Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screening: Combined Sua, Nemc Andunep Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 1
Uploaded by
Fales HauleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screening: Combined Sua, Nemc Andunep Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 1
Uploaded by
Fales HauleCopyright:
Available Formats
Screening
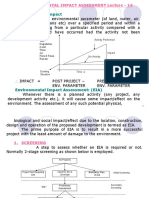
Screening is the process of determining
whether the proposed project has potential
adverse impacts on environment or community.
It determines whether the project is required to
undertake full EIA or requires undertaking of
Preliminary Impact Assessment (Initial
Environmental Examination) or does not
require EIA or should be rejected.
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 1
The objectives of screening
To ensure that all projects with potential
significant impacts are subjected to EIA
To avoid unnecessary expenses of conducting full
EIA for projects that have no potential for
significant adverse impacts
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 2
Outcomes of screening
full or comprehensive EIA required
more limited EIA required
further study needed to determine EIA
requirement
no further requirement for EIA
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 3
Screening and scoping compared
Screening
determines the requirement for EIA
establishes the level of review necessary
Scoping
identifies the key issues and impacts
establishes the terms of reference
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 4
Screening methods
Use of legal/policy definition or EIA
regulation of the host country
Prepared Schedules are showing the project
which are mandatory for EIA and those
which may/may not require EIAs
(e.g EIA and Audit Regulation (Tanzania)
2005 (GN. 349), EA regulations (Northern
Ireland) 1995 (SR 357) etc )
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 5
Screening methods cont..
Use of pre-setting thresholds
Such as to the project characteristics ( e.g 20 ha
and over), to the anticipated project impact (e.g
production of 50,000 tonnes or more of waste per
annum, to project location (e.g a designated
landscape area).
Use of case by case Approach
use of evaluation of characteristics of projects
against checklist of guidelines and criteria.
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 6
Location and environmental criteria for
case-by-case screening
The following are important in determining
significant effects:
assimilative capacity of the natural
environment
environmental sensitivity, e.g. wetlands,
coastal and mountain zones
environmental standards and objectives
adjacent to protected or designated areas
within landscapes of special heritage value
existing land use(s) and commitments
abundance and quality of natural resources
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 7
An illustrative Hybrid Screening Approach
Mand atory EIA
‘Inclu sive’ thres hold
EIA mor e likely to be
requ ired; screen
border line pro posals for
sign ificant en vironme ntal
Case by case effects
Increasing impact of development
consi deration of
req uire ment for ‘Indic ative ’ thres hold
EIA
EIA less l ikely to be req uired
but still scr een for significance
where the location is s ensitive
or if the re is a p otent ial for
cumu l ative eff ect s
‘ Exclusive’ threshol d
EIA ruled out
UNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 8
Extended screening methods
initial environmental examination
– carried out in cases where the environmental
impacts of a proposal are uncertain or unknown
(e.g. new technologies);
environmental overview
– carried out as a rapid assessment of the
environmental issues and impacts of a proposal;
and
class screening
– carried out for a family of small projects or
repetitive activities, where the environmental
effects and means of mitigation are known but
there is potential for cumulative impacts (e.g.
road ).
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 9
An Initial Environmental Examination
(IEE)
describes the proposal
considers alternatives
addresses the concerns of the community
identifies potential environmental effects
establishes mitigation measures
includes monitoring and follow up (as necessary)
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 10
Extended screening – information
required by decision-makers
description of the proposal
conditions and characteristics of the
environment
applicable policy, planning and regulatory
objectives
identification of potential impacts
degree of public concern and interest
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 11
Typical proposals requiring a full EIA
dams and reservoirs
(re)settlement and urban development
infrastructure (e.g. transport and sanitation)
industrial facilities (e.g. manufacturing
plants)
energy and minerals extraction (e.g. oil &
gas, coal)
waste management and disposal of
hazardous and toxic materials
energy development (power stations,
transmission lines, pipelines)
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 12
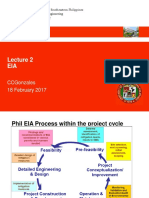
Schematic presentation of screening process
Project Registration
Schedule 3 (May or may not require EIA) Schedule 2 Full EIA
(EIA is
Mandatory)
Located in
Information is not No Serious Environmentall
enough to determine Impacts y Sensitive Area
extent of Impacts
Contradicts laws or
serious adverse impacts
can not be managed
Undertake
Preliminary Impact
Assessment
Exempt from EIA
(rare cases) Reject the
project
Not Potential Potential Serious
Serious adverse Adverse Impacts
impacts Determined
determined
Provide Conditional
Environmental Permit
Combined SUA, NEMC andUNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 4 Slide 13
You might also like
- Experience in the Management of Radioactive Waste After Nuclear Accidents: A Basis for PreplanningFrom EverandExperience in the Management of Radioactive Waste After Nuclear Accidents: A Basis for PreplanningNo ratings yet
- Confronting Climate Uncertainty in Water Resources Planning and Project Design: The Decision Tree FrameworkFrom EverandConfronting Climate Uncertainty in Water Resources Planning and Project Design: The Decision Tree FrameworkNo ratings yet
- EIA in Oil & GasDocument24 pagesEIA in Oil & Gassonara mayurNo ratings yet
- Goals and Impacts of Environmental Impact AssessmentsDocument15 pagesGoals and Impacts of Environmental Impact AssessmentsAADYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Steps in Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument27 pagesSteps in Environmental Impact AssessmentAndreas KanimeNo ratings yet
- Module - 11 EIA-1Document9 pagesModule - 11 EIA-1Faran MasoodNo ratings yet
- Module - 10 EIADocument8 pagesModule - 10 EIAEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- 001 EIA Procedures and Methods-UgandaDocument12 pages001 EIA Procedures and Methods-Ugandajr.No ratings yet
- Environmental Impact: Env. Degradation (Land Water Air Flora & Fauna Human) Activity PerformedDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Impact: Env. Degradation (Land Water Air Flora & Fauna Human) Activity Performedali akmalNo ratings yet
- Manunath 1Document28 pagesManunath 1AE 46 Sourabh PramanikNo ratings yet
- Steps in EIADocument23 pagesSteps in EIAAslam Laghari100% (1)
- Lecture 5 - ARCH 566 - EIA Fall 2021 2022 - 2Document37 pagesLecture 5 - ARCH 566 - EIA Fall 2021 2022 - 2mohmad abo ammoNo ratings yet
- EIA 1st ModuleDocument49 pagesEIA 1st ModuleUttam KonwarNo ratings yet
- 3 - EIA ProcessDocument65 pages3 - EIA ProcessAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 2-Basic Concepts For Assessing Environmental ImpactsDocument22 pagesENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 2-Basic Concepts For Assessing Environmental Impactsmamat8867% (3)
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentSwatiNo ratings yet
- EIA Process OverviewDocument28 pagesEIA Process OverviewAsfand NarejoNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 8-EIA Procedures For Small-Scale ActivitiesDocument21 pagesENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 8-EIA Procedures For Small-Scale Activitiesmamat88100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 - Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)Document28 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)Mohd Azren Tarmizi TapaNo ratings yet
- Enviornmental Engineering II CIA 3Document28 pagesEnviornmental Engineering II CIA 3Chetan JadhavNo ratings yet
- EIA and IEEDocument8 pagesEIA and IEEgopal sapkotaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment-notesDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment-notescarlamae.maquirangNo ratings yet
- 02 Enviromental Impact AssessmentDocument65 pages02 Enviromental Impact AssessmentJulie Anne CristalesNo ratings yet
- EIA-SEA Module 41404 - Lecture - 4 - WS - 2017 - 18 - 01.11.2017Document22 pagesEIA-SEA Module 41404 - Lecture - 4 - WS - 2017 - 18 - 01.11.2017Tobi AkinyemiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AgencyDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Impact AgencyAnurag BorahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentDavid GatesNo ratings yet
- MACC Project feasibility appraisal methodologyDocument9 pagesMACC Project feasibility appraisal methodologyericakmalNo ratings yet
- PAHS 055 Session 3 Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument30 pagesPAHS 055 Session 3 Environmental Impact AssessmentAWENABAH THOMASNo ratings yet
- ESIA-ppt FentaleDocument46 pagesESIA-ppt FentaleKecha Taye100% (4)
- EIA UpscDocument14 pagesEIA UpscDhansingh KokareNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment Follow Up and Its Benefits For IndustryDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Follow Up and Its Benefits For IndustryLyanka LamishNo ratings yet
- Wetlap 2 PDFDocument5 pagesWetlap 2 PDFOyebamiji EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- EIA Process Overview for Mining ProjectsDocument5 pagesEIA Process Overview for Mining ProjectsSOUMYANo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of Environmental Impact Assessment: Location Month YearDocument15 pagesFundamental Concepts of Environmental Impact Assessment: Location Month YearTsihatesfaNo ratings yet
- Aims and Objectives of EIA: UNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 1 Slide 1Document15 pagesAims and Objectives of EIA: UNEP Training Resource Manual Topic 1 Slide 1Min Chan MoonNo ratings yet
- Project Management and Environmental SustainabilityDocument47 pagesProject Management and Environmental SustainabilitysheppyNo ratings yet
- PD 1586 PEISS Dr. Girlie SebarilloDocument109 pagesPD 1586 PEISS Dr. Girlie SebarilloDan AlbertNo ratings yet
- SitescrnDocument2 pagesSitescrnMark CheneyNo ratings yet
- EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment) : Iqra Meshal Lecturer Faculty of Engineering, Lahore Leads UniversityDocument32 pagesEIA (Environmental Impact Assessment) : Iqra Meshal Lecturer Faculty of Engineering, Lahore Leads UniversityKashif NaveedNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Deputy Director, NPTI FaridabadDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment: Deputy Director, NPTI FaridabadashmangautamNo ratings yet
- Strategic Environmental AssessmentDocument14 pagesStrategic Environmental AssessmentEmmanuel NtaleNo ratings yet
- Class EA Process in OntarioDocument13 pagesClass EA Process in OntarioAhmed AbuzourNo ratings yet
- Eia ScreeningDocument17 pagesEia ScreeningHaqiem SuhailiNo ratings yet
- ACE Safeguards Presentation Sept 26 2019Document37 pagesACE Safeguards Presentation Sept 26 2019Dr. Anushika BoseNo ratings yet
- MC005-July2014Revised Guidelines For Coverage Screening and Standardized Reqts PDFDocument36 pagesMC005-July2014Revised Guidelines For Coverage Screening and Standardized Reqts PDFNina Arra Rivera100% (1)
- Lecture 1-EIA PROCEDURESDocument31 pagesLecture 1-EIA PROCEDURESSaiful MunirNo ratings yet
- IEE EIA Introduction and ProcessDocument27 pagesIEE EIA Introduction and ProcessHari PyakurelNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Overview: Dr. Sanjay MathurDocument57 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) : Overview: Dr. Sanjay MathurDebattri DasNo ratings yet
- Module-5 Envirionmental Impact Assessment Dr. Saravanakumar Evs Chy1002Document33 pagesModule-5 Envirionmental Impact Assessment Dr. Saravanakumar Evs Chy1002Asheee100% (1)
- Module 3b Eiaempcra - Mar 2019Document16 pagesModule 3b Eiaempcra - Mar 2019Tarry MudembaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Manual Reference VersionDocument37 pagesEnvironmental Manual Reference VersionfrancisNo ratings yet
- Plenary Paper 2. Environmental Impact Assessment of Development Projects in The Philippines - Some Experiences Q.L., KintanarDocument38 pagesPlenary Paper 2. Environmental Impact Assessment of Development Projects in The Philippines - Some Experiences Q.L., KintanarGraciaVelitarioNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia)Document20 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (Eia)kashyap jyoti gohainNo ratings yet
- Annals of Nuclear Energy: Gopika Vinod, Pavan K. Sharma, T.V. Santosh, M. Hari Prasad, K.K. VazeDocument7 pagesAnnals of Nuclear Energy: Gopika Vinod, Pavan K. Sharma, T.V. Santosh, M. Hari Prasad, K.K. VazeJude OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Screening 25marchDocument15 pagesScreening 25marchHappy CasioNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - EIA - MSEDocument203 pagesUnit 1 - EIA - MSESwasthikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document159 pagesChapter 1Adam M KumNo ratings yet
- Environmental Aspects ProcedureDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Aspects ProcedureAli SalihNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : Scoping Techniques Baseline Data GenerationDocument12 pagesConcepts of Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : Scoping Techniques Baseline Data GenerationUnigwe Chinanu OdinakaNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Environmental Impact Assessment Industry Guide FINALDocument52 pagesCumulative Environmental Impact Assessment Industry Guide FINALPaulo BuenoNo ratings yet
- Scoping: Sua, Nemc Andunep Training Resource ManualDocument17 pagesScoping: Sua, Nemc Andunep Training Resource ManualFales HauleNo ratings yet
- EIA Lecture 3 REGISTRATIONDocument6 pagesEIA Lecture 3 REGISTRATIONFales HauleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nvironmental Mpact Ssessment: E I A (EIA)Document22 pagesIntroduction To Nvironmental Mpact Ssessment: E I A (EIA)Fales HauleNo ratings yet
- An Introduction Lecture To Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) CourseDocument12 pagesAn Introduction Lecture To Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) CourseFales HauleNo ratings yet
- Idebenone Increases Chance of StabilizationrecoverDocument5 pagesIdebenone Increases Chance of StabilizationrecoverRaluca PascalauNo ratings yet
- Ant Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesAnt Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFIwan Arinta100% (1)
- Spent Caustic Recycle at Farleigh MillDocument9 pagesSpent Caustic Recycle at Farleigh MillyamakunNo ratings yet
- Appendix A. Second QuantizationDocument24 pagesAppendix A. Second QuantizationAgtc TandayNo ratings yet
- BonBonB What Map ReviewsDocument396 pagesBonBonB What Map Reviewstoyi kamiNo ratings yet
- Bai TapDocument6 pagesBai TapChi VominhNo ratings yet
- Dec50103 PW2 F1004Document14 pagesDec50103 PW2 F1004Not GamingNo ratings yet
- R. Paul Wil - Rico ChetDocument7 pagesR. Paul Wil - Rico ChetJason Griffin100% (1)
- Understanding Business FinanceDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Business FinanceNathaniel BocautoNo ratings yet
- Ayushi HR DCXDocument40 pagesAyushi HR DCX1048 Adarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Roberson-FRIT 7236 Assessment PlanDocument13 pagesRoberson-FRIT 7236 Assessment PlanMarie RNo ratings yet
- The Open Banking StandardDocument148 pagesThe Open Banking StandardOpen Data Institute95% (21)
- Earth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsDocument4 pagesEarth Works Volume Conversion and Swell FactorsJj BarakaNo ratings yet
- Management The Essentials Australia 4th Edition Robbins Test BankDocument29 pagesManagement The Essentials Australia 4th Edition Robbins Test Bankfidelmanhangmhr100% (38)
- Iit Ashram: Guj - Board Pattern Test-7Document6 pagesIit Ashram: Guj - Board Pattern Test-7rult007No ratings yet
- CHE135 - Ch1 Intro To Hazard - MII - L1.1Document26 pagesCHE135 - Ch1 Intro To Hazard - MII - L1.1SyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- Analie T. Caro: Personal ParticularsDocument4 pagesAnalie T. Caro: Personal ParticularsAnalie Tañamor CaroNo ratings yet
- Visulas Yag III User ManualDocument126 pagesVisulas Yag III User ManualTomNo ratings yet
- Developmental Screening Using The: Philippine Early Childhood Development ChecklistDocument30 pagesDevelopmental Screening Using The: Philippine Early Childhood Development ChecklistGene BonBonNo ratings yet
- (已压缩)721 260 PBDocument879 pages(已压缩)721 260 PBflorexxi19No ratings yet
- LP Exemplar in English 9 Verbal and Non VerbalDocument3 pagesLP Exemplar in English 9 Verbal and Non VerbalBaby Lyn Oamil EusebioNo ratings yet
- FisheryDocument2 pagesFisheryKyle GalangueNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Dbms PDFDocument66 pagesUnit4 Dbms PDFRS GamerNo ratings yet
- Media ExercisesDocument24 pagesMedia ExercisesMary SyvakNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Online Game Addiction To TheDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Online Game Addiction To TheRafuell Amper CablasNo ratings yet
- IBM Global Business ServicesDocument16 pagesIBM Global Business Servicesamitjain310No ratings yet
- Cazul Cyril Burt 3Document3 pagesCazul Cyril Burt 3Cosmina MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Public Health Risks of Inadequate Prison HealthcareDocument3 pagesPublic Health Risks of Inadequate Prison HealthcarerickahrensNo ratings yet
- Generator Honda EP2500CX1Document50 pagesGenerator Honda EP2500CX1Syamsul Bahry HarahapNo ratings yet