Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation: Digital Logic Design
Presentation: Digital Logic Design
Uploaded by
Umme Habiba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesThe document discusses shift registers. It defines a shift register as a collection of flip-flops that can move stored information upon a clock signal. There are two types of shift - unidirectional, which moves in one direction, and bidirectional, which can shift in either direction. Shift registers can transfer data serially (one bit at a time) or in parallel (all bits at once). Examples of different shift register configurations are provided, including serial-in serial-out, serial-in parallel-out, parallel-in parallel-out, and a universal shift register that can perform different operations based on control signals.
Original Description:
Original Title
dld12345
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses shift registers. It defines a shift register as a collection of flip-flops that can move stored information upon a clock signal. There are two types of shift - unidirectional, which moves in one direction, and bidirectional, which can shift in either direction. Shift registers can transfer data serially (one bit at a time) or in parallel (all bits at once). Examples of different shift register configurations are provided, including serial-in serial-out, serial-in parallel-out, parallel-in parallel-out, and a universal shift register that can perform different operations based on control signals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesPresentation: Digital Logic Design
Presentation: Digital Logic Design
Uploaded by
Umme HabibaThe document discusses shift registers. It defines a shift register as a collection of flip-flops that can move stored information upon a clock signal. There are two types of shift - unidirectional, which moves in one direction, and bidirectional, which can shift in either direction. Shift registers can transfer data serially (one bit at a time) or in parallel (all bits at once). Examples of different shift register configurations are provided, including serial-in serial-out, serial-in parallel-out, parallel-in parallel-out, and a universal shift register that can perform different operations based on control signals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Presentation
Digital Logic Design
Presentation Topic:Shift Register
Presentation Group Members:
Umme Habiba: 17221598-148
Sidra Rana: 17221598-114
Sana Ansar: 17221598-112
Sir :Nauman Mazhar
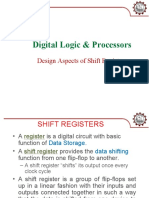
Registers
A collection of flip-flops taken as an entity.
Function: Hold information within a digital system so
that it is available to the logic elements during the
computing process.
Each combination of stored information is known as the
state or content of the register.
Shift register: Registers that are capable of moving
information upon the occurrence of a clock-signal.
Unidirectional
bidirectional
Registers
Two basic ways in which information can be
entered/outputted
Parallel: All 0/1 symbols handled simultaneously. Require
as many lines as symbols being transferred.
Serial: Involves the symbol-by-symbol availability of
information in a time sequence.
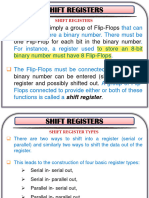
Four possible ways registers can transfer information:
Serial-in/serial-out
Serial-in/parallel-out
Parallel-in/parallel-out
Parallel-in/serial-out
Serial-in, Serial-out,
Unidirectional Shift Register
Serial-in, Parallel-out
Unidirectional Shift Register
Parallel-in, Parallel-out
Unidirectional Shift Register
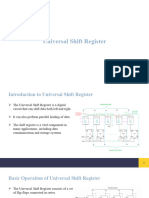
Universal Shift Register
A bidirectional shift register. Capable of shifting contents either left or right depending
upon the signals present on appropriate control input lines.
Universal shift register: Depending on the signal values on the select lines of the
multiplexers, the register can retain its current state, shift right, shift left or be loaded
in parallel. Each operation is the result of a positive edge on the clock line.
You might also like
- 1 Unit - 2 Shift RegistersDocument25 pages1 Unit - 2 Shift RegistersShivangi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amba 4axi StreamDocument2 pagesAmba 4axi StreamNGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Shift Registers and ComparatorsDocument8 pagesShift Registers and ComparatorsAmudha VNo ratings yet
- Digital System Module 4 PDFDocument52 pagesDigital System Module 4 PDFGeethanjali.pNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2: Aim: Ics Required: TheoryDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 2: Aim: Ics Required: Theoryswapnil__gNo ratings yet
- DLLec8d NotesDocument5 pagesDLLec8d NotesChintan MandalNo ratings yet
- DLD Lab#14Document13 pagesDLD Lab#14mubeenyaqub554No ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 6 VerilogDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 6 VerilogudayNo ratings yet
- Shift ReegistersDocument11 pagesShift Reegisterspmclasses28No ratings yet
- Usha Sri DocumentDocument5 pagesUsha Sri Documentsai ramNo ratings yet
- Excel Polytechnic College PallakapalayamDocument9 pagesExcel Polytechnic College PallakapalayamrevathisudhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 RegistersDocument17 pagesUnit 5 RegistersmaruthinmdcNo ratings yet
- Shift RegistersDocument18 pagesShift RegistersOrville V. Balangue50% (2)
- Digital Logic DesignDocument25 pagesDigital Logic DesignGamarJanuzajNo ratings yet
- KNR 1063 Digital Electronics: RegisterDocument28 pagesKNR 1063 Digital Electronics: RegisterCyprian Mikael CorgedoNo ratings yet
- 1589204322coe 312 Ujile AssDocument13 pages1589204322coe 312 Ujile AssnikijestokqtNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Shift RegistersDocument19 pagesSeminar ON: Shift RegistersKrati PradhanNo ratings yet
- " Implement 4 Bit Universal Shift Register ": Omkar S - Jadhav Om Agone Prasad AringaleDocument7 pages" Implement 4 Bit Universal Shift Register ": Omkar S - Jadhav Om Agone Prasad AringaleOmkar JadhavNo ratings yet
- DS II 1 RegistersDocument23 pagesDS II 1 RegistersJilanniyyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Shift RegistersDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Shift RegistersHāRsHNo ratings yet
- Session 15 ShiftregistersDocument18 pagesSession 15 ShiftregistersMaruthi RompicherlaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics (Physics) - Shift RegistersDocument11 pagesDigital Electronics (Physics) - Shift Registersjoyalsaju319No ratings yet
- Shift Registrs and UartDocument13 pagesShift Registrs and UartSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Application of Shift Registers: Guided By: Jeyapandi PrathapDocument9 pagesApplication of Shift Registers: Guided By: Jeyapandi PrathapCC PrintsNo ratings yet
- Presentation:: Topic: Shift Register & TypesDocument12 pagesPresentation:: Topic: Shift Register & TypesAnas AnsariNo ratings yet
- Unit1 P2JSPSinghDocument62 pagesUnit1 P2JSPSinghAryan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Universal Shift RegisterDocument7 pagesUniversal Shift Registerlavanyapachipala12No ratings yet
- Register ApplicationDocument10 pagesRegister ApplicationSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- DECODERDocument2 pagesDECODERSehawi AdamNo ratings yet
- Shift Register - Parallel and Serial Shift RegisterDocument8 pagesShift Register - Parallel and Serial Shift Registerkanimozhi rajasekarenNo ratings yet
- 4 RegistersDocument21 pages4 RegisterslidhisijuNo ratings yet
- 2 - Shift Registers (DLP-2021-22)Document10 pages2 - Shift Registers (DLP-2021-22)SohneaNo ratings yet
- Shift Registers - L14Document16 pagesShift Registers - L14akashtiwariakuNo ratings yet
- Universal Shift RegisterDocument2 pagesUniversal Shift RegisterAromal RajNo ratings yet
- Register Dan Shif RegisterDocument15 pagesRegister Dan Shif RegisterTsamarul HizbiNo ratings yet
- RegistersDocument3 pagesRegistersPaw PaladanNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Synchronous Circuits:: Up-Down CounterDocument7 pagesDigital Electronics Synchronous Circuits:: Up-Down CounterRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- MC9211 - Computer Organisation Unit 2: Combinational and Sequential Circuits Lesson 3 of 3: Register and CountersDocument19 pagesMC9211 - Computer Organisation Unit 2: Combinational and Sequential Circuits Lesson 3 of 3: Register and CountersAbhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture3030 12284 Register 1Document30 pagesLecture3030 12284 Register 1shivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- Shift Register: Serial-In/serial-Out ShiftDocument5 pagesShift Register: Serial-In/serial-Out ShiftSreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- 21 RegistersDocument10 pages21 RegistersHemanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Mod - 5 - Shift Registers - Oct 31Document16 pagesMod - 5 - Shift Registers - Oct 31Ravi CharanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1ece19637ec003No ratings yet
- 40 DLD Lec 40 Registers Dated 15 Jan 2021 Lecture SlidesDocument20 pages40 DLD Lec 40 Registers Dated 15 Jan 2021 Lecture SlidesEhsan MalikNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 4 Sequential LogicDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit 4 Sequential LogicAbelbeen ethioNo ratings yet
- RegistersDocument2 pagesRegistersCelio GalenzogaNo ratings yet
- Shift RegistersDocument23 pagesShift RegistersPedro VieiraNo ratings yet
- Shift Registers1Document8 pagesShift Registers1Gowtham KrishnaBBENo ratings yet
- 6-Registers and CountersDocument40 pages6-Registers and CountersWisdom tabuloNo ratings yet
- STM32 Timers TutorialDocument6 pagesSTM32 Timers TutorialHossein MajidiNo ratings yet
- Shift RegisterDocument25 pagesShift RegisterkumarisudhakarNo ratings yet
- Register and CounterDocument3 pagesRegister and CounterSujal MishraNo ratings yet
- Registers: Digital LogicDocument21 pagesRegisters: Digital LogicAhmed AlqawaqnehNo ratings yet
- 7 Counters PDFDocument23 pages7 Counters PDFIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- InstumentationDocument55 pagesInstumentation200987No ratings yet
- DSD Unit3Document54 pagesDSD Unit3Vikas TiwariNo ratings yet
- MIC Chap 1 NotesDocument15 pagesMIC Chap 1 NotesSonali AhireNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document9 pagesPresentation 1Fernand LamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 DLD 12 ShiftRegistersDocument16 pagesChapter 08 DLD 12 ShiftRegistersHaseebNo ratings yet