Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C3 Leaf Anatomy: QUESTION: What Types of Environments Would Favor C3 Only Plants? C4 Plants? Why?
Uploaded by
nokate konkoorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C3 Leaf Anatomy: QUESTION: What Types of Environments Would Favor C3 Only Plants? C4 Plants? Why?
Uploaded by
nokate konkoorCopyright:
Available Formats
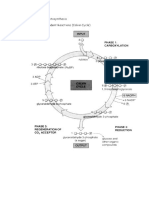
Figure 10.
18 C4 leaf anatomy and the C4 pathway
C4 Carbon Fixation. At the level of the chloroplast, all plants are C3. The C4 adaptation is a CO2 pump that uses PEP carboxylase (has a very high affinity for CO2) to
fix atmospheric CO2 to pyruvate thus generating oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is than converted to malate and transported to the bundle sheath cells where it is
decarboxylated forming CO2 and pyruvate. The CO2 is then used in C3 metabolism - the Calvin Cycle - and the pyruvate is converted back to PEP in a reaction that uses
2 ATP/PEP generated. Because of the high CO2 affinity of PEP carboxylase, the C4 plant will never be short of CO2. However, this changes the cost from 3 ATP/CO2
fixed (for a C3 only plant) to at least 5 ATP/CO2 fixed. Which is why not all plants are C4.
QUESTION: What types of environments would favor C3 only plants? C4 plants? Why?
C3 Leaf Anatomy
You might also like
- STPM Biology Past Year QuestionDocument8 pagesSTPM Biology Past Year QuestionMc Donalds Ohl Ohlsen100% (2)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisAhsan Raza100% (1)
- Catalyst PoisonsDocument21 pagesCatalyst PoisonsXuanMaiBuiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFDocument120 pagesEdexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- C4 PathwayDocument8 pagesC4 PathwayInnocent mugumeNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument55 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Hatch and Slack PathwayDocument8 pagesHatch and Slack Pathwayvijend0% (1)
- Carbon Fixation Activity SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Activity SheetLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes For AGRO 102Document17 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes For AGRO 102Misheck Chandiposha100% (1)
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document6 pagesRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Document47 pagesCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- C4 PlantsDocument4 pagesC4 PlantsIsidro ChanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceDocument39 pagesFundamentals Fundamentals Fundamentals of Crop Science of Crop Science of Crop ScienceAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleVaan ChinNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10-C4 PathwayDocument8 pagesLecture 10-C4 PathwayAtika ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in C4 PlantsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis in C4 PlantsErvin Ade PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Alternative Carbon FixationDocument18 pagesAlternative Carbon Fixationlady ann apple colipanoNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration (Chapter 12)Document10 pagesEnergy and Respiration (Chapter 12)Areej ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Activity10answers PDFDocument6 pagesActivity10answers PDFMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- C4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument28 pagesC4 Carbon Fixation - WikipediaLalit ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 06112012 PDFDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis 06112012 PDFdilleswararaoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Carbon Fixation - WikipediaDocument64 pagesCarbon Fixation - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Hatch and Slack CycleDocument30 pagesHatch and Slack CycleKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
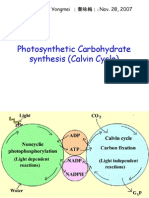
- Photosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007Document55 pagesPhotosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007bbaaddaarrNo ratings yet
- Bio 1130 Outline Week 9Document13 pagesBio 1130 Outline Week 9Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Life and Energy: By: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceDocument33 pagesEcosystem: Life and Energy: By: Trisha Vinch D. NavarceTrisha NavarceNo ratings yet
- C2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesC2 C3 C4 & Cam Variations On The Theme of PhotosynthesisKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- Ynah (Genbio)Document3 pagesYnah (Genbio)nathaniel alcantaraNo ratings yet
- Significance of Krebs Cycle in ATP Formation: and The Production of NADH and FADH, Oxidation and DecarboxylationDocument10 pagesSignificance of Krebs Cycle in ATP Formation: and The Production of NADH and FADH, Oxidation and DecarboxylationBrianna MelbourneNo ratings yet
- Tri-Calcium Phosphates As A BiomaterialDocument5 pagesTri-Calcium Phosphates As A BiomaterialSerdar7tepeNo ratings yet
- Echevarria Jonille S. BSP 2Document4 pagesEchevarria Jonille S. BSP 2Jonille EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesActivity 10 Answer KeyRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 5 and 6 - AQA ADocument19 pagesBiology Unit 5 and 6 - AQA ANalini Ranjan Muduli100% (1)
- 18 PhotorespirationDocument21 pages18 Photorespiration黄心怡No ratings yet
- 4.4 RespirationDocument4 pages4.4 Respirationsmithsashay74No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNo ratings yet
- Ch-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyDocument5 pagesCh-14 Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes BiologyMANDAL VIKRAMNo ratings yet
- Link ReactionDocument19 pagesLink Reactionshani9976614No ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: GlycolysisDocument4 pagesCytoplasm: Glycolysisapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Glycolysis and The Krebs CycleDocument7 pagesGlycolysis and The Krebs CyclekayannaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration and The MitochondrionDocument8 pagesAerobic Respiration and The MitochondrionKawtar MenjraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesDocument18 pagesChapter 7: Photosynthesis: Light Independent Reactions: How Is Chemical Energy Stored in Glucose MoleculesJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Outline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOutline Electron Transport Chain in PhotosynthesisspenzercadienteeNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Biology 3. Photosynthesis 2015 01 03 18 54 20 821Document8 pagesBiology 3. Photosynthesis 2015 01 03 18 54 20 821johnNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 441 Winter 2007 Part A (Bill Parson)Document29 pagesBiochemistry 441 Winter 2007 Part A (Bill Parson)Saad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Study GuideJ15No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionDocument5 pagesBiology Unit 4 Module 4.4 Respiration RevisionRebekah Louise Penrice-RandalNo ratings yet
- Energy & Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesEnergy & Respiration Notesaimee simarnoNo ratings yet
- Explain Why It Is Important To Check The Repeatability of The Results in An Investigation.Document19 pagesExplain Why It Is Important To Check The Repeatability of The Results in An Investigation.Anuki PereraNo ratings yet
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument4 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksSHRAVYA K REDDYNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam PlantDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam Plantwahyunipbiologi100% (1)
- Assembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsFrom EverandAssembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsNo ratings yet
- Nanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFrom EverandNanoporous Catalysts for Biomass ConversionFeng-Shou XiaoNo ratings yet