Professional Documents
Culture Documents
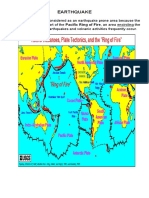
Module4 Earthquake
Uploaded by
Shekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views9 pagesDRRR
Original Title
Module4-earthquake
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDRRR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views9 pagesModule4 Earthquake
Uploaded by
Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaDRRR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Module 4: Earthquake Hazards-50
Earthquakes are the perceptible shakings of the
surface of the Earth, resulting from the sudden release
of energy in the Earth’s crust that creates seismic
waves. Earthquakes can be violent enough to toss
people around and destroy whole cities.
Earthquake Hazards
1. Ground shaking. The first main earthquake
hazard is the effect of ground shaking:
Collapsing buildings, walls, bridges,
falling furniture or objects, shattering
glass windows and mirrors.
Debris from collapsing structures is one of
the principal dangers during an earthquake
since the impact of large, heavy objects can
be fatal to human beings.
2. Ground rupture. Ground rupture is a visible
breaking and displacement of the Earth's
surface along the trace of the fault, which may
be of the order of several meters in the case of
major earthquakes.
3. Liquefaction. Liquefaction happens when
sediments with a high water content are
subjected to prolonged shaking, the pressure
of the water held in pores in the sediment
gradually increases eventually, the sediments
lose all cohesive strength and begin to behave
as if they were liquids.
4. Earthquake-induced ground subsidence.
Land subsidence can occur in various ways
during an earthquake. Movement that occurs
along faults can be horizontal or vertical or have
a component of both. As a result, a large area of
land can subside drastically during an
earthquake.
5. Tsunami. A tsunami, also known as a seismic
sea wave, is a series of waves in a water body
caused by the displacement of a large volume
of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake.
An earthquake is a natural tsunami warning. A
tsunami is sometimes preceded by a noticeable
fall or rise in the water level..
Tsunami signs along the
shoreline
strong ground shaking
from an earthquake
unusual sea-level
fluctuations: a Tsunami hazard sign in California, United
noticeable rapid rise or States
fall in coastal waters
abnormally huge wave
loud ocean roar
Tsunami Siren, Ophir State Park,
Oregon, United States
6. Earthquake-induced landslides
Strong ground motion can also trigger
landslides -- known as earthquake-induced
landslides -- in areas with steep slopes. The
greatest losses of human life are due to rock
avalanches, rapid soil flows and rock falls.
Other Geological Hazards
1.Rainfall-induced landslide. Landslides are
often triggered by rainfall, particularly in the
tropical climate of SE Asia which is
characterized by very intense long duration
rainy seasons.
2. Sinkhole
A sinkhole is a localized depression in the
surface topography, usually caused by the
collapse of a subterranean structure such as a
cave.
Although rare, large sinkholes that develop
suddenly in populated areas can lead to the
collapse of buildings and other structures.
KEY POINTS:
Locations of buildings should be based on
local geology and the subsoil properties which
modify the earthquake ground motion .
Earthquake resistant measures as specified
in building codes must be strictly adopted.
Earthquake drills are important measures for
preparedness.
You might also like
- Chapter 4 DRRRDocument28 pagesChapter 4 DRRRwendell john medianaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument11 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesChimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- DRRMChapt-4 1Document31 pagesDRRMChapt-4 1lester villarealNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Its Potential HazardsDocument6 pagesEarthquake Its Potential HazardsKassandra Cassiopeia MendiolaNo ratings yet
- DRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedDocument38 pagesDRR EARTHQUAKE HAZARDS EditedKaterina TagleNo ratings yet
- Risks of Landslides and SinkholesDocument7 pagesRisks of Landslides and SinkholesRalph Louis RosarioNo ratings yet
- Understanding Earthquake HazardsDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Earthquake HazardsLouray JeanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EarthquakesDocument14 pagesChapter 4 EarthquakesreesespufffNo ratings yet
- Natural DisasterDocument5 pagesNatural DisasterLoren GayudanNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKE What, how and effectsDocument7 pagesEARTHQUAKE What, how and effectsKarun RawalNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument3 pagesDRRRernalelishajeanNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument11 pagesNSTPTim DarvisNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: TsunamiDocument2 pagesEarthquake Hazards: TsunamiNica HuangNo ratings yet
- Effects of Earthquakes: Ground Shaking, Rupture, Landslides & MoreDocument4 pagesEffects of Earthquakes: Ground Shaking, Rupture, Landslides & MoreRichard PascoNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 2Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 2Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- Tsunami in IndiaDocument6 pagesTsunami in IndiaRashmi HazarikaNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument3 pagesEarthquakeRichard V. LomboyNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Architecture BasicsDocument15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Architecture BasicsAr Shubham JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Identifying Various Potential Earthquake HazardsDocument35 pagesIdentifying Various Potential Earthquake HazardsVJ MendozaNo ratings yet
- AssignmenttGeography 3Document3 pagesAssignmenttGeography 3Muhammad Shahzaib AzharNo ratings yet
- Technical Report 3Document6 pagesTechnical Report 3gia myka benigNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 3Document13 pagesEarth Life Science Module 3Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- ExplanationDocument5 pagesExplanationDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- DRRR Module 4 Earthquake HazardDocument28 pagesDRRR Module 4 Earthquake HazardAbia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Disaster: These Hazards Can BeDocument4 pagesDisaster: These Hazards Can Bemarc estebanNo ratings yet
- Disaster: These Hazards Can BeDocument4 pagesDisaster: These Hazards Can BeasdasdasdjdsdNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument12 pagesEARTHQUAKEapolinario mabini elementary schoolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 and Lesson 3 1Document34 pagesLesson 3 and Lesson 3 1Ma IsabelNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesEarthquake Wps OfficeLuis Luigi AsuncionNo ratings yet
- WebinarDocument19 pagesWebinarTim DarvisNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Vivin N VNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes in IndiaDocument12 pagesEarthquakes in IndiaAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- What is a Landslide? - Understanding Causes, Types and EffectsDocument9 pagesWhat is a Landslide? - Understanding Causes, Types and EffectsDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- DisastersDocument8 pagesDisastersjaninepenelope07No ratings yet
- Bhuj Earthquake ReportDocument39 pagesBhuj Earthquake ReportSamridhi ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Ncm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Document27 pagesNcm4225 Disaster Nursing (Pre-Lim)Camille RoqueroNo ratings yet
- HazardsDocument22 pagesHazardsGLADYS OLIVEROS100% (1)
- Effects of Earthquakes: Earth Lithosphere Seismic Waves Seismicity Non-Earthquake Seismic RumblingDocument4 pagesEffects of Earthquakes: Earth Lithosphere Seismic Waves Seismicity Non-Earthquake Seismic RumblingResa Consigna MagusaraNo ratings yet
- 4 DRRRDocument11 pages4 DRRRJohn Lloyd RaponNo ratings yet
- Effects/impacts of Earthquakes: Shaking and Ground RuptureDocument4 pagesEffects/impacts of Earthquakes: Shaking and Ground RuptureAditya A RNo ratings yet
- Module 7 ActivityDocument2 pagesModule 7 Activityjungil casquejoNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q1 M6 PDFDocument13 pagesDRRR Q1 M6 PDFCezar Jhon Gelua Urbano100% (1)
- Potential Earthquake Hazards and Their EffectsDocument16 pagesPotential Earthquake Hazards and Their EffectsBeau Llido CincoNo ratings yet
- 1st DRR ShitDocument4 pages1st DRR ShitARC brillantesNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document29 pagesModule 01dinsha dineshNo ratings yet
- Effects of Earthquakes Include Shaking, Ground Rupture, Landslides and MoreDocument2 pagesEffects of Earthquakes Include Shaking, Ground Rupture, Landslides and MoreRahulKumarNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's College of Baliuag: Subject: DRRR Grade Level: 11 Module Number: 3 (2 Weeks)Document6 pagesSt. Mary's College of Baliuag: Subject: DRRR Grade Level: 11 Module Number: 3 (2 Weeks)akira yuanNo ratings yet
- Eals ReviewerDocument16 pagesEals ReviewerJames Patrick CampoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesDocument2 pagesEarthquake: 1. Volcanic ActivitiesNoellhaJeanetteGabeLiwagonNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Basic Concept of Hazard HazardDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Basic Concept of Hazard HazardChristina UyNo ratings yet
- Geological Hazards FinalDocument42 pagesGeological Hazards FinalMark Elben100% (4)
- G 11 ApolloDocument20 pagesG 11 Apollojuswalim300No ratings yet
- Geologic HazardsDocument26 pagesGeologic HazardsTrisha May Flores67% (9)
- Science: Quarter 2: Earth and SpaceDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2: Earth and Spacecherish calachanNo ratings yet
- 9-10 Origin and Occurrence of Earthquake and Importance of Ground WaterDocument5 pages9-10 Origin and Occurrence of Earthquake and Importance of Ground WaterEzekiel BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Causes of EarthquakeDocument2 pagesThe Causes of Earthquakebugaspearl0No ratings yet
- Geography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityDocument3 pagesGeography Notes - Earthquakes and VulcanicityBlessing ErenNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes: Disaster and Risk AssessmentDocument10 pagesEarthquakes: Disaster and Risk Assessmentlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Test PrepDocument9 pagesEarth Science Test PrepShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument69 pagesChapter 17 - Chemical ThermodynamicsVanessa JabagatNo ratings yet
- Es Q1 Tos-2Document2 pagesEs Q1 Tos-2Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Acid-Base EquilibriaDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Acid-Base EquilibriaShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Table of Specification for Quarter 1Document2 pagesEarth Science: Table of Specification for Quarter 1Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Session No. 2.1. Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument31 pagesSession No. 2.1. Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates and LipidsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16auDocument97 pagesChapter 16auShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Diversity EcologybiogeographyDocument13 pagesDiversity EcologybiogeographyShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.4. The Cell - Transport MechanismsDocument28 pagesSession No. 1.4. The Cell - Transport MechanismsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Es Q1 Tos-4Document1 pageEs Q1 Tos-4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Session No. 2.2. Biological Molecules - Proteins and EnzymesDocument39 pagesSession No. 2.2. Biological Molecules - Proteins and EnzymesShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Physics exam specifications tableDocument5 pagesPhysics exam specifications tableShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Plant vs Animal Tissues Cell CycleDocument43 pagesPlant vs Animal Tissues Cell CycleShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- FIRST QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2Document5 pagesFIRST QUARTERLY EXAMINATION IN PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Session No 1.1. A Tour of The CellDocument40 pagesSession No 1.1. A Tour of The CellShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 q3 Week8 v4Document11 pagesPracticalResearch1 q3 Week8 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Session No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsDocument48 pagesSession No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- TQ - Science12 (Physics 1)Document8 pagesTQ - Science12 (Physics 1)Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Tos Iphp-12Document3 pagesTos Iphp-12Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSON TESTDocument7 pagesPHILOSOPHY OF THE HUMAN PERSON TESTShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 Q3 Week5 v4Document17 pagesPracticalResearch1 Q3 Week5 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key English For Academic and Professional Purposes 12Document1 pageAnswer Key English For Academic and Professional Purposes 12Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - IPHP 12Document1 pageAnswer Key - IPHP 12Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 q3 Week6 v4Document13 pagesPracticalResearch1 q3 Week6 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- AnswerKey - Science12 (Physics 1)Document1 pageAnswerKey - Science12 (Physics 1)Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Summative in Phy Scie Week 3 4Document2 pagesSummative in Phy Scie Week 3 4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 q3 Week2 v4Document12 pagesPracticalResearch1 q3 Week2 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Test ReviewDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science Test ReviewShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Summative in Phy Scie Week 1 2Document2 pagesSummative in Phy Scie Week 1 2Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 q3 Week3 v4Document14 pagesPracticalResearch1 q3 Week3 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Geofabrics Flo Vault Product Brochure Jan23Document4 pagesGeofabrics Flo Vault Product Brochure Jan23Scott McCallumNo ratings yet
- Sees (Ee, Mise, Esm &elst) Timetable Semester Two 2022-2023 Draft 2Document20 pagesSees (Ee, Mise, Esm &elst) Timetable Semester Two 2022-2023 Draft 2el diabloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SurveyingDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Surveyingnurul hafizha100% (2)
- Effect of Seaweeds Sargasssum As Organic Fertilizer in The Growth Performance of EggplantDocument7 pagesEffect of Seaweeds Sargasssum As Organic Fertilizer in The Growth Performance of EggplantKaedi Lynette DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Lithology Other Information Group Subgroup Supergroup Group Formation Member Formation Group Subgroup Formation MemberDocument4 pagesLithology Other Information Group Subgroup Supergroup Group Formation Member Formation Group Subgroup Formation MemberShahrul AshariNo ratings yet
- Takbash2018 - THE PREDICTION OF EXTREME VALUE WIND SPEEDS AND WAVE HEIGHTS FROMDocument1 pageTakbash2018 - THE PREDICTION OF EXTREME VALUE WIND SPEEDS AND WAVE HEIGHTS FROMsaenuddinNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Multi Bed Filter For Rainwater Harvesting System in India-IJRASETDocument9 pagesLow Cost Multi Bed Filter For Rainwater Harvesting System in India-IJRASETIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Theha 1Document579 pagesTheha 1Kebede MichaelNo ratings yet
- Mass Wasting Lesson Teaches Geologic ProcessesDocument4 pagesMass Wasting Lesson Teaches Geologic ProcessesJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument26 pagesClimateJenny ManagoNo ratings yet
- Sequence Stratigraphy Application Arabian GulfDocument132 pagesSequence Stratigraphy Application Arabian GulfNurlia AduNo ratings yet
- Physical Maps Latin AmericaDocument4 pagesPhysical Maps Latin AmericaTravis WrightNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - ERTH 2403Document9 pagesLecture 2 - ERTH 2403Andre YimNo ratings yet
- 8. Abandoned, LostDocument11 pages8. Abandoned, LostValeria BotacheNo ratings yet
- Current Trends of Unsustainable Plastic Production - 2023 - TrAC Trends in AnalyDocument7 pagesCurrent Trends of Unsustainable Plastic Production - 2023 - TrAC Trends in AnalyfeNo ratings yet
- The Biodiversity of Himachal PradeshDocument8 pagesThe Biodiversity of Himachal PradeshVansh KhetarpalNo ratings yet
- Effect_of_high_pH_on_the_growth_and_survival_of_maDocument11 pagesEffect_of_high_pH_on_the_growth_and_survival_of_maRowena BrionesNo ratings yet
- Human Environment System DissDocument25 pagesHuman Environment System DissDaisyl Husain100% (1)
- Natural Disasters Canadian 4th Edition Abbott Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesNatural Disasters Canadian 4th Edition Abbott Solutions ManualPeterSnydercnfp100% (44)
- Class 12 Book 3 Ch-3 Graphical Presentation of DataDocument80 pagesClass 12 Book 3 Ch-3 Graphical Presentation of DataSooraj ChoukseyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science For STEM: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Various Water Resources On EarthDocument19 pagesEarth Science For STEM: Quarter 1 - Module 9: Various Water Resources On EarthSummer VoidNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters 9th Edition Test Bank Patrick L AbbottDocument24 pagesNatural Disasters 9th Edition Test Bank Patrick L AbbottNataliePowelltzik100% (35)
- VSP & Its TypesDocument2 pagesVSP & Its TypesMohan Sharma100% (1)
- 39 Dole - Calumpang - Mangrove PDFDocument1 page39 Dole - Calumpang - Mangrove PDFCirilo Jr. LagnasonNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - Reading 2Document5 pagesUnit 9 - Reading 2Huynh Thi Cam NhungNo ratings yet
- DRRM QuizDocument1 pageDRRM QuizJay-Ar Mario67% (9)
- Phytoplankton: Directional Succession and Forced Cycles: SommerDocument2 pagesPhytoplankton: Directional Succession and Forced Cycles: SommerArnab SinghNo ratings yet
- Evs Project Climatic ChangesDocument6 pagesEvs Project Climatic Changesvansh gandhiNo ratings yet
- Integrated Forest Resources Management PlanningDocument57 pagesIntegrated Forest Resources Management PlanningMarianne SuizoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q1 DW8 1Document4 pagesScience 10 Q1 DW8 1Axcel Nathaniel CasasNo ratings yet