Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Wall and Nucleus
Uploaded by
Abirami santhanam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesHpkyiuyiuuiuyiiiji
Original Title
cell wall and nucleus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHpkyiuyiuuiuyiiiji
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesCell Wall and Nucleus
Uploaded by
Abirami santhanamHpkyiuyiuuiuyiiiji
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
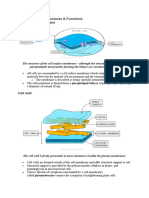
CELL WALL
Composed of substance cellulose which
provides structural strength.
Rigid outer most covering of plant cell.
PLANT CELL IN HYPERTONIC SOLUTION
Exosmosis takes place and the cell loses
water
Protoplasm shrinks away from the cell wall of
a plant cell.This process is known as
plasmolysis.
Plant cell in hypotonic cell
Endosmosis takes place and the cell bulges.
Does not burst due to the turgor pressure
exerted by the cell onto the cell wall .The cell
wall exerts equal pressure onto the cell.
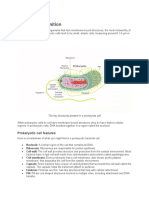
NUCLEUS
Has double layered covering called nuclear
membrane.
Nuclear membrane has pore called nuclear
pore for the transfer of materials from inside
to the cytoplasm.
The matrix of the nucleus is nucleoplasm.
Darkly stained structure in nucleoplasm is
nucleolus.Ribosomes are synthesised here.
Entangled mass of thread like structures
present in nucleoplasm is chromatin network
At the time of cell division,chromatin
network rearrange to form rod-like structure
called chromosomes
Chromosomes have information for
inheritance of features in the form of DNA.
Chromosomes are composed of DNA and
protein
Significance of Nucleus
Stores the hereditary material,DNA
Coordinates the cellular activities. So they
are said to be the controlling centre of the
cell
Manufactures ribosomes
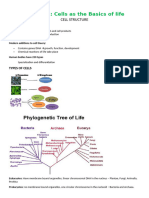
Prokaryotic Cell
PROKARYOTES
Generally small (1 – 10 micrometre)
Lacks nuclear membrane
Has undefined nuclear region with only nucleic
acid called nucleoid
Lacks membrane bound organelles like
mitochondria, golgi, ER
Has single chromosome
Ex. bacteria
EUKARYOTIC CELL - Plant cell
Eukaryotic cell
Generally large in size (5 – 100 micrometre)
Nuclear membrane present
Has well defined nuclear region
Membrane bound organelles are present
Has more than one chromosomes
ex,. Plant and animal cell
You might also like
- CELulas 2Document21 pagesCELulas 2lizetteNo ratings yet
- MaryamDocument23 pagesMaryamHabiba SaeedNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - ContentDocument12 pagesMODULE 3 - Contentjameshajiyavudeen001No ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Chapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesChapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeMonika Mehan100% (20)
- ىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاDocument9 pagesىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Summarising First Chap WipDocument30 pagesSummarising First Chap Wiprehan nimnadaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusDocument25 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusAnita ShuklaNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionDocument62 pagesCHP 2 (N) - Cell Structures and FunctionSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- Sow My ADocument4 pagesSow My AkrajeshgowdaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Document5 pagesClass 9 Fundamental Unit of Life (Notes)Udaya RakavanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Prokaryotic CellsKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- CellDocument28 pagesCellJanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument8 pagesThe CellJessa Nicole ReteracionNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell StructureDocument13 pagesPlant Cell Structureshamosa85.saNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 2 and 3Document26 pagesLESSON - 2 and 3Kerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- As BiologyDocument45 pagesAs BiologyShanzay DkhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- The Cell Nucleus: Chromatin and ChromosomesDocument34 pagesThe Cell Nucleus: Chromatin and ChromosomesMary SolomonNo ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument35 pagesCell Structure2W10No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- Tour of The CellDocument60 pagesTour of The Celladisty sncNo ratings yet
- Module (Cell Nucleus)Document12 pagesModule (Cell Nucleus)Edgie JunelaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (YR11)Document42 pagesBio Notes (YR11)nguyenbohaeNo ratings yet
- CELL in Biology-AnnottedDocument6 pagesCELL in Biology-AnnottedSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- More Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesMore Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesJaveed KassamNo ratings yet
- Cellular FunctionsDocument25 pagesCellular FunctionsDennis KwekNo ratings yet
- 03 The Nature of CellDocument45 pages03 The Nature of CellClarisse Apresurado SapidaNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureAdit KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal ScienceDocument10 pagesPlant and Animal ScienceJason Alejandro Dis-ag IsangNo ratings yet
- What Are The Tools That Biologists Use To Study Cells?Document3 pagesWhat Are The Tools That Biologists Use To Study Cells?Connie PhungNo ratings yet
- Biology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and ImplicationsDocument19 pagesBiology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and Implicationsdjxela89No ratings yet
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124No ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument82 pagesCellsK.R. LiberosisNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument94 pagesThe CellKorean DramaNo ratings yet
- 26 03 2022 - 241421Document9 pages26 03 2022 - 241421Vedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument31 pagesCellular BiologyKhang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- As Level BiologyDocument18 pagesAs Level BiologyAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter #1 Aishka NotesDocument5 pagesChapter #1 Aishka Notessales zfNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Document11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Jaeda BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument10 pagesCell Notesofwargod769No ratings yet
- 2-Cell NucleusDocument35 pages2-Cell NucleusAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument44 pagesCellsTrizia ChanNo ratings yet
- Genbio NotesDocument9 pagesGenbio NotesErika DalmaciaNo ratings yet
- Studied in A Branch of Biology, CITOLOGYDocument38 pagesStudied in A Branch of Biology, CITOLOGYAijul FurqanNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Snake Trying (Poem)Document1 pageThe Snake Trying (Poem)Abirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - Climate - IX - Aug 2020Document4 pagesWork Sheet - Climate - IX - Aug 2020Abirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Letter To Parents - Class 11 - RDX Test - 04 PDFDocument2 pagesLetter To Parents - Class 11 - RDX Test - 04 PDFAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Shikshasadan', 17, Rouse Avenue, Institutional Area, New Delhi - 110002Document2 pagesShikshasadan', 17, Rouse Avenue, Institutional Area, New Delhi - 110002Abirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Youth Day CompetitionDocument2 pagesYouth Day CompetitionAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- VTC Admission ProcedureDocument2 pagesVTC Admission ProcedureAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- How To Make: Online ClassesDocument2 pagesHow To Make: Online ClassesAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Class - Ix English Language and Literature Worksheet-4: Section A - ReadingDocument4 pagesClass - Ix English Language and Literature Worksheet-4: Section A - ReadingAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Class - Ix English Language and Literature Worksheet-4: Section A - ReadingDocument4 pagesClass - Ix English Language and Literature Worksheet-4: Section A - ReadingAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Page No: 10: Thinking About TextDocument12 pagesPage No: 10: Thinking About TextAbirami santhanam100% (1)
- Reco Final (22 7 2014) PDFDocument119 pagesReco Final (22 7 2014) PDFAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Euclid's Fifth PostulateDocument11 pagesEuclid's Fifth PostulateAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Student's Guide To FIITJEE VoD AppDocument14 pagesStudent's Guide To FIITJEE VoD AppAbirami santhanam100% (2)
- Andaman&NicobarIslands PDFDocument76 pagesAndaman&NicobarIslands PDFAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 16uco513 K1-Level Questions UNIT-1Document27 pagesCost Accounting 16uco513 K1-Level Questions UNIT-1Abirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument2 pagesNumber SystemsAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Origami and Partial Differential Equations: Bernard Dacorogna, Paolo Marcellini, and Emanuele PaoliniDocument9 pagesOrigami and Partial Differential Equations: Bernard Dacorogna, Paolo Marcellini, and Emanuele PaoliniAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9th: The Road Not Taken (Poem) Beehive English by Robert ForstDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9th: The Road Not Taken (Poem) Beehive English by Robert ForstAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- Bone and JointsDocument13 pagesBone and JointsAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet
- DiseasesDocument6 pagesDiseasesAbirami santhanamNo ratings yet