Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes - PPT 1
Uploaded by
Darryl Calimlim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views22 pagesThe document discusses the characteristics of fishes. It describes the four primitive characters that all fishes retain: a streamlined body, vertical tail fin, gills for gas exchange, and a lateral line system with no ears. It then outlines the three traditional vertebrate classes that remain aquatic: bony fishes, cartilaginous fishes, and jawless fishes. Each class is well adapted for aquatic life.
Original Description:
Original Title
3a Fishes.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the characteristics of fishes. It describes the four primitive characters that all fishes retain: a streamlined body, vertical tail fin, gills for gas exchange, and a lateral line system with no ears. It then outlines the three traditional vertebrate classes that remain aquatic: bony fishes, cartilaginous fishes, and jawless fishes. Each class is well adapted for aquatic life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views22 pages02 Sept. 2014 Fishes - PPT 1
Uploaded by
Darryl CalimlimThe document discusses the characteristics of fishes. It describes the four primitive characters that all fishes retain: a streamlined body, vertical tail fin, gills for gas exchange, and a lateral line system with no ears. It then outlines the three traditional vertebrate classes that remain aquatic: bony fishes, cartilaginous fishes, and jawless fishes. Each class is well adapted for aquatic life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
FISHES
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 1
Fishes
• All fishes retain four
(4) primitive characters:
• Streamlined body
• Vertical tail fin
• Gills for gas exchange
• Lateral line system,
• No ears
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 2
Fishes
• Three traditional vertebrate classes
that remain aquatic.
Class Bony Fishes
Class Cartilaginous Fishes
Class Jawless Fishes
• All three classes well adapted to
aquatic environment.
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 3
Class Bony Fishes
• Also called “Ray-finned Fishes”
• ~30,000 species.
Majority of living vertebrate species.
Bony skeleton, well developed skull
Fins supported by cartilage or bony “rays”
and minute scales (=lepidotrichia)
• paired fins:
• pectoral, pelvic
• median fins:
• dorsal, anal, caudal
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 4
Bony Fishes
• Fins
• paired fins:
• pectoral, pelvic
• median fins:
• dorsal, anal, caudal
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 5
Bony Fishes
• Bony dermal scales
• covered by thin epidermis
• NOT homologous to reptilian scales.
• Operculum covers gills; one gill slit each side.
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 6
Bony Fishes
• Lungs, often modified to swim bladder.
• Examples:
• sturgeons
• gars
• catfish
• trout
• bass
• Northern pike
• American eel
• note paired fins, jaw, operculum
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 7
Class Cartilaginous Fishes
• 400 - 600 spp.
• Skeleton of cartilage, bone lost.
Fossil placoderms and jawless fishes had bone tissue,
prob. ancestral to both Cartilaginous & Bony fishes.
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 8
Class Cartilaginous Fishes
• Cartilaginous skull poorly developed, esp. dorsal
to brain
• Fins supported by cartilage or horn-like rays
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 9
Cartilaginous Fishes
• No ribs.
• No lungs or swim bladder.
• Separate gill slits, usually 5
• Placoid scales,
– tiny, tooth-like
• Enlarged at edge of mouth
teeth
– Homologous to teeth in all
other vertebrates.
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 10
Cartilaginous Fishes
• Sharks,
• Rays
specialized flattened
sharks
“wings” are pectoral fins
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 11
Development of Jaws
• All animals studied so far are “Jawed Vertebrates”
• Jaws developed from an anterior gill arch,
Allowed diverse diet
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 12
Class Jawless Fishes
• Survivors of earliest vertebrates
• No jaws,
can not close mouth
• No scales
• No paired fins, only median caudal fin
(continues dorsal & ventral to anus)
• Single median nostril on top of head
• Circular gill slits
7 or 12 pairs on sides of pharynx.
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 13
Jawless Fishes
• Hagfishes
tentacles around mouth
predators on worms,
mollusks
scavengers
20 spp. in 4 genera
• Lampreys
circular mouth, no
tentacles
filter feeders, or
external parasites of bony
fishes
30 spp. in 10 genera
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 14
Jawless Fishes
• Life cycle of sea lamprey
• Adult parasitic, feeding
stage
• Adults swim into small
freshwater streams to
breed
• Larvae live in sediment as
filter feeders up to seven
years
• Metamorphosis, migration
to lake or sea to become
parasitic adults
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 15
Jawless Fishes
• Sea lamprey in the Great Lakes
• Lake Ontario since end of last Ice Age, prevented from entering
upper lakes
• Welland canal
• Sea lamprey devastated commercial fishing
• Control
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 16
Overview of where we have been
• All animals studied to date belong to:
• Phylum Chordata
notochord
dorsal nerve cord
pharyngeal arches/clefts
• bear gills in fishes,
• modified to other structures in terrestrial animals
postanal tail
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 17
Review
• Subphylum Vertebrata
Notochord reduced, replaced by bony or
cartilaginous vertebrae
• Some notochord tissue usually remains
Pharyngeal arches bear gills
• or developed into other organs: hyoid bone, larynx
Liver
Pancreas
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 18
Review
• Subphylum Vertebrata
• 6 Classes:
• Jawless fishes
• Cartilaginous fishes
• Bony fishes
• Amphibians
• Reptiles including Birds
• Mammals
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 19
Invertebrate Chordates
• Two more subphyla of Chordata, lack
distinguishing characters of Vertebrates:
Subphylum Urochordata
• tunicates, sea squirts
Subphylum Cephalochordata
• lancelets, amphioxus
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 20
Subphylum Urochordata
• Adult is sessile
filter-feeder
• Larva shows all
characters of
Phylum Chordata
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 21
Subphylum Cephalochordata
• Adult and larva show
characters of Phylum
Chordata
• Live in holes in sandy or
muddy bottoms
• Ciliated pharynx pulls in
water
• Filtered water exits atriopore
• Food directed to intestine ,
feces disposed through anus
02 Sept. 2014 Fishes.ppt 22
You might also like
- Fish DiversityDocument23 pagesFish DiversityHadia KhadijaNo ratings yet
- The Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoDocument100 pagesThe Vertebrates: 500 Million Years AgoShawa DabaNo ratings yet
- SZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1Document5 pagesSZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1jenkionyangoNo ratings yet
- Visual Dictionary of Animals: English - French Visual Dictionaries, #2From EverandVisual Dictionary of Animals: English - French Visual Dictionaries, #2No ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Vertebrate DiversityDocument37 pagesChapter 25: Vertebrate DiversityNanta MulyaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Chapter 25 PPTDocument37 pages2014 Chapter 25 PPTAgus WahyudiNo ratings yet
- STI - Introduction To Feeding Ecology KvDW3Document24 pagesSTI - Introduction To Feeding Ecology KvDW3siwetwakuNo ratings yet
- Arthropods: Armored Achievers Crabs, Lobster, Shrimp, BarnaclesDocument23 pagesArthropods: Armored Achievers Crabs, Lobster, Shrimp, BarnaclesAilyn DecenaNo ratings yet
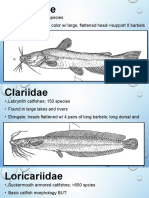
- Ictaluridae: 3 Groups: 1.lagre Species Sought by Angles 2.small, Secretive Madtom Species 3.blind Cave SpeciesDocument6 pagesIctaluridae: 3 Groups: 1.lagre Species Sought by Angles 2.small, Secretive Madtom Species 3.blind Cave SpeciesAllona ReasolNo ratings yet
- PISCESDocument27 pagesPISCESHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- 25 VertebratesDocument41 pages25 Vertebratespurple crocNo ratings yet
- Fish 1Document30 pagesFish 1Adnan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: by Allen Wilhelm and Zach AffolterDocument34 pagesAnimal Kingdom: by Allen Wilhelm and Zach AffolterZachNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - MolluscsDocument38 pagesChapter 7 - MolluscschristianNo ratings yet
- Btc. Herpetology-1-1-1-1Document73 pagesBtc. Herpetology-1-1-1-1Saimons VictorNo ratings yet
- Angler's Guide to Fishes of the Gulf of MexicoFrom EverandAngler's Guide to Fishes of the Gulf of MexicoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- FishDocument37 pagesFishlambatiNo ratings yet
- FISHDocument14 pagesFISHShania DavidsonNo ratings yet
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Document66 pages3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNo ratings yet
- Systematics The Scientific Study of The Kinds and Diversity ofDocument13 pagesSystematics The Scientific Study of The Kinds and Diversity ofjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note: Principles of Aquaculture B.V.SC., 4 Semester, 2071Document29 pagesLecture Note: Principles of Aquaculture B.V.SC., 4 Semester, 2071RabinNo ratings yet
- ZLY 121 Note - Early Vertebrates (Fish-Like Organisms)Document26 pagesZLY 121 Note - Early Vertebrates (Fish-Like Organisms)Femi AdeosunNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata-2Document68 pagesKingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata-2api-285078865No ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata: (Some Invertebrates and All Vertebrates)Document60 pagesPhylum Chordata: (Some Invertebrates and All Vertebrates)nightingale1995No ratings yet
- VertebratesDocument22 pagesVertebratesAnasNo ratings yet
- The Koi: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishFrom EverandThe Koi: An Owner's Guide to a Happy Healthy FishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Amphibians - E-LearningDocument83 pagesAmphibians - E-LearningJustyNo ratings yet
- Fish PowerpointDocument7 pagesFish PowerpointabahtohirNo ratings yet
- Seahorses as Pets. Seahorse Complete Owners Manual. Seahorse care, health, tank, costs and feeding.From EverandSeahorses as Pets. Seahorse Complete Owners Manual. Seahorse care, health, tank, costs and feeding.No ratings yet
- Lesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFDocument37 pagesLesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- 19 Chap 23 ChordataDocument41 pages19 Chap 23 ChordataFarman khanNo ratings yet
- Arthropods: Phylum ArthropodaDocument41 pagesArthropods: Phylum Arthropodarakhmawati SpiMsiNo ratings yet
- K-2 Teacher Guide - 0Document3 pagesK-2 Teacher Guide - 0Tran ThamNo ratings yet
- Osteichthyes PDFDocument50 pagesOsteichthyes PDFmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- FN&H 1Document12 pagesFN&H 1bszool006No ratings yet
- General Characteristics of FishesDocument29 pagesGeneral Characteristics of FishesSamad SheikhNo ratings yet
- LAS 34 Vertebrates & InvertebratesDocument27 pagesLAS 34 Vertebrates & InvertebratesAls Centre A OpolNo ratings yet
- Fishery ArtsDocument29 pagesFishery ArtsAngelica LoboNo ratings yet
- 9.filum MolluscaDocument55 pages9.filum MolluscaAditiya Nurrahma100% (1)
- The Rise of Fishes 500 Million Years of Evolution by John A. LongDocument236 pagesThe Rise of Fishes 500 Million Years of Evolution by John A. LongIstvan DanielNo ratings yet
- 4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairDocument5 pages4 - Jurnal FKH - Perubahan Bentuk Eritrosit - Journal - UnairEvi SintaNo ratings yet
- Fish GnathostomesDocument27 pagesFish GnathostomesIqra MujeebNo ratings yet
- Animals From Around The WorldDocument6 pagesAnimals From Around The Worldapi-26314086No ratings yet
- FinsDocument19 pagesFinsPuran BistaNo ratings yet
- TAS0938 JohnAntonyOspinoDiaz DEEPENDRA SITHCCC013Document17 pagesTAS0938 JohnAntonyOspinoDiaz DEEPENDRA SITHCCC013John Antony Ospino DiazNo ratings yet
- Nekton and Fisheries OceanographyDocument7 pagesNekton and Fisheries OceanographyrawrNo ratings yet
- Frogs The Amazing Frog Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Frog Facts, Photos, Quiz + MoreFrom EverandFrogs The Amazing Frog Book for Kids: 100+ Amazing Frog Facts, Photos, Quiz + MoreNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia: Phylum MolluscaDocument26 pagesKingdom Animalia: Phylum Molluscateszaiie selartaNo ratings yet
- Kaitu'u2018 Fish ColoringBook AmerSamoaDocument34 pagesKaitu'u2018 Fish ColoringBook AmerSamoaJasna RistićNo ratings yet
- AntarcticfoodweDocument7 pagesAntarcticfoodwePadmaja DodlaNo ratings yet
- TetrapodDocument83 pagesTetrapodyafetNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates & InvertebratesDocument55 pagesVertebrates & Invertebratescharis m. alejoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 in Your Prac Class This Week: Don't ForgetDocument14 pagesQuiz 4 in Your Prac Class This Week: Don't ForgetTimothy Au-yeungNo ratings yet
- Vertebrtes (Fishes)Document46 pagesVertebrtes (Fishes)zubariaiqbal61No ratings yet
- External Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaDocument9 pagesExternal Anatomy of Vertebrates Class AgnathaJerico YoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Repro SystemDocument19 pagesQuarter 3 Repro SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Simple MotorsDocument23 pagesSimple MotorsDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Individual Act. No. 1Document2 pagesIndividual Act. No. 1Darryl Calimlim100% (1)
- CerebrumDocument3 pagesCerebrumDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- 5 BiomoleculesDocument67 pages5 BiomoleculesDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument45 pagesChemical ReactionsDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- G10 - Cot1lp - Calimlim, Darryl O.Document12 pagesG10 - Cot1lp - Calimlim, Darryl O.Darryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Distribution of Earthquakes Volcanoes and MountainsDocument19 pagesLesson 1 Distribution of Earthquakes Volcanoes and MountainsDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Seafloor Spreading TheoryDocument28 pagesSeafloor Spreading TheoryDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Document2 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8Darryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Professional Education: Father of KNDRGRTNDocument4 pagesProfessional Education: Father of KNDRGRTNDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- DLL 19 Sept 23 2022Document4 pagesDLL 19 Sept 23 2022Darryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 SolidarityDocument21 pagesLesson 5 SolidarityDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument14 pagesVOLCANOESDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Kingdoms and Classes: ClassificationDocument37 pagesKingdoms and Classes: ClassificationDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesDivisions of The Nervous SystemDarryl CalimlimNo ratings yet
- OsteichthyesDocument49 pagesOsteichthyesmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- Listening Script 9Document10 pagesListening Script 9asachdeva17No ratings yet
- The Fishes: Vertebrate Success in WaterDocument55 pagesThe Fishes: Vertebrate Success in WaterGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Calcium and Phosphorus: (Trans) Lesson 4: Skeletal System BonesDocument12 pagesCalcium and Phosphorus: (Trans) Lesson 4: Skeletal System BonesDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Origin & Evolution of Otracoderms & Placoderms - JawsDocument17 pagesOrigin & Evolution of Otracoderms & Placoderms - JawsJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- Fish, Amphibians, and Reptiles: Can I Find One?Document34 pagesFish, Amphibians, and Reptiles: Can I Find One?Rehan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Describe The Taxonomical of Identification of Cultivable FishesDocument5 pagesDescribe The Taxonomical of Identification of Cultivable FishesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- AnkiDocument6 pagesAnkisachaNo ratings yet
- Marine FishesDocument57 pagesMarine FishesMD. SAKIB MUBALLIGNo ratings yet
- 013 Seafood Dishes PDFDocument38 pages013 Seafood Dishes PDFusama0% (2)
- 25 VertebratesDocument41 pages25 Vertebratespurple crocNo ratings yet
- 24 - FishesDocument83 pages24 - FishesKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- ZLY 412 - LIFE OF CHORDATE - (PISCES) University of IlorinDocument26 pagesZLY 412 - LIFE OF CHORDATE - (PISCES) University of IlorinGaniu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Both Animals and Fungi Are HeterotrophicDocument30 pagesBoth Animals and Fungi Are HeterotrophicLaura SampathNo ratings yet
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Module Abebe Getahun2Document157 pagesFisheries and Aquaculture Module Abebe Getahun2Zinabu Tunu Jillo100% (1)
- Fish TaxonomyDocument28 pagesFish TaxonomyAntonette OngNo ratings yet
- Fish Anatomy: Ventral Fin Vertical StabilizerDocument16 pagesFish Anatomy: Ventral Fin Vertical Stabilizerlinda_restiNo ratings yet
- Module For Ichthyology (Fish 1) : Instructional Materials and Development Office (IMDO)Document32 pagesModule For Ichthyology (Fish 1) : Instructional Materials and Development Office (IMDO)Leah Jane Arandia0% (1)
- Chapter 1: Introduction The Phylum Chordata: Big Four Protochordates HeadDocument14 pagesChapter 1: Introduction The Phylum Chordata: Big Four Protochordates HeadMacy MarianNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChordataDocument203 pagesIntroduction To ChordataYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates Chordata VertebratesDocument62 pagesInvertebrates Chordata VertebratesDao Ming SiNo ratings yet
- Animal Evolution and DiversityDocument20 pagesAnimal Evolution and DiversityRob YickNo ratings yet
- Woodward H.-Guide To The Collection of Fossil Fishes in The British Museum (1888) PDFDocument62 pagesWoodward H.-Guide To The Collection of Fossil Fishes in The British Museum (1888) PDFandrea.torelliNo ratings yet
- 129 2Document134 pages129 2Waqar HaiderNo ratings yet
- LESSON II: External Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsDocument32 pagesLESSON II: External Parts of Fish and Their FunctionsLourdicel De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Shark Traveling Trunk (Inglés) Autor Varios AutoresDocument72 pagesShark Traveling Trunk (Inglés) Autor Varios AutoresVerónicaNo ratings yet
- Anthropological Concepts in Clinical OrthodonticsDocument42 pagesAnthropological Concepts in Clinical Orthodonticsayesha rathore100% (1)
- Fusilier Fishes of The World-1988Document79 pagesFusilier Fishes of The World-1988Андрей БорщикNo ratings yet