Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ttttttygbhb
Uploaded by
Neeraj Jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesjhgfdxcvbnhgfdcvbnmnbg
Original Title
ttttttygbhb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjhgfdxcvbnhgfdcvbnmnbg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesTtttttygbhb
Uploaded by
Neeraj Jainjhgfdxcvbnhgfdcvbnmnbg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Cardiac cycle
The repeating pattern of contraction and
relaxation of the heart is called cardiac cycle.
It consists of two events –
(i) Systole – contraction on heart chambers
(either atrium or ventricles) is known as systole.
(ii) Diastole – relaxation of heart chambers
(either atrium or ventricles) is known as diastole
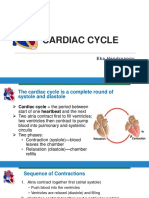
EVENTS OF CARDIAC CYCLE
Blood flows from vena cava and pulmonary artery and fills
left and right atria respectively.
Pressure in atria increases which causes opening of AV
valves and blood flows into ventricles (semilunar valves
are closed to prevent back flow of blood).
SAN generates action potential (impulse) which stimulates
atrial contraction – atrial systole
This increases the blood flow by 30% .
Now the pressure in both the ventricles is increasing.
As soon as the impulse reaches the ventricles, they undergo
contraction – ventricular systole.
At this time relaxation of atria occurs – atrial diastole.
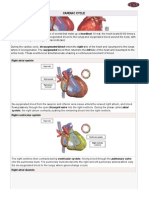
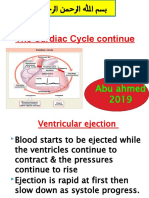
•The ventricular systole causes opening of
semilunar valves. (at this time the AV valve
remains closed)
•Due to this, the blood flow from left and right
ventricles to pulmonary artery and aorta
respectively.
•The blood gets circulated in the entire body.
•Now the ventricles relax – ventricular
diastole.
•At this time, both atria and ventricles are in
relaxed state – joint diastole.
DURATIONS
Duration of one cardiac diastole is 0.4 seconds.
atrial systole occurs for 0.1 seconds.
ventricular systole occurs for 0.3 seconds.
Thus one complete cardiac cycle occurs in 0.8 seconds.
You might also like
- Cardiac Cycle ExplainedDocument5 pagesCardiac Cycle ExplainedCai Peng FeiNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle ExplainedDocument18 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle ExplainedKundan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology: October 25, 2010Document51 pagesCardiovascular Physiology: October 25, 2010VinuPrakashJ.No ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatDocument14 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatAswathy KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatDocument14 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatLaiba AsimNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatDocument14 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Describing The Sequence of Events in One Heart BeatMadds06No ratings yet
- CARDIAC CYCLE-laDocument12 pagesCARDIAC CYCLE-latehillahkabwe100No ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - WikipediaDocument13 pagesCardiac Cycle - WikipediaHarshal GaikwadNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument14 pagesThe Cardiac CycleShreeraj ShahNo ratings yet
- The cardiac cycle 2Document7 pagesThe cardiac cycle 2Abigail ChristisnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle Events & PhasesDocument12 pagesCardiac Cycle Events & Phasesanupam manu100% (1)
- 04-The Cardiac Cycle - Wigger's Diagram (J Swanevelder)Document6 pages04-The Cardiac Cycle - Wigger's Diagram (J Swanevelder)Patrick WilliamsNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle NotesDocument5 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle NotesAsad Khan Khalil100% (1)
- CVS - IiDocument12 pagesCVS - IiBinta Elsa JohnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument4 pagesCardiac CycleDivya RanasariaNo ratings yet
- KP 1.3.2.1 Aktivitas Mekanik Jantung (2 Jam)Document68 pagesKP 1.3.2.1 Aktivitas Mekanik Jantung (2 Jam)Try MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument6 pagesCardiac Cyclearavind kishanNo ratings yet
- DOC-20220905-WA0036. (1) - WDocument6 pagesDOC-20220905-WA0036. (1) - WPizzaNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cardiac CycleKaylababy Hamilton BlackNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument30 pagesCardiac CycleAdel100% (1)
- Assessing the Heart and Great VesselsDocument55 pagesAssessing the Heart and Great VesselsMc Ramil B. PraderoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesCardiac CycleU Than HanNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument4 pagesThe Cardiac CycleAlvinNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals: The Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesTransport in Animals: The Cardiac CyclejennieNo ratings yet
- Functions of Cardiovascular System:: The Gross AnatomyDocument6 pagesFunctions of Cardiovascular System:: The Gross AnatomyShreyasi PatankarNo ratings yet
- Oral PathologyDocument23 pagesOral PathologyRuba AbbassNo ratings yet
- A.a.ngurah Surya Wira Mahotama Putra - SP 2 Blok 1.7Document13 pagesA.a.ngurah Surya Wira Mahotama Putra - SP 2 Blok 1.7123Agung SNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conduction in The HeartDocument35 pagesElectrical Conduction in The HeartNormasnizam Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: Right Atrial SystoleDocument6 pagesCardiac Cycle: Right Atrial SystoleBeatriz De Vicente MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac CycleDocument19 pagesThe Cardiac CycleRebi NesroNo ratings yet
- Blok 1.2 Kuliah 2. Siklus JantungDocument20 pagesBlok 1.2 Kuliah 2. Siklus JantungGinesha Hafidzy GarishahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: The Events of the HeartbeatDocument37 pagesCardiac Cycle: The Events of the Heartbeatindra_jeet2009No ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Cardiac CycleDocument28 pagesLecture-5 Cardiac Cyclettalhalatif99No ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle StagesDocument19 pagesCardiac Cycle StagesKhalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Cardiac Cycle Continue: Abu Ahmed 2019Document19 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle Continue: Abu Ahmed 2019Khalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology ExplainedDocument33 pagesCardiovascular Physiology ExplainedHanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument5 pagesCardiac Cyclen_nkNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument304 pagesCirculatory Systemyapyihao2100% (1)
- Cardiac Cycle: Prepared By: Mineshkumar Prajapati Roll No: 05 Biomedical Science (2021-22)Document21 pagesCardiac Cycle: Prepared By: Mineshkumar Prajapati Roll No: 05 Biomedical Science (2021-22)minesh prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1) : A-V Valves Open Semilunar Valves ClosedDocument10 pagesCardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1) : A-V Valves Open Semilunar Valves ClosedFatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Cvs PPT 2) BpehssDocument35 pagesCvs PPT 2) BpehssAmbreen GhafoorNo ratings yet
- K3 - CardiacCycle and Heart Sound Physiology-Cv13Document40 pagesK3 - CardiacCycle and Heart Sound Physiology-Cv13Raka Notgoing Anywherebut AlwayseverywhereNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1)Document10 pagesCardiac Cycle - Atrial Contraction (Phase 1)Fatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle CardiodynamicsDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle Cardiodynamicseverforyou2023No ratings yet
- Riya Arya - 21msc1279 - Biology For ChemistsDocument13 pagesRiya Arya - 21msc1279 - Biology For ChemistsSwadesh SenNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The HeartDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The HeartThereseNo ratings yet
- PC Cardiac CycleDocument29 pagesPC Cardiac CycleSebontu HasenNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument36 pagesHeartSoovendran VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EventsDocument3 pagesCardiac Eventshannahangella5949No ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle ABHINADocument11 pagesCardiac Cycle ABHINAAbhinav Thakur100% (1)
- Circulatory System: Project ReportDocument11 pagesCirculatory System: Project ReportrajivpoplaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the HeartAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Cardiac Cycle, Heart Sounds, Blood Pressure & Pulse (39Document24 pagesUnderstanding the Cardiac Cycle, Heart Sounds, Blood Pressure & Pulse (39Tristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The HeartDocument13 pagesPhysiology of The HeartHoàngBảoLongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureDocument9 pagesCardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureMohammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Transport in Humans 2 Heart and Cardiac CycleDocument74 pagesTransport in Humans 2 Heart and Cardiac Cycleloycoy008No ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument1 pageProjectNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- TtttttygbhbDocument4 pagesTtttttygbhbNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices SQPDocument7 pagesInformatics Practices SQPSonia barmaseNo ratings yet
- 5 6255674734831206500 PDFDocument8 pages5 6255674734831206500 PDFNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Questions: Class: Xii Sub: Biology DATE: 19-AUGDocument8 pages1 Mark Questions: Class: Xii Sub: Biology DATE: 19-AUGNeeraj JainNo ratings yet