Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 4 Circulatory System 2
Uploaded by
Glaisa Cudia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesLesson 4 Circulatory System 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLesson 4 Circulatory System 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesLesson 4 Circulatory System 2
Uploaded by
Glaisa CudiaLesson 4 Circulatory System 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
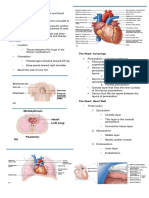
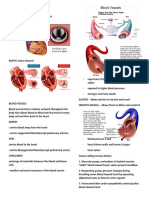
• Pulmonary Semilunar Valve
LESSON 3 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM • Lungs
• Pulmonary Vein
The Closed Circulatory System • Bicuspid Valve
Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all • Left Ventricle
vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is • Aortic Semilunar Valve
distinct from the interstitial fluid. • Aorta
The heart pumps blood into large vessels • To the bodies organs & cells
that branch into smaller ones leading into the organs.
Materials are exchanged by diffusion between the blood and 2. Blood Vessels -A network of tubes
the interstitial fluid bathing the cells. – Arteriesarterioles move away from the heart
• Elastic Fibers
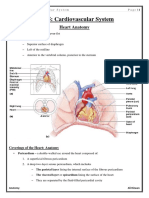
The Cardiovascular System • Circular Smooth Muscle
• Three Major Elements – Heart, Blood Vessels, & Blood – Capillaries – where gas exchange takes place.
1. The Heart- cardiac muscle tissue • One cell thick
– highly interconnected cells • Serves the Respiratory System
– four chambers – VeinsVenules moves towards the heart
• Right atrium • Skeletal Muscles contract to force blood back
• Right ventricle from legs
• Left atrium • One way values
• Left ventricle • When they break - varicose veins form
Pathway of the blood
• Superior Vena Cava
• Right Atrium
• Tricuspid Valve
• Right Ventricle
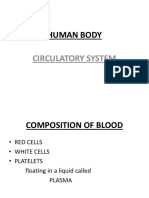
D. Thrombocytes – Platelets.
3. The Blood – These are cell fragment that are formed in the bone
A. Plasma marrow from magakaryocytes.
Liquid portion of the blood. Contains clotting factors, hormones, – Clot Blood by sticking together – via protein fibers called
antibodies, dissolved gases, nutrients and waste fibrin.
B. Erythrocytes - Red Blood Cells
– Carry hemoglobin and oxygen. Do not have a nucleus Type of Circulation
and live only about 120 days. • Pulmonary Circulation – movement of the blood from the heart
– Can not repair themselves. to the lungs and back to the heart.
• Coronary Circulation - Movement of blood through the tissues
of the heart
• Systemic Circulation - Movement of blood from the heart to
the rest of the body, excluding the lungs
Disorders of the Circulatory System
C. Leukocytes – White Blood cells • Anemia - lack of iron in the blood, low RBC count
– Fight infection and are formed in the bone marrow
Five types – neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and • Leukemia - white blood cells proliferate wildly, causing anemia
monocytes.
• Hemophilia - bleeder’s disease, due to lack of fibrinogen in
thrombocytes
• Heart Murmur - abnormal heart beat, caused by valve
problems
• Heart attack - blood vessels around the heart become blocked
with plaque, also called myocardial infarction
You might also like
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesThe Circulatory System in 40 CharactersMark Lee AggaraoNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems in Animals: Strand 2Document49 pagesTransport Systems in Animals: Strand 2Roxy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes PDFDocument8 pagesBio Notes PDFRashid WongNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Blood TypesDocument84 pagesThe Circulatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Blood TypesAprille CastroNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Components of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pages2.1 The Components of The Circulatory SystemgalvezchestertimothyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Latest3Document67 pagesCirculatory System Latest3Gosego SepengNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesClemente Castañeda MontillaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular SystemVernice LopezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument45 pagesCardiovascular System Explainednurhidayati harunNo ratings yet
- 10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument140 pages10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Vessels PDFDocument10 pagesCH 11 Vessels PDFIbra TutorNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ExplainedDocument23 pagesThe Circulatory System ExplainedJustin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System GuideDocument29 pagesCirculatory System GuideFerry SofatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument37 pagesCirculatory Systemcale suarezNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andDocument62 pagesCirculatory System:, ,,, and The and That and Through The Body. - ,, andBlister Count100% (1)
- Anaphy Reviewer MidtermDocument30 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Midtermjuayma maureen importanteNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typescut irnandaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood TypesDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System: The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Typesghisma ocvintiaNo ratings yet
- Biology Tuition (Circulatory System)Document42 pagesBiology Tuition (Circulatory System)muffindidiNo ratings yet
- Organismal Biology: Course Outcome 2BDocument32 pagesOrganismal Biology: Course Outcome 2BThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular SystemNashreen QtqtNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System ExplainedDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory System ExplainedJonalynCollodChewacheoNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 LEC Module 3Document8 pagesPMLS 2 LEC Module 3Peach DaquiriNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System ExplainedJosh DeeNo ratings yet
- NATSCI Pre Final Lec Notes CARDIOVASCULARDocument4 pagesNATSCI Pre Final Lec Notes CARDIOVASCULARNIKKANo ratings yet
- Bio Rev CardsDocument21 pagesBio Rev CardsTamannaBhatiaNo ratings yet
- circulatory-system grade 10Document34 pagescirculatory-system grade 10amulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- Human Body Systems - Circulatory System-3Document11 pagesHuman Body Systems - Circulatory System-3benjaminblakkNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System 1Document4 pagesCirculatory System 1Jhes D.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System LEC 10Document36 pagesCardiovascular System LEC 10Moiz Ahmed BhattiNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesHuman Body: Circulatory SystemAndra HijratulNo ratings yet
- Blood Composition and CirculationDocument46 pagesBlood Composition and CirculationAlvin U. DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Myocardium - The heart muscle that surrounds the ventricles and atriaDocument19 pagesMyocardium - The heart muscle that surrounds the ventricles and atriaFilane AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary SystemDocument47 pagesCardiopulmonary SystemMaxxdlc 16No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Circulatory System NotesDocument4 pagesICSE Class 10 Circulatory System NotesYash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesHuman Body Circulatory SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Transport: Blood Vessels & HeartDocument38 pagesCirculatory System Transport: Blood Vessels & HeartAnggun Kharisma RaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument24 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Christian TiczonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesCirculatory SystemSamiksha ChettriNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument149 pagesThe Cardiovascular System ExplainedGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument24 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Christian TiczonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System 78698524Document24 pagesCardiovascular System 78698524Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Life SciencesDocument46 pagesGrade 10 Life SciencesclimateclubNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEM ANATOMY AND FUNCTIONchelliNo ratings yet
- Human Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationDocument41 pagesHuman Performance For ATPL Class: Blood CirculationListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Histology of Circulatory SystemDocument156 pagesHistology of Circulatory SystemErmiyas BeletewNo ratings yet
- Handout 10 Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesHandout 10 Circulatory SystemKyle QuietaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemDocument35 pagesLecture - Chapter 32 - Circulatory SystemKaseylene CabansagNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument41 pagesCirculatory SystemxiliannapaveyxNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy Cardiovascular SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- 2b Chapter 09 Transport in AnimalsDocument45 pages2b Chapter 09 Transport in Animalsemre2serinNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System: EpicardiumDocument17 pagesThe Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System: Epicardiumlourd nabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Document33 pagesScience 9 - First Quarter Reviewer: Biology 9Ace AligoraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: More Than Just The HeartDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System: More Than Just The HearteliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- The Mammali An Circulator y SystemDocument21 pagesThe Mammali An Circulator y SystemFern BaldonazaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Systems: Transporting Nutrients & WastesDocument39 pagesCirculatory Systems: Transporting Nutrients & WastesSebastian IbañezNo ratings yet
- Biology IGCSE Human Circulatory SystemDocument17 pagesBiology IGCSE Human Circulatory SystemNiharika100% (1)
- Lesson 7 GeneticsDocument6 pagesLesson 7 GeneticsGlaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Sex TraitsDocument2 pagesLesson 8 Sex TraitsGlaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 HeartDocument2 pagesLesson 5 HeartGlaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Respiratory System1Document2 pagesLesson 1 Respiratory System1Glaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Rubric TemplateDocument1 pageRubric TemplateGlaisa CudiaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Study Guide: How To Draw Lewis StructuresDocument15 pagesPeriodic Table Study Guide: How To Draw Lewis StructuresGuillermo Narváez LozanoNo ratings yet
- KINE 2031 Test 4 NotesDocument16 pagesKINE 2031 Test 4 NotesnokiaNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Medications & TablesDocument71 pagesMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Readingtest 3Document19 pagesReadingtest 3SevvalNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Physiotherapy After Thoracic Surgery - What Physiotherapists Need To Know. A Narrative ReviewDocument15 pagesEssentials of Physiotherapy After Thoracic Surgery - What Physiotherapists Need To Know. A Narrative ReviewMariana MadridNo ratings yet
- DIVE THEORY STUDY GUIDEDocument40 pagesDIVE THEORY STUDY GUIDEdegwiiNo ratings yet
- Cap. 04 - LizardsDocument19 pagesCap. 04 - LizardsNailson JúniorNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine-Chapter XI & XIXDocument8 pagesLegal Medicine-Chapter XI & XIXwichupinunoNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis With Case StudyDocument27 pagesCystic Fibrosis With Case StudyAviva Tuteja100% (1)
- Respirotary MnemonicsDocument9 pagesRespirotary MnemonicsAymen Omer0% (1)
- Forensic MnemonicsDocument9 pagesForensic MnemonicsVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Choanal AtresiaDocument9 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale Exchange: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Choanal AtresiaJinaan MahmudNo ratings yet
- (2013) Respiratory Diseases of The HorseDocument238 pages(2013) Respiratory Diseases of The Horsekaren montoyaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0140673622014854 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0140673622014854 Mainsilvia100% (1)
- Understanding BronchopneumoniaDocument16 pagesUnderstanding BronchopneumoniaUday Kumar88% (17)
- Havan Research PaperDocument8 pagesHavan Research PaperSwami AbhayanandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document42 pagesChapter 12Zabu CastilloNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Body Systems Student Edition 1Document37 pages6th Grade Body Systems Student Edition 1Martha RincónNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) #12Document4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) #12Nica MarieNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Bronchitis Dengan AsmaDocument5 pagesJurnal Bronchitis Dengan AsmaMauLan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Abg AnalysisDocument6 pagesAbg AnalysisAxsa Alex100% (2)
- Revised MedPro International Nursing Resume TemplateDocument4 pagesRevised MedPro International Nursing Resume TemplateAnonymous 8DYcTgd100% (3)
- 22 Lecture PresentationDocument88 pages22 Lecture PresentationLeilaNo ratings yet
- Preterm infant care planDocument21 pagesPreterm infant care planGil Aswigui81% (27)
- Filamin A Mutations: Jesse Hansen-BartelDocument8 pagesFilamin A Mutations: Jesse Hansen-BartelJesse Helmut Hansen-BartelNo ratings yet
- Exams MedsurgDocument29 pagesExams MedsurgUy Jezrielle MicahNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Items by Strand Grade 7 ScienceDocument31 pagesSample Test Items by Strand Grade 7 ScienceRam Russel Casao PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Adamjee Biology XDocument7 pagesAdamjee Biology XRafiq AfridiNo ratings yet
- Specific Types of DysnpeaDocument14 pagesSpecific Types of DysnpeaPiyush Agarwal100% (1)
- Diver First Aid CPRDocument108 pagesDiver First Aid CPREthanBrandtNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument51 pagesNeonatal ResuscitationAbdulkadir HasanNo ratings yet