Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Mark Lee Aggarao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
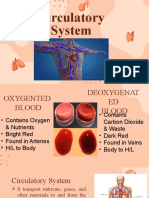
5 views11 pagesThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through vessels into organs, where materials are exchanged between blood and tissues through diffusion. It has four chambers - two atria that receive blood and two ventricles that pump blood. Blood contains plasma, red blood cells that carry oxygen, white blood cells that fight infection, and platelets that help clotting. Together this closed system transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and wastes around the body.
Original Description:
This is the circulatory system of a person
Original Title
CirculatorySystem (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through vessels into organs, where materials are exchanged between blood and tissues through diffusion. It has four chambers - two atria that receive blood and two ventricles that pump blood. Blood contains plasma, red blood cells that carry oxygen, white blood cells that fight infection, and platelets that help clotting. Together this closed system transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and wastes around the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesCirculatory System
Uploaded by
Mark Lee AggaraoThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through vessels into organs, where materials are exchanged between blood and tissues through diffusion. It has four chambers - two atria that receive blood and two ventricles that pump blood. Blood contains plasma, red blood cells that carry oxygen, white blood cells that fight infection, and platelets that help clotting. Together this closed system transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and wastes around the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
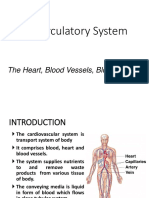
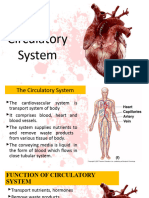
The Circulatory System
The Closed Circulatory System
•Humans have a closed circulatory system,
typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is
confined to vessels and is distinct from the
interstitial fluid.
–The heart pumps blood into large vessels
that branch into smaller ones leading into the
organs.
–Materials are exchanged by diffusion between
the blood and the interstitial fluid bathing the
cells.
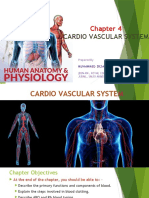
The Cardiovascular System
•Three Major Elements –
Heart, Blood Vessels, &
Blood
–1. The Heart- cardiac
muscle tissue
–highly interconnected
cells
–four chambers
•Right atrium
•Right ventricle
•Left atrium
•Left ventricle
•Superior Vena Cava Pathway of the blood
•Right Atrium
•Tricuspid Valve
•Right Ventricle
•Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
•Lungs
•Pulmonary Vein
•Bicuspid Valve
•Left Ventricle
•Aortic Semilunar Valve
•Aorta
•To the bodies organs & cells
The Cardiovascular System
2. Blood Vessels -A network of tubes
–Arteriesarterioles move away from the heart
•Elastic Fibers
•Circular Smooth Muscle
–Capillaries – where gas exchange takes place.
•One cell thick
•Serves the Respiratory System
–VeinsVenules moves towards the heart
•When they break - varicose veins form
The Cardiovascular System
3. The Blood
A. Plasma
Liquid portion of the blood.
Contains clotting factors,
hormones, antibodies,
dissolved gases, nutrients
and waste
The Cardiovascular System
•The Blood
B. Erythrocytes - Red
Blood Cells
–Carry hemoglobin and
oxygen. Do not have a
nucleus and live only
about 120 days.
–Can not repair
themselves.
The Cardiovascular System
•The Blood
C. Leukocytes – White
Blood cells
–Fight infection and are
formed in the bone marrow
–Five types – neutrophils,
lymphocytes, eosinophils,
basophils, and monocytes.
The Cardiovascular System
The Blood
•D. Thrombocytes –
Platelets.
–These are cell fragment
that are formed in the
bone marrow from
megakaryocytes.
–Clot Blood by sticking
together – via protein
fibers called fibrin.
You might also like
- 2.1 The Components of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pages2.1 The Components of The Circulatory SystemgalvezchestertimothyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- Gen Bio 2 Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesGen Bio 2 Circulatory SystemJustin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Circulatory System 2Document2 pagesLesson 4 Circulatory System 2Glaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemDocument35 pagesLecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemKaseylene CabansagNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and Hormones Chapter #32, Pg. 650 - 665Document38 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and Hormones Chapter #32, Pg. 650 - 665Anggun Kharisma RaniNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument84 pagesCirculatory SystemAprille CastroNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesUnit 3 Circulatory SystemSebastian IbañezNo ratings yet
- تشريح 6Document20 pagesتشريح 6mustafasalaheldin2003No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument29 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesFerry SofatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument37 pagesCirculatory Systemcale suarezNo ratings yet
- Human Body Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesHuman Body Circulatory SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Best Basic Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesBest Basic Circulatory SystemJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory SystemDocument39 pagesDokumen - Tips - Sbi3u The Circulatory System Introduction and Human Circulatory Systempacheco TimeNo ratings yet
- Heart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheDocument44 pagesHeart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheAnnah JeanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument44 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemDocument78 pagesComparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemElaine MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: MVZ Carinthia ZapataDocument50 pagesCirculatory System: MVZ Carinthia ZapataFernando ZendejasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemDiane YapNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular System 1 2Document19 pagesCardio Vascular System 1 2hamafron05No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemIan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Human Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationDocument41 pagesHuman Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument20 pagesThe Circulatory Systemhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- THR Circulatory System (HSB)Document37 pagesTHR Circulatory System (HSB)levilevandreaNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Circulatory SystemDocument38 pagesLecture - Circulatory SystemJanith VimukthiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Human Circulatory System OFFICIALDocument65 pagesGrade 9 Human Circulatory System OFFICIALEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- 07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredDocument47 pages07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredCatherine SyNo ratings yet
- Organismal Biology: Course Outcome 2BDocument32 pagesOrganismal Biology: Course Outcome 2BThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesThe Circulatory SystemPerson AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document22 pagesWeek 2Jesseryl MargalloNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SDDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System SDJosh DeeNo ratings yet
- Transport System in AnimalsDocument21 pagesTransport System in Animalssonia sonNo ratings yet
- 10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument140 pages10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- HUman Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesHUman Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument56 pagesCirculatory SystemillyaniNo ratings yet
- hUMAN BODY GRD 10Document95 pageshUMAN BODY GRD 10Maha YounusNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument16 pagesCardioMaxNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Systemand Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesCirculatory Systemand Respiratory SystemLV BENDANANo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesCirculatory SystemA K AcademyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PDFDocument149 pagesCardiovascular System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE Human Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesBiology IGCSE Human Circulatory SystemNiharika100% (1)
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument22 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFbilly sauraNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemkangaanushkaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Circulatory System NotesDocument4 pagesICSE Class 10 Circulatory System NotesYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesDocument22 pagesCirculatory System: Transporting Gases, Nutrients, Wastes, and HormonesMariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Identify and Describe The Functions of The Organs of Circulatory SystemDocument28 pages6.1 Identify and Describe The Functions of The Organs of Circulatory SystemKRISTINE JOAN BARREDONo ratings yet
- Circulation: Chapters 13 and 14Document50 pagesCirculation: Chapters 13 and 14Anni SholihahNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemDocument18 pagesThe Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology - Chapter 4 - Cardiovascular System-1Document33 pagesAnatomy Physiology - Chapter 4 - Cardiovascular System-1Sujok SNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typescut irnandaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Latest3Document67 pagesCirculatory System Latest3Gosego SepengNo ratings yet
- 07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredDocument54 pages07 - Cardiovascular System DeclutteredFRANCINE JANE PATI�ONo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems (Autosaved)Document17 pagesHuman Body Systems (Autosaved)K. Thenuja MihinNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Parts 1Document38 pagesCirculatory System and Parts 1Atasha Ivory RagragioNo ratings yet
- محاضرة فسلجة 6 رقم 638097619114528622Document26 pagesمحاضرة فسلجة 6 رقم 638097619114528622محمد عليNo ratings yet