Variation in pressure
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Variation in pressure
10
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Solid set system
11
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Hand move laterals
12
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Hop along system
13
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Drag hose system
14
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Drag hose system
15
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Centre pivot system
16
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Centre pivot system
17
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Centre pivot system
18
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Centre pivot system
19
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Linear move system
20
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Linear move system
21
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Linear move system
22
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Mobile raingun
23
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Mobile raingun
24
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Appropriateness
Type
Divisibility
Maintenance
Risk
Operator
skill
Durability
Hand move
Drag Hose
Low-tech
Perforated pipe
Side roll
Side move
Static gun
Boom
Traveling gun
Centre Pivot
Liner move
Solid set
Piped distribution
4
25
B3.2.3 Irrigation techniques
Sprinkler irrigation: Appropriateness
Type
Score
Crops
Piped distribution
16
All
Low tech
16
All
Drag hose
15
All
Solid set
14
Orchards
Hand move laterals
12
All
Perforated pipe
11
Soft fruit and veg
Static gun
10
Cereals, Row crops
Side roll
Short cereals, row crops
Traveling gun
Cereals, Row crops
Boom
Cereals, Row crops
Centre pivot
Cereals, Row crops
Linear move
Cereals, Row crops
Side move
Cereals, Row crops
26
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation
Excellent efficiency (>0.9)
little and often - plants have ideal water all
the time
As little as 30% of the root zone is wetted
Not sensitive to slope
Good for mineralised water
Good for injected fertiliser
But
Very expensive
Needs well filtered water
Can be complex to operate ands maintain
27
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Improvements
Crop
Yield Increase (%)
Water saving (%)
Bananas
52
45
Grapes
23
48
Sweet lime
50
61
Pomegranate
98
45
Papaya
75
68
Tomato
50
39
Watermelon
88
36
Okra
16
40
60
Chillies
44
62
Sweet Potato
39
60
Beetroot
79
Radish
77
Sugar cane
33
56
Cotton
26
53
Cabbage
28
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Layout
29
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Drip irrigation
30
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Root zone
31
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Infiltration
Sandy soil
Clay soil
32
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Emitters
33
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Thick walled drip hose
34
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Thin walled drip hose
35
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Bubblers
36
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Microsprinklers
37
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Microsprinklers
38
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness
Type
Divisibility
Maintenance
Risk
Operator
skill
Durability
Drip emitters
Drip hose (thick)
Drip hose (thin)
Micro sprayers
Pressurised bubbler
Gravity fed bubbler
39
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness
Type
Score
Crops
Cost (USD
1990)
Piped distribution
16
All
800
Low tech Sprinkler
16
All
Pressurised bubbler
16
Orchard
Drag hose Sprinkler
15
All
Solid set Sprinkler
14
Orchards
Hand move laterals Sprinkler
12
All
Micro sprayers
12
Orchard, Soft fruit and
3,500
Gravity fed bubbler
12
Orchard
3,500
Perforated pipe Sprinkler
11
Soft fruit and vegetables
800
Static gun Sprinkler
10
Cereals, Row crops
950
3,000
675
3,500
675
Drip emitters
Wide row fruit and vegetables
3,500
Drip hose (thick)
Wide row fruit and vegetables
5,000
Drip hose (thin)
Wide row fruit and vegetables
3,000
Side roll Sprinkler
Short cereals, row crops
1,500
Traveling gun Sprinkler
Cereals, Row crops
1,500
Note: Skilled workers wages in Sri Lanka $4/day, Uganda, $2.5/day
40
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness:
Methods based on imported components
Manufactured drip emitters and
microsprayer assemblies are carefully
supervised and maintained.
Ancillary equipment such as screen
and media filters, metering valves,
pressure regulators and fertilizer
injectors are used in various
combinations.
Note: These options will be justified only for cash crops in a
stable market economy.
From Small-scale irrigation for arid zones; Principles and options:
http://www.fao.org/docrep/w3094e/w3094e00.htm
41
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness:
Methods based on imported materials but
local fabrication
Moulded plastic pipes or extruded plastic
tubing are perforated manually and laid
over the ground to simulate drip irrigation.
Vertical sections of plastic pipes (or even
discarded plastic containers such as
bottles) are embedded in the ground.
Thin-walled plastic vessels are filled with
sand or gravel to provide mechanical
resistance to crushing.
42
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness:
Methods based on imported materials but
local fabrication
Slit plastic sleeves cover the perforated
sections of the tubes to prevent root
penetration into the outlet holes.
Sand filters prevent suspended particles or
algae from clogging the outlets.
Auxiliary containers are used to dissolve and
inject fertilizer into the irrigation water.
Vertical standpipes are used to deliver water
from an underground pipe to small basins.
43
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness:
Methods based entirely on local materials
and workmanship
Low-fired porous ceramic pots are
placed on the surface or embedded in
the soil within the root zone. When
filled with water and dissolved
fertilizers, the permeable clay
receptacles ooze water and nutrients
into the soil.
Sectioned ceramic pipes constitute line
sources that feed elongated beds.
44
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Micro irrigation: Appropriateness: Clay
pot method
45
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Modern irrigation technologies:
Appropriateness
(from Cornish)
The technology must offer the farmer
sufficient financial return or a
reduction in labour demand, to justify
the investment
Farmers need to grow high value crops
for an assured market in order to
cover costs
Increasing national or regional water
shortage is an important factor
motivating governments to promote
the use of modern irrigation
technologies
46
B3.2.4 Irrigation techniques
Modern irrigation technologies:
Appropriateness
Governments must enact policies
promoting the technologies for the
smallholder, making it attractive to
manufacturers and dealers to develop
and promote them
Suitable systems must be relatively
cheap and straightforward to operate
and maintain
Farmers require effective technical
support in the initial years failure =
ruin
47
You might also like
- Weibull AnalysisDocument2 pagesWeibull AnalysisSebastián D. GómezNo ratings yet
- Command Line CalculatorDocument15 pagesCommand Line CalculatorShipra MishraNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Water RequirementsDocument49 pagesIrrigation Water RequirementsShaun Sundawn TeruelNo ratings yet
- Micro IrrigationDocument4 pagesMicro IrrigationKowalski2008No ratings yet
- Sprinkler PresentationDocument21 pagesSprinkler PresentationRajabu HatibuNo ratings yet
- Precision FarmingDocument43 pagesPrecision FarmingParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation DesignDocument44 pagesDrip Irrigation DesignSimranjeet Chawla75% (4)
- ST Report TTTDocument38 pagesST Report TTTSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- TKP3501 Farm Mechanization & Irrigation Topic: Irrigation MethodsDocument45 pagesTKP3501 Farm Mechanization & Irrigation Topic: Irrigation MethodsIain Choong WK100% (1)
- Water Resources MicroprojectDocument18 pagesWater Resources MicroprojectCE 230 Akash KharabeNo ratings yet
- Hydrology, Irrigation and Flood Management L4/T1 (Civil Engineering Department)Document21 pagesHydrology, Irrigation and Flood Management L4/T1 (Civil Engineering Department)Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Water Conservation: Vedaant Pandit 1728Document24 pagesWater Conservation: Vedaant Pandit 1728vedaant panditNo ratings yet
- Pub HandbookDocument22 pagesPub HandbookMin Htut WinNo ratings yet
- Afa - Oct 4Document30 pagesAfa - Oct 4marjorie gomezNo ratings yet
- Extensive-Survey PA CollegeDocument16 pagesExtensive-Survey PA CollegeRoyal RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Micro Irrigation PDFDocument9 pagesMicro Irrigation PDFAVISHKAR AVISHKARNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Sem-V Welcome: 1 04/28/2023 Add A FooterDocument15 pagesMini Project Sem-V Welcome: 1 04/28/2023 Add A FooterNilima SinghaNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Ppt-1-1Document19 pagesFinal Year Project Ppt-1-1Rishikesh GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Industries That Uses BoilerDocument4 pagesIndustries That Uses BoilerLuningning F SenaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Irrigation System On Sensing Soil Moisture ContentDocument12 pagesAutomatic Irrigation System On Sensing Soil Moisture ContentRashmi Prava NayakNo ratings yet
- Bhavliya Pressure IrrigationDocument40 pagesBhavliya Pressure Irrigationkaran ahariNo ratings yet
- RITWIK PAUL - CA1 - Water Resource EngineeringDocument10 pagesRITWIK PAUL - CA1 - Water Resource EngineeringRitwik PaulNo ratings yet
- Pressurized Irrigation SystemsDocument196 pagesPressurized Irrigation SystemsYoussefNo ratings yet
- IRRIGATIONDocument19 pagesIRRIGATIONsarah joyNo ratings yet
- Irrigation HandbookDocument68 pagesIrrigation HandbookGrundfosEgypt83% (6)
- Irrigation 01Document14 pagesIrrigation 01Surendra MalluNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler IrrigationDocument16 pagesSprinkler IrrigationAnusha NomulaNo ratings yet
- Water MGTDocument19 pagesWater MGTArchana NancyNo ratings yet
- Answer For Assignment #2Document11 pagesAnswer For Assignment #2Chanako DaneNo ratings yet
- Micro Irrigation Systems Design BookDocument247 pagesMicro Irrigation Systems Design BookNguyen Van Kien100% (1)
- Maintenance and Repairs in Irrigation SystemDocument28 pagesMaintenance and Repairs in Irrigation SystemBasavaraj A GadigeppagolNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Water Supply HandbookDocument42 pagesChap4 Water Supply HandbooksimoniaNo ratings yet
- Answer For Assignment #2Document10 pagesAnswer For Assignment #2Duge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Pressurized Irrigation PrincipleDocument61 pagesPressurized Irrigation PrincipleRoy PelegNo ratings yet
- The Implementation of A Control Circuit For A Microcontroller Based Automated Irrigation SystemDocument10 pagesThe Implementation of A Control Circuit For A Microcontroller Based Automated Irrigation SystemDershana LachmanNo ratings yet
- Project On Food Security: Automatic Control of Agricultural Pump Measuring Soil Moisture LevelDocument2 pagesProject On Food Security: Automatic Control of Agricultural Pump Measuring Soil Moisture LevelPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- 27-Establishing and Managing Waterpoints For Village LivestockDocument74 pages27-Establishing and Managing Waterpoints For Village LivestockSeyha L. AgriFoodNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 B Disinfection and Water Distribution SystemDocument29 pagesUNIT 3 B Disinfection and Water Distribution SystemDeepak Narayan PaithankarNo ratings yet
- TKP3501 Farm Mechanization & Irrigation Topic: Micro IrrigationDocument41 pagesTKP3501 Farm Mechanization & Irrigation Topic: Micro IrrigationIain Choong WKNo ratings yet
- Value Chain For Watering EquipmentDocument20 pagesValue Chain For Watering EquipmentHaftamuNo ratings yet
- Handbook On Pressurized Irrigation TechniquesDocument282 pagesHandbook On Pressurized Irrigation TechniquesWarricktheGrey100% (1)
- 2-Water Distribution SystemDocument38 pages2-Water Distribution SystemCak IzaTyNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation Benguet FinalDocument185 pagesDrip Irrigation Benguet Finalcacadcadaan14No ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument15 pagesChapter FourEphrem GizachewNo ratings yet
- Pub HandbookDocument40 pagesPub HandbookZaw Moe KhineNo ratings yet
- Industries That Uses BoilerDocument4 pagesIndustries That Uses BoilerLuningning F SenaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Irrigation SystemDocument5 pagesAutomatic Irrigation SystembabuNo ratings yet
- Handbook On Application For Water SupplyDocument40 pagesHandbook On Application For Water Supplywilther89100% (1)
- Standard: Philippine NationalDocument27 pagesStandard: Philippine NationalCHRISTIAN JOEFEL BESSATNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportSaurabh100% (1)
- Water Supply and Sanitary EngineeringDocument12 pagesWater Supply and Sanitary Engineeringash100% (1)
- SynopsisDocument12 pagesSynopsisAnonymous aYm8hnODINo ratings yet
- Operations and MaintainanceDocument58 pagesOperations and MaintainancemeenakshiNo ratings yet
- CTB - ADocument8 pagesCTB - ANathania RandyNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment Plant Design ProjectDocument30 pagesSewage Treatment Plant Design Projectgk mNo ratings yet
- Mid 2 WsseDocument14 pagesMid 2 Wssesarvaiyasamrat8No ratings yet
- Major Components of Micro-Irrigation SystemDocument40 pagesMajor Components of Micro-Irrigation Systempink girlNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Smart Irrigation System: July 2022Document9 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Smart Irrigation System: July 2022seth fernandoNo ratings yet
- Portable Centre Pivot Irrigation System With Advanced Control Through Sensors A ReviewDocument4 pagesPortable Centre Pivot Irrigation System With Advanced Control Through Sensors A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation : Efficient Water Delivery for Crop GrowthFrom EverandDrip Irrigation : Efficient Water Delivery for Crop GrowthNo ratings yet
- Advanced Techniques and Methods in Aquaculture EngineeringFrom EverandAdvanced Techniques and Methods in Aquaculture EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Precast Presentation by PrasadDocument98 pagesPrecast Presentation by Prasadbhavyata katyalNo ratings yet
- Image Quality Problem Bizhub C450Document52 pagesImage Quality Problem Bizhub C450Hugo Luis Escalante100% (1)
- Hotel Management in VBDocument3 pagesHotel Management in VBrakeshkumar_29880% (3)
- BC On The Move: A 10-Year Transportation PlanDocument60 pagesBC On The Move: A 10-Year Transportation PlanCKNW980No ratings yet
- Lsj320ap04 e Samsung PDFDocument24 pagesLsj320ap04 e Samsung PDFJosé Manuel Izea NavarroNo ratings yet
- S LT Ovenpack400Document22 pagesS LT Ovenpack400James JamesNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Concrete ColumnDocument37 pagesTopic 8 Concrete ColumnnasyahrahNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Design: Water Supply Code of Australia Agency RequirementsDocument12 pagesPart 1 - Design: Water Supply Code of Australia Agency RequirementsTailieukythuat DataNo ratings yet
- ESA Lab Report #1 - OP AmpsDocument9 pagesESA Lab Report #1 - OP AmpsAndrew Jordan YancoffNo ratings yet
- Blasting StandardsDocument37 pagesBlasting StandardsEgyiri FrederickNo ratings yet
- cns19 LecDocument24 pagescns19 LecZaid NaeemNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic PumpDocument15 pagesHydraulic PumpAnas Abandeh100% (1)
- Docslide - Us - Parts Catalag 70zv 2 93308 00312 2007 PDFDocument512 pagesDocslide - Us - Parts Catalag 70zv 2 93308 00312 2007 PDFAyaz Khan100% (1)
- BTS3203E V100R012C10SPH116 ENodeBFunction Performance Counter ReferenceDocument3,955 pagesBTS3203E V100R012C10SPH116 ENodeBFunction Performance Counter ReferenceYasir Adin SaputroNo ratings yet
- DrillingDocument24 pagesDrillingYassir Hindi100% (3)
- 161che572 L115 HazopDocument24 pages161che572 L115 HazopMalak HindiNo ratings yet
- Lec 02 SQADocument70 pagesLec 02 SQAJames RiddleNo ratings yet
- Corporative Offer FacilitadoresDocument3 pagesCorporative Offer FacilitadoresCesar Benitez01No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1364032116304191 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S1364032116304191 MainthomasfebyantoNo ratings yet
- ISCAMUL Explosive EmulsifiersDocument7 pagesISCAMUL Explosive EmulsifiersSabariyantoNo ratings yet
- Development and Intersection: Learning CompetenciesDocument31 pagesDevelopment and Intersection: Learning CompetenciesezedinNo ratings yet
- A Review On Modelling Techniques For Formability Prediction of Sheet Metal FormingDocument11 pagesA Review On Modelling Techniques For Formability Prediction of Sheet Metal Formingankita awasthiNo ratings yet
- 349D2/D2 L Hydraulic Excavator SpecificationsDocument2 pages349D2/D2 L Hydraulic Excavator SpecificationsMy FamilyNo ratings yet
- Oim DbsaDocument38 pagesOim DbsaHendi HendriansyahNo ratings yet
- 0 A 78279Document9 pages0 A 78279Igmar Franco NegreteNo ratings yet
- Slip Type Elevator Cat. IVDocument2 pagesSlip Type Elevator Cat. IVRanjithNo ratings yet
- LC 45 - 450-1050 - 54 O4a NF SR EXC3Document3 pagesLC 45 - 450-1050 - 54 O4a NF SR EXC3Xin XiNo ratings yet
- Autoclaved Aerated Concrete 1Document22 pagesAutoclaved Aerated Concrete 1Abhi NandNo ratings yet