Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Green Technology Guide
Uploaded by
Salvacion Prince0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesGreen technology refers to environmentally friendly technologies that minimize pollution and carbon footprint. It uses renewable resources and innovative methods to create environmentally friendly products. The goals of green technology include rethinking systems radically, recycling waste streams like paper and plastic, renewing energy sources through options like solar, wind and biofuels, reducing waste, energy consumption and pollution. Examples include green energy, green buildings, green purchasing, green chemistry and green nanotechnology.
Original Description:
Original Title
GREEN TECH.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGreen technology refers to environmentally friendly technologies that minimize pollution and carbon footprint. It uses renewable resources and innovative methods to create environmentally friendly products. The goals of green technology include rethinking systems radically, recycling waste streams like paper and plastic, renewing energy sources through options like solar, wind and biofuels, reducing waste, energy consumption and pollution. Examples include green energy, green buildings, green purchasing, green chemistry and green nanotechnology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesGreen Technology Guide
Uploaded by
Salvacion PrinceGreen technology refers to environmentally friendly technologies that minimize pollution and carbon footprint. It uses renewable resources and innovative methods to create environmentally friendly products. The goals of green technology include rethinking systems radically, recycling waste streams like paper and plastic, renewing energy sources through options like solar, wind and biofuels, reducing waste, energy consumption and pollution. Examples include green energy, green buildings, green purchasing, green chemistry and green nanotechnology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
GREEN
TECHNOLOGY
By: PRINCE EMMEL S. DEL ROSARIO & ANDREA LYN DIAZ
What is Green Technology?
It is a technology which is
environmentally friendly,
developed and used in
such a way so that it
doesn’t disturb our
environment and
conserves natural
resources.
It is also known as
Environmental Technology
and Clean Technology.
What is Green Technology?
Green technology is a system that uses
innovative methods to create an
environmental friendly products.
It uses renewable natural resources that
never depletes, so future generation can
also benefit form it.
It can effectively change waste pattern
and production in a way that it won’t
harm the planet.
Goals of Green Technology
Rethinking
Recycling
Renewing
Reducing
Responsibility
1. RETHINKING
Radical thinking for fundamental changes
2. RECYCLING
Aggregates and concrete
Paper
Plastic
Can
Batteries
Clothing
3. RENEWING
Renewing Energy
1. Wind Power
2. Water Power
3. Solar Energy
4. Bio-fuel
4. REDUCING
Fuels
Waste
EnergyConsumption
Wastage of clean water
5. RESPONSIBILITY
Don’t waste electricity
Don’t waste water
Don’t waste fuel
Don’t waste food
TYPES OF GREEN
TECHNOLOGY
GREEN ENERGY
GREEN BUILDING
GREEN PURCHASING
GREEN CHEMISTRY
GREEN NANOTECHNOLOGY
GREEN ENERGY
Reasonsfor the need of Green
Technology
Natural resources used in the energy
generation process is on the decline.
Increasing pollution caused by the non
renewable sources.
GREEN BUILDING
Hindrances
High initial cost of setting up
the projects
Emerging technology, so
risk involved
Doesn’t cater to the
promoters short term
interest of profit making
• Advantages
Reduces cost of operation in
the long term
Consumers now more
environment conscious
GREEN PURCHASING
Product
Product dimension includes
providing and using
engineering with market-
driven trends for green
product attributes such as
energy savings, organic
clothing, low volatile organic
compounds, green chemical
etc.
Greener selection and use of
resources results in savings
from less waste, less
chemicals and less
processing.
GREEN CHEMISTRY
Design of processes to
maximize the amount of raw
material that ends up in the
product.
Use of safe, environmental-
benign substances, including
solvents, whenever possible.
Design of energy efficient
processes.
Best form of waste disposal,
not to create in the first
place.
GREEN
NANOTECHNOLOGY
Green nanotechnology refers to the use of
nanotechnology to enhance the environmental-
sustainability of processes currently producing
negative externalities.
Aims to minimize potential environment and
human health risk associated with the
manufacture and use of nanotechnology
products, and to encourage replacement of
existing products with new nano-products that are
more environmental friendly throughout their
lifecycle.
APPLICATION
Theuse of green technology can reduce
the amount of waste and pollution and
provide early warming message that is
created during production, consumption,
and impact of natural disaster.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
Responsibilityfor the environment
Rethinking the way we live
Reducing Exhaustion
Recycling waste
Renewing Energy
You might also like
- Excel Workbook No. 05 Atterberg LimitsDocument4 pagesExcel Workbook No. 05 Atterberg LimitsEngr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- New Standard - List Price 2023 Update - New - Ra Ac Sky VRV List Price - Updating 16 Feb'23Document73 pagesNew Standard - List Price 2023 Update - New - Ra Ac Sky VRV List Price - Updating 16 Feb'23zhuzzhiz channubinNo ratings yet
- Green TechnologyDocument12 pagesGreen TechnologyNitasha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nitasha Sharma (Bca-1609) Ppt-Green TechnologyDocument12 pagesNitasha Sharma (Bca-1609) Ppt-Green TechnologyNitasha sharmaNo ratings yet
- GREEN TECHNOLOGY EditedDocument18 pagesGREEN TECHNOLOGY EditedAkshay Krishnan VNo ratings yet
- 101 Math Short Cuts (WWW - Qmaths.in)Document12 pages101 Math Short Cuts (WWW - Qmaths.in)Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Department of Management Studies Masters in Business Administration Semester IDocument11 pagesDepartment of Management Studies Masters in Business Administration Semester IFerheen WaniNo ratings yet
- Report On Green Manufacturig (Pankaj Kumar)Document23 pagesReport On Green Manufacturig (Pankaj Kumar)pankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument11 pagesFinaldeeshansheikh143No ratings yet
- Eco Friendly TechnologyDocument30 pagesEco Friendly TechnologyDebaditya Bhattacharyya50% (2)
- Sustainable Green Chemical Technology For Developments in Process IndustriesDocument13 pagesSustainable Green Chemical Technology For Developments in Process IndustriesAradhana KanchanNo ratings yet
- Arnaldo M4 DQ PDFDocument2 pagesArnaldo M4 DQ PDFRadie ArnaldoNo ratings yet
- Eco Friendly TechnologiesDocument9 pagesEco Friendly TechnologiesAmar Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- Green Manufacturing TYCHDocument6 pagesGreen Manufacturing TYCHSnehal KutheNo ratings yet
- Report On Green Manufacturing by Aditya Srivastava 03Document30 pagesReport On Green Manufacturing by Aditya Srivastava 03Aditya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Evs Presentation of Group 12Document18 pagesEvs Presentation of Group 12yashhurmade090No ratings yet
- Green Tech Advances for Urban SustainabilityDocument45 pagesGreen Tech Advances for Urban SustainabilityMark Lester RealNo ratings yet
- Green TechnologyDocument9 pagesGreen Technologysaidivyansi6002No ratings yet
- Green Chemistry PDFDocument8 pagesGreen Chemistry PDFAsAdullah KhAjaNo ratings yet
- Control of Exhaust With CatconDocument16 pagesControl of Exhaust With CatconitsmeadityaNo ratings yet
- Green ManufacturingDocument21 pagesGreen Manufacturingpankaj kumar100% (1)
- Green ManufacturingDocument9 pagesGreen Manufacturingraymun c100% (1)
- Green Engineering: The Way To Save The PlanetDocument5 pagesGreen Engineering: The Way To Save The PlanetJenny CastroNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument12 pagesFinaldeeshansheikh143No ratings yet
- Sustainable Design: Ar. Asia JabeemDocument32 pagesSustainable Design: Ar. Asia JabeemKhiZra ShahZadNo ratings yet
- What Is Green Technology ?Document10 pagesWhat Is Green Technology ?psr1992No ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument20 pagesGreen ChemistryMarianne MonroeNo ratings yet
- Green Technology PaperDocument8 pagesGreen Technology PaperCream FamilyNo ratings yet
- Actividad 2. InglishDocument6 pagesActividad 2. InglishselenegonzalezfcoNo ratings yet
- Exciting New Technologies For A Green FutureDocument5 pagesExciting New Technologies For A Green FutureIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- 24.8.18 GctiDocument112 pages24.8.18 GctiReena SinghalNo ratings yet
- AN_OVERVIEW_OF_THE_GREEN_BUILDING_CONSTRUCTION_IN_Document7 pagesAN_OVERVIEW_OF_THE_GREEN_BUILDING_CONSTRUCTION_IN_jalindarmunde.9403336895No ratings yet
- Green Technologies for Wastewater TreatmentDocument17 pagesGreen Technologies for Wastewater TreatmentSORIN AVRAMESCUNo ratings yet
- Green ArchitectureDocument6 pagesGreen ArchitectureAbhishek Jani100% (1)
- Applications of Green Chemistry PrinciplesDocument7 pagesApplications of Green Chemistry PrinciplesTK Gyaan SagarNo ratings yet
- Luego - Bsarch-3a - Research-No.01 (Sustainability)Document5 pagesLuego - Bsarch-3a - Research-No.01 (Sustainability)Luego, Brent Jarryd P.No ratings yet
- Green Technology and Environment - Vi.enDocument3 pagesGreen Technology and Environment - Vi.enHoàng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering Dharmsinh Desai University B.Tech CH Semester-VIDocument13 pagesFaculty of Technology Department of Chemical Engineering Dharmsinh Desai University B.Tech CH Semester-VIDivyamNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction Cleaner ProductionDocument28 pages1 Introduction Cleaner ProductionHome SltNo ratings yet
- What is Green Technology? Benefits of Eco-Friendly SolutionsDocument8 pagesWhat is Green Technology? Benefits of Eco-Friendly SolutionsKirtika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sakshi Green ChemistryDocument20 pagesSakshi Green ChemistryAyushi JainNo ratings yet
- Sa7 Mod 1 SummaryDocument11 pagesSa7 Mod 1 SummarySheshu KNo ratings yet
- Green Technology and SustainabilityDocument10 pagesGreen Technology and SustainabilityTamil RockersNo ratings yet
- Green Engineering PDFDocument23 pagesGreen Engineering PDFYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- ResearchArticle Green DRDocument8 pagesResearchArticle Green DRrajjjjjkumarNo ratings yet
- Green DesigningDocument5 pagesGreen DesigningTanvir KaisarNo ratings yet
- Green ChemistryDocument40 pagesGreen Chemistryjara6896No ratings yet
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering and Technology: Topic: Green Building ConceptDocument6 pagesInfant Jesus College of Engineering and Technology: Topic: Green Building ConceptBEN NARENDRANNo ratings yet
- Green DesignDocument3 pagesGreen DesignShaira Patrice CalesaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ChemistryDocument112 pagesUnit 3 ChemistryAjawin EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Green Building: Vibhav Kaushal Civil Engg (Iiiyr) Roll No. 134062Document2 pagesGreen Building: Vibhav Kaushal Civil Engg (Iiiyr) Roll No. 134062utsavNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document23 pagesSession 3Ethiopia Ethiopia EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Green HospitalDocument34 pagesGreen HospitalUluwi Hilmal100% (3)
- Chapter 16 Green ChemistryDocument32 pagesChapter 16 Green ChemistryMaitha AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Green Technology: Better FutureDocument5 pagesGreen Technology: Better FutureASHISH JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Greenchemistry BiofuelDocument9 pagesGreenchemistry BiofuelsumitNo ratings yet
- Green ManufacturingDocument8 pagesGreen ManufacturingYabert Yanuar SantosoNo ratings yet
- Android Recyclerview pptDocument10 pagesAndroid Recyclerview ppthunterdii9879No ratings yet
- Building Green: How Material Science Drives Sustainable ProductsDocument6 pagesBuilding Green: How Material Science Drives Sustainable ProductskovalitskajaninaNo ratings yet
- Eco-Friendly Innovations: Applications of Green Chemistry in Everyday LifeFrom EverandEco-Friendly Innovations: Applications of Green Chemistry in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- TitleDocument3 pagesTitleSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
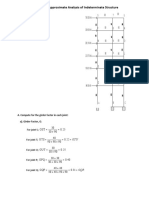
- Factor Method in Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate StructureDocument5 pagesFactor Method in Approximate Analysis of Indeterminate StructureSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Transportation Infrastructure Problems in My Community (At Least 3)Document2 pagesTransportation Infrastructure Problems in My Community (At Least 3)Salvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Pahirap Sa Buhay KoDocument12 pagesPahirap Sa Buhay KoSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- B) - Column Factor: CM 1 - GDocument6 pagesB) - Column Factor: CM 1 - GSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Transportation Infrastructure Problems in My Community (At Least 3)Document2 pagesTransportation Infrastructure Problems in My Community (At Least 3)Salvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Platic LimitDocument2 pagesPlatic LimitSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Liquid LimitDocument3 pagesLiquid LimitSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
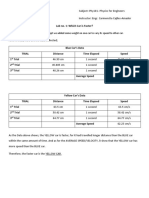
- Lab No. 1: Which Car Is Faster?Document6 pagesLab No. 1: Which Car Is Faster?Salvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
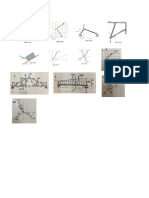
- Prob Set 1 FiguresDocument1 pageProb Set 1 FiguresSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Green Technology GuideDocument18 pagesGreen Technology GuideSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Soil SieveDocument2 pagesSoil SieveSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Banana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiDocument7 pagesBanana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Banana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiDocument7 pagesBanana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Area Computation Using Trapezoidal RuleDocument2 pagesArea Computation Using Trapezoidal RuleSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Banana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiDocument7 pagesBanana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Banana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiDocument7 pagesBanana Peels Based Bio-Palstic: Prince Emmel S. Del Rosario Bsce IiiSalvacion PrinceNo ratings yet
- Design Scaffolding TKBT 2 NewDocument2 pagesDesign Scaffolding TKBT 2 NewAnnisa TassiaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Lab TanahDocument4 pagesHasil Lab TanahHamidAffandyNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document1 pageSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Bart LuceñaNo ratings yet
- Pwcic: Bricklayer Description Unit Rate (RM) Percentage (%) No. Increase/DecreaseDocument2 pagesPwcic: Bricklayer Description Unit Rate (RM) Percentage (%) No. Increase/DecreaseHazwan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Art of Upcycling-GreenducationDocument23 pagesArt of Upcycling-Greenducationcruzser100% (1)
- CBR - 3 - EnergyDocument187 pagesCBR - 3 - EnergyEnd End100% (1)
- Annex#3 EQRA Progress DetailsDocument80 pagesAnnex#3 EQRA Progress Detailswafiullah sayedNo ratings yet
- Final Material consumption for road construction projectsDocument7 pagesFinal Material consumption for road construction projectsRakesh AryaNo ratings yet
- 04 Chapter 5 - Classification of SoilDocument35 pages04 Chapter 5 - Classification of SoilhieputcNo ratings yet
- Conquest CXAX Air-to-Water Heat PumpDocument6 pagesConquest CXAX Air-to-Water Heat PumpAlexandre LopesNo ratings yet
- Pep Rep Geo Technical SolutionsDocument34 pagesPep Rep Geo Technical SolutionsShafiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Ad-212-Raq-Dwg-Dd-Mec-000002 - 01 - Detailed Design Drawing For Hvac SystemDocument14 pagesAd-212-Raq-Dwg-Dd-Mec-000002 - 01 - Detailed Design Drawing For Hvac Systembassels929No ratings yet
- Basic Soil Properties From CPT in Bangkok Clay For Highway DesignDocument8 pagesBasic Soil Properties From CPT in Bangkok Clay For Highway DesigntangkokhongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Green BuildingsDocument19 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Green BuildingsSunil BeheraNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems ExplainedDocument7 pagesHVAC Systems ExplainedJunatan DinglasaNo ratings yet
- Lining Pattern & Bar Chart Line - 3Document10 pagesLining Pattern & Bar Chart Line - 3harikrushnaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical FormulasDocument15 pagesGeotechnical FormulasDavid King100% (1)
- Control VAV Systems Air ConditioningDocument9 pagesControl VAV Systems Air ConditioningAnh Cao Minh NgocNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of FrictionDocument1 pageCoefficient of FrictionLiladhar Ganesh DhobleNo ratings yet
- Spek Teknis HvacDocument30 pagesSpek Teknis Hvacdhani7No ratings yet
- Importance of Soil TextureDocument3 pagesImportance of Soil TextureChinBoon LimNo ratings yet
- Be Eg Doas 100 54 Eg1 517Document114 pagesBe Eg Doas 100 54 Eg1 517naser712No ratings yet
- Typical Values of Soil Friction Angle For Different Soils According To USCSDocument5 pagesTypical Values of Soil Friction Angle For Different Soils According To USCSCHIKARANo ratings yet
- Soft Copy Laporan Sandcone Gudang - JIIPEDocument2 pagesSoft Copy Laporan Sandcone Gudang - JIIPEardaloevera_63818328No ratings yet
- Comparison of Ashrae Standard 90.1, 189.1Document14 pagesComparison of Ashrae Standard 90.1, 189.1Arafa SalemNo ratings yet
- Ledeg Traineesrsquo Hostel LehDocument23 pagesLedeg Traineesrsquo Hostel LehAr Nizya NoushadNo ratings yet
- Use Low Energy Materials for Sustainable Interior DesignDocument2 pagesUse Low Energy Materials for Sustainable Interior DesignKunjal tawdeNo ratings yet
- Learning To LEED: Day 2 Materials & Resources QuizDocument5 pagesLearning To LEED: Day 2 Materials & Resources Quizvico1982No ratings yet