Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Main Memory: Storing A Bit
Uploaded by
bc200200813 JUNAID ARSHAD0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views8 pagesOriginal Title
CS101-Topic 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views8 pagesMain Memory: Storing A Bit
Uploaded by
bc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
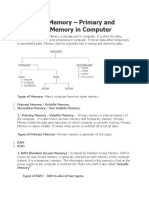
Main Memory
Storing a Bit
Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Storing a bit
Flip-Flop
2 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Flip-flop characteristics
If both inputs are 0, then it retains its value.
If upper bit is changed to 1, stored value
changes to 1
If lower bit is changed, stored value changes
to 0
3 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Main memory Organization
Manageable units Cells – 8 bits
Household devices have few hundred of cells
Large computer may have billions of cells
4 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Byte size Organization
5 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Cell Address
6 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Main memory
Other circuits can store/retrieve data at any
address – RAM
Stores bits as tiny electric Charge, refreshes
many times a second- DRAM
Reduced time to retrieve content from cell
– SDRAM
7 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
Summary
Main Memory:
Flip-flop
Memory
Organization
Cell Address
RAM/DRAM/SD
RAM
8 Dr. M. Tanvir Afzal
You might also like
- Mass Storage: Magnetic SystemDocument12 pagesMass Storage: Magnetic Systembc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Memory DevicesDocument3 pagesMemory Devicespdkufos1 - KUFOSNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument3 pagesComputer MemoryAashima GuptaNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2023 101649790Document77 pagesMUCLecture 2023 101649790محمد عقيل عبد الامير ستارNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory2Document8 pagesComputer Memory2Rajeev DebnathNo ratings yet
- Ferroelectric Ram (FRAM) : Presented by Javad.P N0:30Document17 pagesFerroelectric Ram (FRAM) : Presented by Javad.P N0:30Gautam Maingi100% (1)
- Microprocessor in PacemakerDocument5 pagesMicroprocessor in PacemakerAbdullah JavaidNo ratings yet
- Ferroelectric RamDocument17 pagesFerroelectric RamAshish RajNo ratings yet
- Puter MemoryDocument28 pagesPuter MemoryMDSR AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Two Basic Categories of Computer Memory:: Primary Storage and Secondary StorageDocument7 pagesTwo Basic Categories of Computer Memory:: Primary Storage and Secondary StorageRahul ShrivasNo ratings yet
- On YogiDocument16 pagesOn YogiYogesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization: Hierarchical SpeedDocument25 pagesComputer Organization: Hierarchical SpeedAbin KurianNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory SystemDocument14 pagesComputer Memory SystemBidrohi TollatNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Primary and Secondary Memory Gate Notes 35Document3 pagesDifference Between Primary and Secondary Memory Gate Notes 35pratimadwivedi090192No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Memory OrganizationDocument22 pagesLecture 02 - Memory OrganizationSandeep SahaNo ratings yet
- FRAMDocument23 pagesFRAMNidhin MangodeNo ratings yet
- (Memory) : Prepared By: Superviced By: Taban Omer Rozhan Sarkawt SalihDocument8 pages(Memory) : Prepared By: Superviced By: Taban Omer Rozhan Sarkawt SalihRezdar HawramiNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument37 pagesComputer Memoryhadirehman488No ratings yet
- Difference Between RAM & ROMDocument2 pagesDifference Between RAM & ROMAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Storage Technology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument15 pagesStorage Technology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle Stylemaha_barakat_iakNo ratings yet
- Chma Unit - ViDocument19 pagesChma Unit - ViSayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Pps - Unit-1 Bcs101 NotesDocument19 pagesPps - Unit-1 Bcs101 NotesdailybhaktifeedNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 Archi1Document49 pagesChap 6 Archi1lynaamara591No ratings yet
- Sram & DramDocument3 pagesSram & Dramsakibsultan_308No ratings yet
- Storage DevicesDocument4 pagesStorage Devicesarmygamer0007No ratings yet
- Memory and Storage DevicesDocument3 pagesMemory and Storage DevicesTithi KumawatNo ratings yet
- RAM and RomDocument4 pagesRAM and Rommanoj22490No ratings yet
- Name Ibrahim Fareed Subject ITC Roll No. BCSM-F18-406 Class BSCS (1I) Superior University Lahore Ram, Hard DriveDocument3 pagesName Ibrahim Fareed Subject ITC Roll No. BCSM-F18-406 Class BSCS (1I) Superior University Lahore Ram, Hard DriveIbrahim fareedNo ratings yet
- Primary MemoryDocument5 pagesPrimary MemoryLogeswari Govindaraju100% (1)
- Semiconductor MainMemoryDocument18 pagesSemiconductor MainMemoryShruti ChandraNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory Is A Temporary Storage AreaDocument3 pagesComputer Memory Is A Temporary Storage AreaMilitary BaseNo ratings yet
- XI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Document9 pagesXI CSC Computer Chapter 1 1 of 6Tanay PhadeNo ratings yet
- Computer ProficiencyDocument165 pagesComputer ProficiencyMani RaiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Neural Network?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Neural Network?Abhisek SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lec 03 Storage DevicesDocument34 pagesLec 03 Storage DevicesSajjad YousufNo ratings yet
- SS 1 COMPUTER STUDIES 3RD TERM Updated NoteDocument10 pagesSS 1 COMPUTER STUDIES 3RD TERM Updated NoteDAYONo ratings yet
- Primary MemoryDocument34 pagesPrimary MemoryMalini MohanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Memory DevicesDocument53 pagesLecture 2 - Memory Devicesjonathan stevenNo ratings yet
- Computer Memory: New Syllabus 2022-23Document20 pagesComputer Memory: New Syllabus 2022-23kalen chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Memory OrganizationDocument16 pagesChapter Four: Memory OrganizationbelihuNo ratings yet
- Ferroelectric RamDocument20 pagesFerroelectric RamRijy LoranceNo ratings yet
- 2.BCI Unit2 R19Document16 pages2.BCI Unit2 R19chariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: MotherboardDocument17 pagesUnit 1: MotherboardAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- Internal Memory: Presented By: SELINA YOUSAF ROLL NO: 0632-BH-MB-19 Section: H1Document10 pagesInternal Memory: Presented By: SELINA YOUSAF ROLL NO: 0632-BH-MB-19 Section: H1Selina YousafNo ratings yet
- Primary or Main MemoryDocument6 pagesPrimary or Main MemoryChiranjib MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Peripherals VivaDocument6 pagesPeripherals VivaManogna MarisettyNo ratings yet
- Memory DevicesDocument20 pagesMemory DevicesMD AZIZUL HOQUENo ratings yet
- Sp23 - Chapter 05 - Internal MemoryDocument5 pagesSp23 - Chapter 05 - Internal MemoryTrương Việt HoàngNo ratings yet
- Computing Part2Document9 pagesComputing Part2Senko San-JapanNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument5 pagesComputer MemorySophiya PrabinNo ratings yet
- Memory OrganizationDocument70 pagesMemory OrganizationrahqansayeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer OrganisationDocument45 pagesChapter 1 Computer OrganisationPriya YadavNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report of Nano-RamDocument34 pagesSeminar Report of Nano-RamSrivatsa Rao75% (12)
- Chapter - 08 MemoryDocument59 pagesChapter - 08 Memoryhiếu vũNo ratings yet
- Computer System Organisation - NotesDocument9 pagesComputer System Organisation - NotesNiti Arora0% (1)
- MemoryDocument42 pagesMemoryDINESH RAWATNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyDocument5 pagesTypes of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyMunim RajpootNo ratings yet
- MP Unit 5Document76 pagesMP Unit 5AJAY VIGNESHNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chris Case, Dr. John Mandrola & Lennard Zinn's The Haywire HeartFrom EverandSummary of Chris Case, Dr. John Mandrola & Lennard Zinn's The Haywire HeartNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat AliDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat Alibc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- 09 PpsDocument5 pages09 Ppsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Hexadecimal Notation: RepresentationDocument6 pagesHexadecimal Notation: Representationbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Boolean Operations: George Boole (1815-1864)Document7 pagesBoolean Operations: George Boole (1815-1864)bc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- 09 PpsDocument5 pages09 Ppsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- 08 PpsDocument7 pages08 Ppsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication: Lecture # 03 Mr. Shoukat AliDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication: Lecture # 03 Mr. Shoukat Alibc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- MCM101 07Document9 pagesMCM101 07Fahad NabeelNo ratings yet
- 06 PpsDocument9 pages06 Ppsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat AliDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat Alibc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat AliDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat AliFahad NabeelNo ratings yet
- 05 PpsDocument16 pages05 Ppsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat AliDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication: Mr. Shaukat Alibc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Mass Media - Historical PerspectiveDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Mass Media - Historical Perspectivebc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Types and Forms of CommunicationDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Types and Forms of Communicationbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Message - Root of Communication IDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Message - Root of Communication Ibc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Communication Models - Graphic Presentation of Complex IssuesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Communication Models - Graphic Presentation of Complex Issuesbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Elements of Communication and Early Communication ModelsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VU: Elements of Communication and Early Communication Modelsbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- MCM401 Lecture No 01: Introduction & Brief HistoryDocument3 pagesMCM401 Lecture No 01: Introduction & Brief Historybc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication - MCM 101 VUbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Data Storage: Dr. M. Tanvir AfzalDocument8 pagesData Storage: Dr. M. Tanvir Afzalbc200200813 JUNAID ARSHADNo ratings yet