100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views11 pagesF Distribution
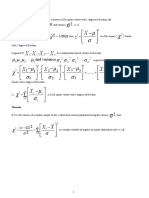
The document discusses the F distribution and its properties. It is used to test the equality of variances between two populations. The F distribution is right-skewed and depends on two degrees of freedom: the numerator df and denominator df. An example demonstrates how to find the critical F value from tables using the df and a significance level to test whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis of equal variances between two samples.
Uploaded by
Anik AlamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views11 pagesF Distribution
The document discusses the F distribution and its properties. It is used to test the equality of variances between two populations. The F distribution is right-skewed and depends on two degrees of freedom: the numerator df and denominator df. An example demonstrates how to find the critical F value from tables using the df and a significance level to test whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis of equal variances between two samples.
Uploaded by
Anik AlamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd