0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views12 pagesOverview of Coal Power Plants
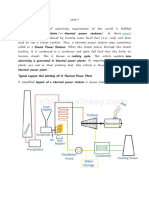
Coal power plants generate electricity through the combustion of coal. Coal is pulverized, burned in boilers to produce steam, which spins turbines connected to generators. This process produces electricity but also emits greenhouse gases and other pollutants. Newer plants try to reduce emissions through pollution controls and lower-sulfur coal. While coal power is reliable and affordable due to coal's abundance, it significantly contributes to air pollution and climate change issues due to the greenhouse gas emissions produced.
Uploaded by
Naomi Aira Gole CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views12 pagesOverview of Coal Power Plants
Coal power plants generate electricity through the combustion of coal. Coal is pulverized, burned in boilers to produce steam, which spins turbines connected to generators. This process produces electricity but also emits greenhouse gases and other pollutants. Newer plants try to reduce emissions through pollution controls and lower-sulfur coal. While coal power is reliable and affordable due to coal's abundance, it significantly contributes to air pollution and climate change issues due to the greenhouse gas emissions produced.
Uploaded by
Naomi Aira Gole CruzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd