0% found this document useful (0 votes)
693 views14 pagesComposite and Inverse Fun
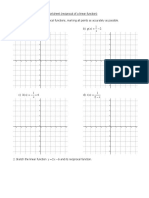
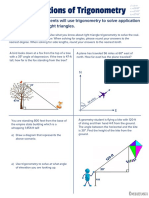
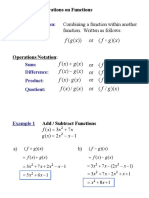
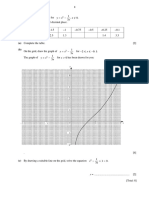
This document discusses operations on functions including composite functions, function operations using notation, and examples of adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing functions. It also covers inverse functions and relations, including finding the inverse of a function using ordered pairs or graphically, and verifying two functions are inverses of each other. Examples are provided to illustrate composite functions, inverses, and determining if a function is one-to-one.
Uploaded by
Niejay Arcullo LlagasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
693 views14 pagesComposite and Inverse Fun
This document discusses operations on functions including composite functions, function operations using notation, and examples of adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing functions. It also covers inverse functions and relations, including finding the inverse of a function using ordered pairs or graphically, and verifying two functions are inverses of each other. Examples are provided to illustrate composite functions, inverses, and determining if a function is one-to-one.
Uploaded by
Niejay Arcullo LlagasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Operations on Functions
- Examples of Function Operations
- Inverse Functions and Relations