Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Micromaster MM420: Simatic S7
Uploaded by
Gnana DeepOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Micromaster MM420: Simatic S7
Uploaded by
Gnana DeepCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Micromaster MM420
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.1
Objectives
Upon completion of the chapter the participant will ...
... understand the principle of an inverter
… be able to reset the inverter to factory defaults
... be able to operate the BOP standard operating panel
... be able to set basic parameters using the Basic Operator Panel
(BOP)
… be able to integrate the Micromaster into the hardware
configuration
… be able to monitor and control the Micromaster
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.2
Principle of an Inverter
Infeed DC Power module
(Rectifier) link (Inverter)
Three-phase mains system
such as 3 AC, 400V, 50 Hz
Induction
motor
Inverter Variable
speed
Voltage Voltage Voltage
t t t
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.3
Overview: Standard Drives
Application example:
Controlled pumps and
fans in an air
conditioner
MICROMASTER 4 Inverter
(here the different sizes with a Application example:
performance of about 0.1 to 250 kW) Conveyor belt
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.4
Communication: PROFIBUS DP
PROFIBUS Module
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.5
Main Tasks of the Master – Slave Communication
Master-Slave Communication
Reading and writing of parameters Controlling the drive process
Reading out of fault and diagnostic values Permanent setting of control bits and setpoints
Reading and modifying function values Constant reading of status bits and actual values
Parameter index value (PKW) Process data (PCD)
Size of the main setpoint
to the inverter
Source of the main setpoint Level of the control bit
Source of the control bit
Size of the main actual value
from inverter
Level of the status bit
How does data transmission take place?
• Only triggered if required • Fast and permanently triggered
• Freely accessible to all parameters • With fixed “wiring“ to the process
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.6
Configuration of the MM420, PPO Types
PPO Type 1: all parameters can
be changed
PPO Type 3: only the setpoints
can be changed
PKW PCD
PCD1 PCD2
PKE IND PWE STW1 MS PCD3 PCD4 PCD5 PCD6 PCD7 PCD8 PCD9 PCD10 PCD11 PCD12 PCD13 PCD14 PCD15 PCD16
ZSW1 MAV
1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16.
Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word Word
PPO1 Access only via SFC
PKW = Parameter Index Value
PPO3 Access with load and transfer instructions PKE = Process ID
PWE = Process Value
STW = Control Word
Free ZSW = Status Word
max. for MM420 MS = Main Setpoint
MAV = Main Actual Value
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.7
Assigning Parameters to the Command Source and Setpoint Channel
Control parameterizing path:
P0927 = 0000 0000 0000 1111 Status word
Command source
Bits 0 to 15
BOP/AOP keys 1
internal sequence control system Micromaster
Digital inputs 2
USS bus using RS232 Control word
4
PC-inverter mounting set Bits 0 to 15
USS from BOP Link 5
Communications module 6 P0700 =
Ramp-function generator Control reference frequency:
Fixed frequencies Additional setpoint P2000 = 50 [Hz]
FF1 ... ...
Setpoint
FF2 ... ... frequency
FF3 ... ...
Actual
Motor potentiometer 1 frequency
Starter
Analog setpoint 2
3
a Main setpoint
b
USS from BOP Link 4 Additional setpoint
Communications module 6 P1000 =
Setpoint source P1000 = b, a
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.8
Communication with PPO Type 3
CPU MM 420
T QW 42 Control word
QD 42
T QW 44 Main setpoint
PROFIBUS-DP
L IW 42 Status word
L IW 44 ID 42
Main actual value
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.9
Structure of the Control Word
W # 16 # 0 4 7 F = Motor ON
1 1 1 1
Rising edge for switching on !
W # 16 # 0 4 7 E
1 1 1 0 = Motor OFF
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ON/OFF 1
OFF 2
OFF 3
Pulse-Enable
Ramp-function Generator-Enable
Ramp-function Generator-Startup
Setpoint-Enable
Fault-Acknowledge
JOG right
JOG left
Control from PLC
Reverse
---
Motor-Poti up
Motor-Poti down
Command Data Set Bit 0
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.10
Structure of the Status Word
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Drive ready
Drive ready to run
Drive running
Drive fault active
OFF2 active
OFF3 active
Switch on inhibit active
Drive warning active
Deviation Setpoint / Actual
PCD control (PLC)
Maximum frequency reached
Warning motor current max.
Motor holding brake active
Motor overload
Motor running direction right
Inverter overload
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.11
Integrating a Drive in the HW-Config
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.12
Controlling the MM420 with Monitor/Modify Variables
Switch off: W#16#047E
Switch on: W#16#047F
Actual Value (Hexa) Act. Value (Decimal) Act.Val. (Frequency) Speed under rated load (rpm)
4000 16384 50 1350
3000 12288 37.5 1012.5
2000 8192 25 675
1500 5376 16.4 443
1000 4096 12.5 337.5
500 1280 3.91 105.5
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.13
S7 Program for Controlling the Drive
Control word for Motor ON:
Hex Bit Function
0 ON/OFF 1
F 1 OFF 2
2 OFF 3
3 Pulse enable
4 RFG enable
5 RFG start
7
6 Setpoint enable
7 Fault acknowledge
8 JOG right
9 JOG left
4
10 Control from PLC)
11 Reverse (setpoint inversion)
12 ---
0 13 Motorpoti (MOP) up
14 Motorpoti (MOP) down
15 Command data set Bit 0
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.14
BOP (Basic Operator Panel) Standard Operator Panels
SDP (= Status BOP (= Basic
Operator Panel) Setting parameters (changeable parameters):
Display Panel)
SIEMENS
SIEMENS
5.00
I <> Fn
O Jog P
MICROMASTER 440
MICROMASTER 440
Index of a parameter (sub-parameters):
Parameter keypad
As delivered from factory
for easy
LED Status display
commissioning
Monitoring parameters:
or changing
individual parameters
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.15
Keys on the Operator Panel
Start the converter with parameterized ramp-up time
Bring the converter to a standstill with parameterized ramp
down rate. Press twice and the converter coasts to a
standstill.
Changes the direction of rotation
Motor starts and rotates at the preset jog frequency. Motor
rotates as long as the button remains pressed
Parameter access. Is used to select the parameter number
and to accept the value
Increase parameter number or value
Decrease parameter number or value
This key has a series of functions:
- Roll function to display the 5 most important values
- More exact setting of parameters, e.g. decimal places
- Jump to Parameter 0000. The display shows r0000
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.16
PROFIBUS Communications Module: Setting the Address
Switch number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Add to address 1 2 4 8 16 32 64
Example 1: Address = 9 on off off on off off off
Example 1: Address = 88 off off off on on off on
Some addresses have a “particular“ meaning
Address Meaning
PROFIBUS address is specified
0
by Parameter P0918
1 to 125 valid PROFIBUS address
126, 127 invalid PROFIBUS address
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.17
Exercise 1: Reset to Factory Default
Parameter Value Comment
P0010 30 Reset to
Factory Default
P0970 1 End
S1 = Drive On/Off
P0010 = Commissioning filter S2 = Reverse direction of rotation
P0970 = Reset to factory defaults S3 = Acknowledge fault
P3900 = End of quick commissioning H1 = Fault (is lit when there is no fault)
P1 = Potentiometer for the frequency/speed
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.18
Exercise 2: Setting the MM420 Parameters with the BOP
If the PROFIBUS Parameter number Value Comment
address was set from the
hardware side, P0003 2 Expanded parameter access
P0918 can only display
P0700 6 Control signals from PROFIBUS
P0918 9 PROFIBUS address of the MM420
P1000 2 Frequency setpoint from Potentiometer
P1120 2.00 Ramp-up time 2 seconds
P1121 2.00 Ramp-down time 2 seconds
Setpoint before ramp-function generator: Setpoint after ramp-function generator:
Internally generated
Setpoint frequency Setpoint frequency ramp-function
50 Hz
50 Hz
t t
P1120 P1121
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.19
Exercise 3: Integrating a Drive in HW-Config
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.20
Exercise 4: Controlling the MM420 via PROFIBUS
Switch off: W#16#047E
Switch on: W#16#047F
Actual Value (Hexa) Act. Value (Decimal) Act.Val. (Frequency) Speed under rated load (rpm)
4000 16384 50 1350
3000 12288 37.5 1,012.5
2000 8192 25 675
1500 5376 16.4 443
1000 4096 12.5 337.5
500 1280 3.91 105.5
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.21
Exercise 5: Controlling a Drive via the Touchpanel
CPU
P
R
O
F
I
B
U
S
MM420
D
P
SIMATIC S7 Date: 08/28/20 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG 2008. All rights reserved. File: PRO1_10E.22
You might also like
- Introduction to Micromaster MM420 (1Document22 pagesIntroduction to Micromaster MM420 (1ING. OSCAR PACHECONo ratings yet
- PRO1 10E Introduction MicromasterDocument20 pagesPRO1 10E Introduction MicromasterLộc QuangNo ratings yet
- PRO1 10E Introduction Micromaster PDFDocument20 pagesPRO1 10E Introduction Micromaster PDFTinhNguyenNo ratings yet
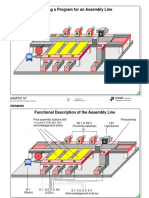
- Creating an Assembly Line ProgramDocument24 pagesCreating an Assembly Line ProgramNeagoe CristianNo ratings yet
- PRO1 10E IntroductionMicromasterDocument22 pagesPRO1 10E IntroductionMicromasterSeVictor Rudas CajaNo ratings yet
- EA_PortfolioDocument17 pagesEA_Portfoliovz2502105No ratings yet
- 7SJ80Document44 pages7SJ80indrajit mondalNo ratings yet
- HMI To HMI CommunicationDocument3 pagesHMI To HMI CommunicationTHANGABALU RAJENDIRANNo ratings yet
- 6DMD SIP5 - Bay ControllerDocument51 pages6DMD SIP5 - Bay ControllerProteccion MedicionNo ratings yet
- MicroMaster 6SE92Document170 pagesMicroMaster 6SE92chiaranovelloNo ratings yet
- S7-300 Module SpecificationDocument564 pagesS7-300 Module SpecificationJuan RoaNo ratings yet
- Introduction MEKATRO 2018Document23 pagesIntroduction MEKATRO 2018prasetya faizNo ratings yet
- Pme120-Ai ManualDocument46 pagesPme120-Ai Manual이태규No ratings yet
- Application Note: Custom Delta Robot Motor TuningDocument34 pagesApplication Note: Custom Delta Robot Motor TuningAlberto EnestrillaNo ratings yet
- Ternary en PDFDocument36 pagesTernary en PDFJuanJo LlamasNo ratings yet
- MD380 AC Drive User Manual-20121225Document292 pagesMD380 AC Drive User Manual-20121225Ks Bharathiyar100% (2)
- Simatic S7-200Document30 pagesSimatic S7-200Bui Hong PhongNo ratings yet
- Abb Rem630Document8 pagesAbb Rem630mohammed yousifNo ratings yet
- 13 Functions and Function BlocksDocument25 pages13 Functions and Function Blockshaftu gideyNo ratings yet
- Reliability Analysis of Aircraft Starter Generator Drive ConverterDocument6 pagesReliability Analysis of Aircraft Starter Generator Drive Convertersezgin bayramNo ratings yet
- PRO2 01E Training UnitsDocument10 pagesPRO2 01E Training UnitsNguyen HauNo ratings yet
- MD380 USER MANUAL (English Version)Document296 pagesMD380 USER MANUAL (English Version)Ingeniería AplicacionesNo ratings yet
- 07 Storage Tank ReqsDocument13 pages07 Storage Tank ReqswahyoeNo ratings yet
- Training Units Addressing SetupDocument10 pagesTraining Units Addressing SetupING. OSCAR PACHECONo ratings yet
- PRO1 02E TrainingUnits and AddressingDocument10 pagesPRO1 02E TrainingUnits and AddressingIsmael GraciaNo ratings yet
- SCE en 030-020 R1209 Timers and CountersDocument41 pagesSCE en 030-020 R1209 Timers and CountersYoga AdiNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Related IssuesDocument30 pagesHoneywell Related IssuesChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Arrancadores Suaves Sirius 3RW SiemensDocument54 pagesArrancadores Suaves Sirius 3RW SiemensJOSE ARTURO CRUZ AIQUENo ratings yet
- ST-SERV3 V58 enDocument262 pagesST-SERV3 V58 enAhmed Khairy100% (3)
- Hardware Commissioning ChecklistDocument33 pagesHardware Commissioning ChecklistChihebJmaaNo ratings yet
- SICAM MicroRTU 6MD203 Remote Terminal UnitDocument16 pagesSICAM MicroRTU 6MD203 Remote Terminal UnitwavetauNo ratings yet
- PSIM Catalog PDFDocument8 pagesPSIM Catalog PDFkarthikp207No ratings yet
- G1 - Introduction Generator ProtectionDocument21 pagesG1 - Introduction Generator ProtectionOoi Ban JuanNo ratings yet
- DRV Sinumerik Simodrive Catalog Nc60Document536 pagesDRV Sinumerik Simodrive Catalog Nc60Rogério PereiraNo ratings yet
- Siemens Manual BookDocument82 pagesSiemens Manual BookDwi Gilang R ANo ratings yet
- Inovance IS580Document151 pagesInovance IS580Panca Arief100% (1)
- Startdrive MotorData FAQ enDocument7 pagesStartdrive MotorData FAQ enpatulakeNo ratings yet
- Serv1 06e HW ComDocument16 pagesServ1 06e HW ComNeagoe CristianNo ratings yet
- Et200sp Base Units Manual en-US en-USDocument195 pagesEt200sp Base Units Manual en-US en-USFilipe FernandesNo ratings yet
- Simatic st70 Chap01 English 2015Document18 pagesSimatic st70 Chap01 English 2015MarceloNo ratings yet
- CMMS ST G2 - 2014 04 - 8034431g1Document4 pagesCMMS ST G2 - 2014 04 - 8034431g1Nelson KempNo ratings yet
- Sinumerik 808D Commissioning Guide: Training ManualDocument62 pagesSinumerik 808D Commissioning Guide: Training ManualSam eagle goodNo ratings yet
- Md380 SeriesDocument298 pagesMd380 SeriesRulo Hdez LazoNo ratings yet
- Result Paper On IOT Based Induction Motor Speed Control and Parameter MonitoringDocument8 pagesResult Paper On IOT Based Induction Motor Speed Control and Parameter MonitoringIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7-300: The Universal Controller For System Solutions With Factory Automation As Focal PointDocument81 pagesSIMATIC S7-300: The Universal Controller For System Solutions With Factory Automation As Focal PointDeath ZoneNo ratings yet
- Power System ModelingDocument27 pagesPower System ModelingFrancisco AndradeNo ratings yet
- CT - IKPI PROFINET 2008 Short - 76 PDFDocument164 pagesCT - IKPI PROFINET 2008 Short - 76 PDFNeagoe CristianNo ratings yet
- Delta MS 300 Series CatalogDocument40 pagesDelta MS 300 Series Catalogaymn slahNo ratings yet
- 6ra7031 6dv62 0 Siomreg DC Converter Siemens ManualDocument234 pages6ra7031 6dv62 0 Siomreg DC Converter Siemens ManualBorislav ChavdarovNo ratings yet
- ABB Megatrol V7Document2 pagesABB Megatrol V7mostafagoly1358No ratings yet
- SIM908 Reference Design Guide Application Note V1.00Document17 pagesSIM908 Reference Design Guide Application Note V1.00jonydanceNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC S7-200: Simatic Hmi The Human Machine Interface SIMATIC S7-200Document30 pagesSIMATIC S7-200: Simatic Hmi The Human Machine Interface SIMATIC S7-200gaston100% (1)
- Inverter Freqrol Cs80Document40 pagesInverter Freqrol Cs80riadhNo ratings yet
- s7300 Et200m Ex Io Modules Manual en en-USDocument274 pagess7300 Et200m Ex Io Modules Manual en en-USMozhdeh HeydariNo ratings yet
- ABB ACS800 Drives PDFDocument52 pagesABB ACS800 Drives PDFrobertoNo ratings yet
- BLDC Simulink TutorialDocument27 pagesBLDC Simulink Tutorialyouzi WuNo ratings yet
- SENTRON LV10-PH01 Complete English 04-2018 201808090842560250Document62 pagesSENTRON LV10-PH01 Complete English 04-2018 201808090842560250Ivan FlorezNo ratings yet
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Toc MapDocument1 pageToc MapGnana DeepNo ratings yet
- Overview of Time Synchronization in Tia Portal and Wincc V7Document29 pagesOverview of Time Synchronization in Tia Portal and Wincc V7Gnana DeepNo ratings yet
- Excel 2021 CalendarDocument12 pagesExcel 2021 CalendarGnana Deep100% (1)
- Startup ClubDocument2 pagesStartup ClubGnana DeepNo ratings yet
- Alarm MSGDocument39 pagesAlarm MSGGnana DeepNo ratings yet
- Auto Transformer Starter PDFDocument6 pagesAuto Transformer Starter PDFShubhankar KunduNo ratings yet
- Bee 1l1 (Bee & Bec) Lab ManualDocument39 pagesBee 1l1 (Bee & Bec) Lab ManualSanoj SureshNo ratings yet
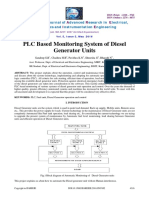
- PLC Based Monitoring System of Diesel Generator UnitsDocument7 pagesPLC Based Monitoring System of Diesel Generator UnitsHitesh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Bhavishyapuranam Telugu PDFDocument385 pagesBhavishyapuranam Telugu PDFraja50% (2)
- Thesis - Water Level MeasurementDocument57 pagesThesis - Water Level MeasurementSumathi AnandNo ratings yet
- KVK (Krishi Vigyan Kendra)Document29 pagesKVK (Krishi Vigyan Kendra)Gnana DeepNo ratings yet
- All About Pak Affairs (DMG Officer) - Recommended - CSS ForumsDocument5 pagesAll About Pak Affairs (DMG Officer) - Recommended - CSS ForumsAzeem ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- How To Fix A Bricked Linksys RouterDocument2 pagesHow To Fix A Bricked Linksys RouterBogdan CacuciNo ratings yet
- Gega Infotech Private Limited (Employer)Document2 pagesGega Infotech Private Limited (Employer)Rishi PawarNo ratings yet
- Infomaker 7 Quick StartDocument33 pagesInfomaker 7 Quick StartAndreea FilipNo ratings yet
- Measuring Stradivari Violin "Cremonese" (1715) by 3D ModelingDocument5 pagesMeasuring Stradivari Violin "Cremonese" (1715) by 3D ModelingAdriano AngelicoNo ratings yet
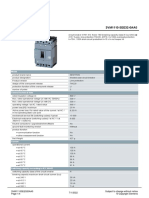
- Data Sheet 3VM1110-3EE32-0AA0: ModelDocument4 pagesData Sheet 3VM1110-3EE32-0AA0: ModelJanaina SouzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CAD CAM MasterCAMDocument28 pagesIntroduction To CAD CAM MasterCAMMuhammad TausiqueNo ratings yet
- Adobe CS6 Master CollectionDocument2 pagesAdobe CS6 Master CollectionjuuuuuangNo ratings yet
- VT82C686B Delivers ValueDocument130 pagesVT82C686B Delivers Valueanacer55No ratings yet
- Sabai Firmware UpgradeDocument2 pagesSabai Firmware Upgrade00001010No ratings yet
- Syllabus Web DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSyllabus Web DevelopmentJhun Ngipol Jr.No ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document6 pagesQuiz 2Shaukat Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Cyber Insurance - Author Mansi ThaparDocument3 pagesCyber Insurance - Author Mansi Thaparaloksingh1980No ratings yet
- Appscan Enterprise V9.0.3.X Planning & Installation GuideDocument157 pagesAppscan Enterprise V9.0.3.X Planning & Installation GuideHuynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nokia Brand EvolutionDocument14 pagesNokia Brand Evolutionsunnysandeep4uNo ratings yet
- Generation V Technology Ultra Low On-Resistance Dual N-Channel MOSFET Surface Mount Fully Avalanche RatedDocument7 pagesGeneration V Technology Ultra Low On-Resistance Dual N-Channel MOSFET Surface Mount Fully Avalanche Rateddayne81sNo ratings yet
- Sample Dipum2e Project StatementsDocument14 pagesSample Dipum2e Project Statementsreky_georgeNo ratings yet
- Test 1-Ces525 Question EndorsedDocument4 pagesTest 1-Ces525 Question EndorsedLAYLA SALIKIN CHE ROSMINNo ratings yet
- What Is Manufacturing Engineering?Document50 pagesWhat Is Manufacturing Engineering?mariappanNo ratings yet
- Benfenske: 6 Basics of Landscape PaintingDocument7 pagesBenfenske: 6 Basics of Landscape PaintingBruno SanromanNo ratings yet
- Customer Thank You - Flows - KlaviyoDocument1 pageCustomer Thank You - Flows - KlaviyoAdeps SmithsNo ratings yet
- NetWorker Cloning Integration GuideDocument100 pagesNetWorker Cloning Integration GuideMalyaj ShankerNo ratings yet
- Useful Celerra CommandsDocument5 pagesUseful Celerra CommandsKumar PallavNo ratings yet
- CT2 Coa KCS-302Document3 pagesCT2 Coa KCS-302nandini sharmaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Integration by Substitution: Activity OverviewDocument4 pagesCalculus Integration by Substitution: Activity Overviewrolando ojedaNo ratings yet
- Serverless Architectures The Evolution of Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesServerless Architectures The Evolution of Cloud ComputingciaoNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcome C Using Characters To Manipulate Data in ProgramsDocument10 pagesLearning Outcome C Using Characters To Manipulate Data in ProgramsKutyla AlfredoNo ratings yet
- ADP Connection For PayForce Requirements20303Document2 pagesADP Connection For PayForce Requirements20303claokerNo ratings yet
- Unit-I DBMSDocument29 pagesUnit-I DBMSMrs. Vasanthi MuniasamyNo ratings yet
- MarkDown BibleDocument7 pagesMarkDown BibleRAHAOUI MehdiNo ratings yet