Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa: Mapping and Surveing Department
Uploaded by
Herdi Yudirachman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views33 pagesDKK
Original Title
007.dkksp-01(introduction)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDKK
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views33 pagesTeknologi Dan Rekayasa: Mapping and Surveing Department
Uploaded by
Herdi YudirachmanDKK
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
Teknologi Dan Rekayasa
Mapping And Surveing Department
INTRODUCTION
The science of Geology
Why Geology?
Related to our daily life, such as:
Water and soil
Provide guide to use of natural resources
Provide knowledge of avoiding natural hazards
Helping protecting the environment
• Physical geology : examines Earth
materials, understand surface and
subsurface processes
Geology incorporates principles from physics,
chemistry, biology, engineering
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
The Science of Geology
Some historical notes about geology
Catastrophism – mid 1600’s, James
Ussher
Sudden and violent change shape landscapes
Religious belief of Earth created in 4004 B.C.
Uniformitarianism – late 1700’s, James
Hutton
processes that operate today also operated in
past
geologic processes occur over extremely long
time
birth of modern geology
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Earth as a system
Earth is a dynamic planet with many
interacting parts or spheres
Parts of the Earth system are linked
Characterized by processes that
• Vary on spatial scales from fractions
of millimeter to thousands of
kilometers
• Have time scales that range from
milliseconds to billions of years
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Earth as a system
Powered by Sun - drives external processes
• Atmosphere
• Hydrosphere
• At Earth’s surface
Powered by the Earth’s interior
• Heat remaining from Earth’s formation
• Heat generated continuously by
radioactive decay - powers internal
processes that produce volcanoes,
earthquakes, & mountains
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
A view of Earth
Earth is a planet that is small and self-
contained, fragile, sensitive to change
Environment is highly integrated with
interactions between air, water, rock, life
Earth’s four spheres
• Atmosphere- air
• Biosphere- life
• Hydrosphere - water
• Solid Earth- rock
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Atmosphere
Gaseous environment that surrounds Earth
– provides life
90% of atmosphere within 10 miles of Earth
surface (thin relative to radius of the solid
Earth at 4000 miles)
Provides air for breathing and protects from
Sun’s heat and ultraviolet radiation
Recent concern with atmosphere regarding
Ozone holes and Global Warming
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Hydrosphere
Water makes our “Blue” plant unique –sustains life
Water in motion – Hydrologic cycle
evaporation from oceans, precipitation from
atmosphere, run off back to ocean
97% ocean water, 3% fresh water
fresh water includes: surface water (lakes,
streams), ground water and glaciers
Ocean covers 71% of Earth surface -average depth of
3800 m (12,500 feet)
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Earth’s Water Balance
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Biosphere
Biosphere includes all life (including us!)
Extends from ocean floor to several miles into
atmosphere; however, concentrated at Earth
surface
Life responds to countless interaction with the
environment
Successful adaptation to changing
environment – evolution of species
Non-successful adaptation – Extinction
Survival of the “fittest” – Darwin’s
Legacy
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Solid Earth
Solid Earth: between atmosphere and
oceans – rocks and soil
Surface and subsurface features reveal
dynamic processes – Plate Tectonics
Face of the Earth
Earth’s Interior
Rock cycle - the loop that involves the
processes by which one rock type changes
to another
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
The face of Earth
Earth’s surface - two principal divisions
• Continents
• Ocean basins
Significant difference between the continents
and ocean basins is their relative elevations
• continents average 2750 feet above msl
• ocean floor average 12,500 feet below msl
• continents average 15,250 feet above ocean
floor
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Continents and Ocean Basins
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Continents
Mountain belts – linear features, active
Youngest Mountains
• Circum-Pacific Belt (surrounds Pacific Ocean)
• Island arcs – active volcanic mountains,
Older mountains
• Appalachian – eastern United States
• Urals – Russia
Shields – continental interiors, stable craton, oldest
rocks (4 billion yrs)
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Ocean basins
Continental shelf – gently sloping platform
adjacent to shore
Continental slope – steep dropoff from shelf
to deep ocean floor
Ocean ridge system – most prominent
topographic feature on Earth (43,000 mi)
Deep-ocean trenches – deep narrow
depressions (36,000 feet)
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
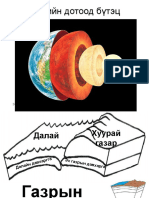
Earth’s internal structure
Layers defined by chemical composition Layers defined by physical
Crust – thin, rocky outer skin properties
Mantle – solid, rocky shell Lithosphere – sphere of
Core – iron-nickel alloy center rock
Asthenosphere – weak
sphere
Mesosphere – middle
sphere
Core – outer (liquid),
inner (solid)
Earth’s Layered Structure
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Layers Defined by Composition
Crust
• Oceanic – 7 km thick, dark igneous rock basalt,
young (<180 my), dense (3.0 g/cm3)
• Continental – 70 km thick, granitic rock, old (up to
4000 my), less dense (2.7 g/cm3)
Mantle
• contains 82% Earth’s volume, depth 2900 km
• rock called peridotite, more dense (3.3 g/cm3)
Core
• iron-nickel w/ minor oxygen, silicon, sulfur
• extreme pressure – highly dense (11 g/cm3)
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Layers by Physical Properties
Lithosphere
• cold, strong rock exhibits rigid behavior
• 5 to 250 km thick
Asthenosphere (upper Mantle)
• soft weak layer, partial melting
• depth of 660 km
Mesosphere (lower Mantle)
• between 660 and 2900 km depth
• very hot, gradual flow of convection currents
Core (differing mechanical strengths)
• Outer – liquid, generates Earth’s magnetic field
• Inner – behaves as solid due to immense pressure
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Earth’s internal structure
How do we know about the Earth’s interior?
Study of seismic wave generated by
earthquakes
Chapter 17
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Dynamic Earth
The theory of plate tectonics
• continental drift – the idea that continents
moved about the face of the planet
• not widely accepted for more than 50 years
because driving mechanism unknown
• magnetic patterns on sea floor (found from
chasing submarines during WWII) suggested
sea floor spreading
• Plate Tectonics accepted in 1965 as driving
mechanism
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Theory of plate tectonics
Symmetric magnetic
pattern around ocean
spreading ridges
Black: north magnetic
pole, white south magnetic
pole
New ocean crust records
magnetic pole
Crust moves away from
spreading ridges
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Plate Tectonics
Earth’s rigid outer shell composed of numerous
slabs (plates)
• mobile, continually changing size and
shape
• create, consume, transform lithosphere
Plate boundaries
• Most major interactions among individual
plates occurs along their boundaries
Plate tectonics – first comprehensive model of
Earth’s surface and internal workings
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Plate Boundaries
Divergent – two plates move apart, resulting in
upwelling of material from the mantle to create new
seafloor
Convergent – two plates move together with subduction
of oceanic plates or collision of two continental
plates consuming old lithosphere
Transform – located where plates grind past each other
without either generating new lithosphere or
consuming old lithosphere
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Mosaic of Earth’s Outer Shell
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Plate Boundaries
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Divergent Boundaries
Plate spreading – occurs mainly at mid-ocean ridges
(sea floor spreading), rate of 2 to 20 cm/yr
Molten rock rises from asthenosphere through
fractures (cracks) in hard rock, encounters sea
water, cools to new rock.
New ocean crust is continually created – oldest
ocean floor rock is 180 million years.
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Convergent Boundaries
Older ocean plates consumed by
subduction zone and returned to mantle
One plate descends beneath another – high
temperature, high pressure environment
producing molten rock
Pacific “ring of fire” – volcanic chains result
in explosive eruptions
Mount Saint Helens, WA – 1980
Mount Pinatubo, Philippines – 1991
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Transform Fault Boundaries
Plate grind past each other without creating or
consuming lithosphere
San Andreas Fault Zone, CA – Pacific plate moving
northwest relative to North American plate
Capable of producing strong earthquakes
• Loma Prieta, San Francisco, CA in 1989 – 7.4
• Northridge, Los Angeles, CA in 1994 – 6.7
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Plate Collisions formed the Himalayas
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Geologic time
Geologists today - accurate dates to geologic events in
Earth
history
Relative dating and geologic time scale
• Relative dating – events dates in sequence or
order without knowing their age in years
• Law of superposition – oldest sedimentary rock
layer on bottom
• Principle of fossil succession – fossils appear in a
definite order, represent time period
Absolute (radiometric) dating – Chapter 8
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Geologic time
The magnitude of geologic time
• Age of Earth – 4.5 billion yrs (4500 million)
• Humans arrived – 0.01 million yrs
• Count one year per second 24/7– take 150 yrs
(two lifetimes) to reach 4.5 billion yrs
An appreciation for the magnitude of geologic time is
important
• many geologic processes are very gradual
• we are just a fraction of Earth’s history
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Geologic Time Scale
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
Teknologi dan Rekayasa
You might also like
- L1 Intro TectonicsDocument26 pagesL1 Intro TectonicsMayur ShindeNo ratings yet
- 03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMDocument84 pages03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMCarlo Bryan Ramento100% (1)
- Enviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedDocument26 pagesEnviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedAlaiza mae BongcayNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 CB361 (Earth) by AhitlDocument28 pagesLec 2 CB361 (Earth) by Ahitlzebit5eenNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology: Over View of The CourseDocument21 pagesPhysical Geology: Over View of The Course邵純慧No ratings yet
- Earth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ExplainedDocument79 pagesEarth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ExplainedHyres Almerina AlturasNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument19 pagesLayers of The EarthRenz RazonNo ratings yet
- GMT102 L-001Document37 pagesGMT102 L-001Tasnim Alam NafijNo ratings yet
- Introducing Geology and An Overview of Important ConceptsDocument15 pagesIntroducing Geology and An Overview of Important ConceptsAbdulrhman AlselwiNo ratings yet
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- L3 - Geosphere TectonicsDocument51 pagesL3 - Geosphere TectonicsbhaveshreddygunNo ratings yet
- Geology Module 1Document33 pagesGeology Module 1Olga Soephia SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Structure of The EarthDocument71 pagesLecture 3 Structure of The EarthFuad AlAsadNo ratings yet
- GEOLOGY FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING-Topic 2Document33 pagesGEOLOGY FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING-Topic 2Jannica Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument5 pagesReviewer in ScienceJosh Deinille ManarinNo ratings yet
- Earths InteriorDocument64 pagesEarths InteriorBuuye ChNo ratings yet
- 3.-GeosphereDocument16 pages3.-GeosphereEgo sum CatholicaeNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - General GeologyDocument18 pagesGroup 1 - General GeologyAbram Nathaniel AbayanNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument36 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleBartclethon L. DelfinNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTDocument84 pagesChapter1-Introductiontogeology PRTSky FireNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 (Internal Structure of The Earth & Plate Tectonics)Document31 pagesMODULE 1 (Internal Structure of The Earth & Plate Tectonics)Giane Jae MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic2Document27 pagesPlate Tectonic2eduardocarlbituin15No ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroductionDocument37 pagesTopic 1 Introductionh.heedayah2000No ratings yet
- MPDF1 - Introduction To Engineering GeologyDocument52 pagesMPDF1 - Introduction To Engineering GeologyMARTIN CRAIG FOZNo ratings yet
- Summary in Module 2Document2 pagesSummary in Module 2Mabellee CabreraNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument38 pagesPlate TectonicsAlfVera RectoNo ratings yet
- C1 GeoDocument46 pagesC1 GeoAfiq IrfanNo ratings yet
- Formation of EarthDocument54 pagesFormation of Earthniaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Lec 3-4Document106 pagesLec 3-4zaki.farhanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Theory ExplainedDocument33 pagesPlate Tectonics Theory ExplainedAhmad AshourNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology02Document233 pagesPhysical Geology02Siari Ann Iligan100% (1)
- Science g10Document4 pagesScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNo ratings yet
- Earth's Geosphere LayersDocument17 pagesEarth's Geosphere LayersConsuelo BriceñoNo ratings yet
- NAT ReviewerDocument4 pagesNAT ReviewerAllen Aquino PradoNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument37 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleJade QuitoNo ratings yet
- IEQ-05 Earthquake Geology and Geoinformatics CourseDocument23 pagesIEQ-05 Earthquake Geology and Geoinformatics CourseShubham BansalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geology 1Document31 pagesIntroduction To Geology 1Bonsu Osei AgyapongNo ratings yet
- Eart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreDocument23 pagesEart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreRhiza Mae Lax100% (1)
- Celine Jamaica Q SciDocument5 pagesCeline Jamaica Q SciCygresy GomezNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - ReviewerDocument18 pagesGroup 1 - ReviewerAbram Nathaniel AbayanNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure and SubsystemsDocument61 pagesEarth Structure and SubsystemsKuudan FusionNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document21 pagesLecture 1Ibrahim Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 1 - 4Document95 pagesGeology Chapter 1 - 4Yoni RebumaNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDocument2 pagesEarth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDudrey Anne SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Understanding of The EarthDocument23 pagesUnderstanding of The Earthهشام رعد ناجيNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 & 6 Biogeochemical Cycles: Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument107 pagesLecture 5 & 6 Biogeochemical Cycles: Introduction To Environmental ScienceJubair SyedNo ratings yet
- Interior Structure and Properties of the EarthDocument28 pagesInterior Structure and Properties of the EarthTasnim Alam NafijNo ratings yet
- EarthSubsystemDocument60 pagesEarthSubsystemLyra Virgilia AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorDocument34 pagesChapter 2: Plate Tectonics and The Ocean FloorCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Module O3 Tektonika: Gerak Dan Sifat Interaksi Lempeng LitosferikDocument26 pagesModule O3 Tektonika: Gerak Dan Sifat Interaksi Lempeng LitosferikRidho MuhariNo ratings yet
- FGE I-Chapter 2Document37 pagesFGE I-Chapter 2FiraolNo ratings yet
- LayerDocument36 pagesLayerKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- Layers of the Earth: Structure and CompositionDocument36 pagesLayers of the Earth: Structure and CompositionKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- MODULE-1-2-3-4 - GeologyDocument24 pagesMODULE-1-2-3-4 - GeologyLIM KESSAH MARIENo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Environmental ManagementDocument6 pagesPlate Tectonics: Environmental Managementvero1curziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Physical EnvironmentDocument48 pagesLesson 3 - Physical EnvironmentFrancis De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Geology & Earth's TreasureDocument34 pagesGeology & Earth's TreasureHelaina MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- Geology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksFrom EverandGeology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ME6511 Dynamics Lab ExperimentsDocument3 pagesME6511 Dynamics Lab Experimentsraj_klnceNo ratings yet
- Mansoura University Construction Project Management Resource LevelingDocument2 pagesMansoura University Construction Project Management Resource LevelingRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT Dragged To US Court Over AI Copyright - WorldDocument13 pagesChatGPT Dragged To US Court Over AI Copyright - WorldAlexia JacksonNo ratings yet
- 101 Daily Dissertation Writing TipsDocument8 pages101 Daily Dissertation Writing TipsHelpWritingAPaperForCollegeLittleRock100% (1)
- GENEX Assistant Wireless Post-Processing Software User ManualDocument248 pagesGENEX Assistant Wireless Post-Processing Software User ManualHamid Hussain83% (6)
- ISED1-English (2nd Set)Document3 pagesISED1-English (2nd Set)Heneral JimboiNo ratings yet
- Social ConstructivismDocument2 pagesSocial Constructivismleeza dizonNo ratings yet
- Touch Screens: A Pressing TechnologyDocument6 pagesTouch Screens: A Pressing TechnologyNitesh Mishra100% (1)
- Virginia Woolf's ThesisDocument71 pagesVirginia Woolf's ThesisLorenaNo ratings yet
- The 20 Point ScaleDocument7 pagesThe 20 Point ScaleTinskiweNo ratings yet
- Spataro, M. Et Al. Non-Destructive Examination Porcelain. 2009Document11 pagesSpataro, M. Et Al. Non-Destructive Examination Porcelain. 2009Trinidad Pasíes Arqueología-ConservaciónNo ratings yet
- Educ 5 - Activity 7Document1 pageEduc 5 - Activity 7Jr Castrodes100% (1)
- Key AnswersDocument7 pagesKey AnswersMaybelyn de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ilya Prigogine - Creativity in Art and Nature PDFDocument4 pagesIlya Prigogine - Creativity in Art and Nature PDFameliaNo ratings yet
- MBA 612 OB Ch.4Document26 pagesMBA 612 OB Ch.4Asegid H/meskelNo ratings yet
- Ancheta, Mark Honey M. CE175-3C/A73 Course Expectation Sir. Timothy Daniel FeliciaDocument2 pagesAncheta, Mark Honey M. CE175-3C/A73 Course Expectation Sir. Timothy Daniel FeliciaMark AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Sainik Guess 3Document7 pagesSainik Guess 3Janardhan ChakliNo ratings yet
- PAC - Catalog - All-20120720 Vol. PAC 2.0.00Document216 pagesPAC - Catalog - All-20120720 Vol. PAC 2.0.00Pedro BortotNo ratings yet
- ASTM E193 - 2017 - Standard Specification For Laboratory Glass MicropipetsDocument6 pagesASTM E193 - 2017 - Standard Specification For Laboratory Glass MicropipetsHelio C. SouzaNo ratings yet
- Kierkegaard's Complex Views on Ethics ExploredDocument14 pagesKierkegaard's Complex Views on Ethics ExploredjuanevaristoNo ratings yet
- Political Challenges To Women Empowerment in PakistanDocument21 pagesPolitical Challenges To Women Empowerment in Pakistanماہ گل عباسNo ratings yet
- System Testing TemplateDocument12 pagesSystem Testing TemplateSE ProjectNo ratings yet
- Small Business & Entrepreneurship - Chapter 13Document27 pagesSmall Business & Entrepreneurship - Chapter 13Muhammad Zulhilmi Wak JongNo ratings yet
- Coding DecodingDocument6 pagesCoding DecodingDeepjyoti BarmanNo ratings yet
- Probability ProblemsDocument3 pagesProbability Problemsembers poggerNo ratings yet
- Fiber Attenuation CalculationDocument3 pagesFiber Attenuation CalculationBrett AtkinsNo ratings yet
- TSL Syllabus - Geography 0460 Yr8 (Ver.2)Document12 pagesTSL Syllabus - Geography 0460 Yr8 (Ver.2)Ezra NathanaelNo ratings yet
- EndgameDocument2 pagesEndgameJose Jacob Ortiz MoralesNo ratings yet
- STM - Grp4 - Sec - B - ThedaCare..... Ques OneDocument3 pagesSTM - Grp4 - Sec - B - ThedaCare..... Ques OneAdam MorganNo ratings yet