0% found this document useful (0 votes)
841 views26 pagesOverview of CNC Machine Technology
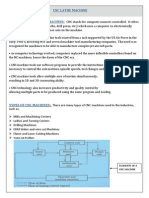
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on CNC machines. It discusses the history of CNC, parts of CNC machines, types of CNC machines like lathes and milling machines. It also covers CNC programming basics including coordinate systems, G and M codes, and common turning operations. Advantages of CNC include accuracy, reduced errors and time, while limitations include high costs and needing programming skills. CNC is widely applied in metalworking, aerospace, automotive and other industries.
Uploaded by
Rahul KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
841 views26 pagesOverview of CNC Machine Technology
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on CNC machines. It discusses the history of CNC, parts of CNC machines, types of CNC machines like lathes and milling machines. It also covers CNC programming basics including coordinate systems, G and M codes, and common turning operations. Advantages of CNC include accuracy, reduced errors and time, while limitations include high costs and needing programming skills. CNC is widely applied in metalworking, aerospace, automotive and other industries.
Uploaded by
Rahul KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26