Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Renal Calculi: Ahmednagar Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital Ahmednagar
Uploaded by
Suhas Ingale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views15 pagesOriginal Title
RENAL CALCULI.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views15 pagesRenal Calculi: Ahmednagar Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital Ahmednagar
Uploaded by
Suhas IngaleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Seminar On
RENAL CALCULI
Presented By –
Ms. Priyanka Sidankar
Guided By
Dr. Dapse
Ahmednagar Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital
Ahmednagar
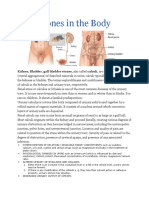
INTRODUCTION
O Renal stone or calculus or lithiasis is one of the most
common diseases of the urinary tract. It occurs more
frequently in men than in women and in whites than in
blacks. It is rare in children. It shows a familial
predisposition.
O Urinary calculus is a stone-like body
composed of urinary salts bound together by a colloid
matrix of organic materials. It consists of a nucleus
around which concentric layers of urinary salts are
deposited.
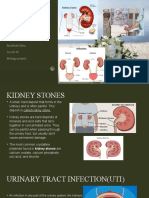
TYPES AND CAUSES
O Kidney stones form when there are more solid waste particles filtered
by the kidneys than there is urine to dissolve them. When these wastes
cannot dissolve, they stay in a solid form and are called kidney stones.
Different types of kidney stones form based on the type of waste
particle present.
O
O The most common type of kidney stone is made of calcium. Calcium is
the most abundant mineral found in the body. Specifically, kidney
stones are made of calcium oxalate, phosphate, or maleate. The amount
of calcium consumed in food doesn't affect the formation of kidney
stones, but the amount of oxalate (natural substance found in some
food items) in the diet does. Spinach, beets, nuts, and potato chips are
all foods high in oxalate, which can increase the development of
kidney stones.
Types & Causes
O Kidney stones can also be made of uric acid, and these are most commonly
found in men and in people with conditions like gout or who are undergoing
chemotherapy. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines,
which are substances found in certain foods. These usually form when
someone isn't getting enough fluids or they are losing too much fluid.
O
O Kidney stones made of struvite form due to an infection, most commonly a
urinary tract infection. Struvite is a substance composed of magnesium,
ammonium, and phosphate. Women are more at risk of this type than men.
O
O A rare form of kidney stone made of cystine occurs in people with the genetic
disorder cystinuria, where their kidneys excrete too much of certain amino
acids. Other types of stones can form as a side effect of certain medications.
AETIOLOGY
O (1) HYPEREXCRETION OF RELATIVELY INSOLUBLE
URINARY CONSTITUENTS such as oxalates, calcium, uric acid,
cystine and certain drugs (such as magnesium trisilicate in the treatment
of peptic ulcer).
O (2) PHYSIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN URINE such as Urinary
pH (which is influenced by diet and medicines), Colloid content,
Decreased concentration of crystalloids, Urinary magnesium/calcium
ratio.
O (3) ALTERED URINARY CRYSTALLOIDS AND COLLOIDS
O · Either there is an increase in the crystalloid level or a fall in the
colloid level, urinary stones may be formed.
O · If there is any modification of the colloids e. g. they lose their solvent
action or adhesive property, urinary stones may develop.
O (4) DECREASED URINARY OUTPUT OF CITRATE
O (5) VITAMIN A DEFICIENCY
O · The desquamated cells form nidus for stone formation. This is more applicable to
bladder stones.
O (6) URINARY INFECTION
O · Infection disturbs the colloid content of the urine, also causes abnormality in the
colloids (which may cause the crystalloid to be precipitated).
O · Infection also changes urinary pH and also causes increase in concentration of
crystalloids.
O (7) URINARY STASIS
O · It causes a shift of the pH of the urine to the alkaline side, predisposes urinary infection,
and allows the crystalloids to precipitate.
O (8) HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
O · Due to overproduction of parathormone the bones become decalcified and calcium
concentration in the urine is increased. This extra calcium may be deposited in the renal
tubules or in the pelvis to form renal calculus.
O (9) PROLONGED IMMOBILISATION
O (10) NIDUS OF STONE FORMATION
TYPES
O (I) PRIMARY STONES
O They appear in apparently healthy
urinary tract without any antecedent
inflammation.
O (a) Calcium oxalate
O (b) Uric acid calculi
O (c) Cystine calculi
O (d) Xanthine calculi
O (e) Indigo calculi
TYPES
O (II) SECONDARY STONES
O They are usually formed as the result
of inflammation.
O (a) Triple phosphate calculus
O (b) Mixed stones
INVESTIGATION
O (a) Blood examination
O (b) Urinalysis
O (c) Radiography
O · Straight X-ray
O · Excretory urogram
O (d) Ultrasonography
O (e) Computed tomography
O (f) Renal Scan
O (g) Cystoscopy
O (h) stone analysis
PREVENTION
O Ø Fluid intake should he high at all times. Fluids should be taken at
bed time so that nocturia will occur. This will prevent dehydration.
O Ø Avoidance of milk, cheese and great deal of calcium should be
advised. If renal function is satisfactory, sodium cellulose phosphate 5 g
T.D.S. with meals should be prescribed to reduce calcium absorption.
O Ø Urine should be kept acid all the time. Alkalies should be
prohibited or used in lesser quantities in those patients who are
suffering from peptic ulcer.
O Ø Vitamin D should be stopped or used in very low quantity.
O Ø Patients with hyperuricemia should avoid red meats, offal and fish,
which are rich in purines, and should receive treatment with allopurinol.
O Ø Eggs, meat and fish are high in sulphur containing proteins and
should be restricted in patients with cystinuria.
HOMOEOPATHIC REMEDIES
O 1. Berberis Vulgaris mother tincture- One of the best
Homeopathic remedies for kidney stones on the left side
O If the kidney stone or renal calculus is on the left side of
the body ie left kidney or left ureter, homeopathic
medicine Berberis Vulgaris is more than likely to remove
the stone. There is sore bruised pain in the kidney region.
There may also be numbness or stiffness in the kidney
region, more so in the morning. A characteristic sensation
is the bubbling sensation that is aggravated by stepping
or any other movement. The pain extends from the back
to the urinary bladder or the urethra.
O 2. Cantharis- One of the best Homeopathic medicines for
kidney stones or renal calculi with burning in urine
O In cases, where there is intense burning in the urethra while
passing urine, Cantharis is an excellent homeopathic
medicine. Sometimes the pain is described as cutting pain.
There is intense urging to urinate. Another characteristic
symptom of this remedy is the frequent urge to urinate. One
feels like passing urine just a few minutes after having
emptied the bladder. Only a little urine may pass when one
goes to urinate. Sometimes there is difficulty in passing urine
and is passed drop by drop. Haemorrhage with urine may
also be present.
O 3. Lycopodium- One of the best Homeopathic medicines for
kidney stones or renal calculi in the right kidney
O I have had great success in the treatment of right sided kidney
stones or renal calculi with Lycopodium. Of course one needs to
find other symptoms that match this great deep acting medicine.
The characteristic symptom is the presence of red sand in the
urine. There is intense pain in the back which gets better after
urination. The urge to urinate is more during the night. Often the
pain gets aggravated during the afternoon or in the evening.
Lycopodium is a deep acting homeopathic medicine and is often
used as a constitutional medicine. It has the power to stop the
formation of kidney stones in case the other symptoms of the
medicine match with the patient.
O 4. Sarsaparilla- One of the best Homeopathic
remedies for kidney stones with white sand in
urine
O While Lycopodium works very well in patients
that have red sand in urine, Sarsaparilla is much
more suited to patients that have white sediment
in urine. There is intense pain at the end of
urination. There is also burning and cutting in the
urethra after urination. Urine passes in a stream
that is thin and feeble.
THANK YOU....!!!
You might also like
- Oromia Pension FormDocument3 pagesOromia Pension FormAboma Mekonnen86% (7)
- Gallup-12-Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesGallup-12-Questions With Answersjeanette4hijadaNo ratings yet
- Scheme Samsung NT p29Document71 pagesScheme Samsung NT p29Ricardo Avidano100% (1)
- Stones in The BodyDocument14 pagesStones in The BodyMichaelNo ratings yet
- Rinary Tone Isease: Dr. Nurul Akbar, Sp.UDocument54 pagesRinary Tone Isease: Dr. Nurul Akbar, Sp.USiti NurdiantiNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument30 pagesRenal CalculiAnaiah Jaaziel KhanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Stone Disease Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument43 pagesUrinary Stone Disease Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentfldnazizNo ratings yet
- Types, Symptoms, and Treatment of Kidney StonesDocument6 pagesTypes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Kidney StonesKatte VillenasNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument8 pagesUrolithiasisvictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- NephrolithiasisDocument10 pagesNephrolithiasisGERSON RYANTONo ratings yet
- Adult Nursing 1 Renal Calculi 1Document25 pagesAdult Nursing 1 Renal Calculi 1ChonnetteAshlynKingNo ratings yet
- Aka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicDocument4 pagesAka: Urolithiasis, Kidney Stone, Renal Calculi, Ureteral Calculus, Renal ColicMarlin Nouelle Agpalza SacramedNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lithiasis 161269200418Document14 pagesUrinary Lithiasis 161269200418ተሣለነ ወልድNo ratings yet
- UROLITHIASISDocument25 pagesUROLITHIASISPaulo ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis Guide: Causes, Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment of Urinary CalculiDocument4 pagesUrolithiasis Guide: Causes, Signs, Diagnosis & Treatment of Urinary CalculiJoyce Ramos CadondonNo ratings yet
- Renal Calculi (Nephrolithiasis) Notes By:Justin Sir: EtiologyDocument8 pagesRenal Calculi (Nephrolithiasis) Notes By:Justin Sir: Etiologygeorgejhon1949No ratings yet
- Renal Stone and Renal FailureDocument14 pagesRenal Stone and Renal FailurereboNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014Document11 pagesNursing Care of Urolithiasis: Nursing Faculty Chatolic University of Widya Mandala Surabaya 2014victor zhefaNo ratings yet
- 31 - Renal Caliculi PDFDocument33 pages31 - Renal Caliculi PDFEITHAR OmarNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Urinary and Kidney Stones: On Completion of This Chapter, The Learner Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesManagement of Patients With Urinary and Kidney Stones: On Completion of This Chapter, The Learner Will Be Able TojhcacbszkjcnNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis Case ReportDocument14 pagesUrolithiasis Case ReportCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- Surgery for Urinary Lithiasis: Dr. Hazim's Guide to Kidney Stone Causes and TreatmentDocument8 pagesSurgery for Urinary Lithiasis: Dr. Hazim's Guide to Kidney Stone Causes and Treatmenthussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument1 pageUrolithiasisNovitaNo ratings yet
- Renalandurinarydisorders3 190508202142Document30 pagesRenalandurinarydisorders3 190508202142Jonah Rei BeatoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Group 7 Mt3DDocument12 pagesCase Analysis: Group 7 Mt3DAlfred ChowNo ratings yet
- Definition of NephrolithiasisDocument30 pagesDefinition of Nephrolithiasiszz_13No ratings yet
- Kidney StoneDocument24 pagesKidney StoneBula nagasaNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis Renal CalculiDocument19 pagesUrolithiasis Renal CalculiArva Glazel Defensor GallofinNo ratings yet
- Stone FormationDocument16 pagesStone Formationkulsum fatimaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Kidney StoneDocument36 pagesCase Study On Kidney Stonemanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- RENAL CALCULI ADN Group 2Document10 pagesRENAL CALCULI ADN Group 2Akhalia BrownNo ratings yet
- Renal Calculi SeminarDocument18 pagesRenal Calculi SeminarBeulah DasariNo ratings yet
- 1 Urinary StonesDocument11 pages1 Urinary StonesMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Meat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisDocument9 pagesMeat Pract 03 - NephrolithiasisKetty MupakwaNo ratings yet
- Renal Stone Types, Causes and SymptomsDocument29 pagesRenal Stone Types, Causes and Symptomsarim100% (1)
- Research AssignmentDocument3 pagesResearch AssignmentmhengdioNo ratings yet
- Renal StonesDocument12 pagesRenal StonesDamandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- UrolithasisDocument58 pagesUrolithasisHELL RISER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones AdultsDocument12 pagesKidney Stones AdultsMahesh Babu.KNo ratings yet
- NRSE 3540 Exam 2 Study GuideDocument12 pagesNRSE 3540 Exam 2 Study GuideNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- Cure Kidney Stone With Homoeopathy - by K.S. GopiDocument46 pagesCure Kidney Stone With Homoeopathy - by K.S. GopiHomeNo ratings yet
- Stones in KidneyDocument7 pagesStones in Kidneygujji111No ratings yet
- 51 Tips For Dealing With Kidney StonesDocument16 pages51 Tips For Dealing With Kidney StonesFeenyxNo ratings yet
- Kidney StonesDocument6 pagesKidney StonesChris ChanNo ratings yet
- KB 10Document5 pagesKB 10Reband AzadNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones: Causes and TreatmentDocument4 pagesKidney Stones: Causes and TreatmentVanessa ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis and UrolithiasisDocument4 pagesNephrolithiasis and UrolithiasisHaseeb RayhanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones: Risk Factors, Presentation, DiagnosisDocument11 pagesKidney Stones: Risk Factors, Presentation, DiagnosisQorry AmandaNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis - Modified LectureDocument35 pagesUrolithiasis - Modified Lecturemarina_shawkyNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument6 pagesRenal CalculiShiraishiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease GuideDocument6 pagesChronic Kidney Disease GuideKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Urinary Calculi Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentsDocument34 pagesUrinary Calculi Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentsOnkar SinghNo ratings yet
- LP NefrolitiasisDocument19 pagesLP NefrolitiasisSigit YuwanNo ratings yet
- Calcium Oxalate StonesDocument3 pagesCalcium Oxalate Stonesbagas rachmadiNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument24 pagesRenalshamiyahNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis: An Overview of Kidney Stone Types and PathogenesisDocument81 pagesNephrolithiasis: An Overview of Kidney Stone Types and PathogenesisOmar Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Dbu Collage of Medicine Suregery Lecter For Medical Students by Shitahun ADocument83 pagesDbu Collage of Medicine Suregery Lecter For Medical Students by Shitahun ASisay FentaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Urinary Stones, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Urinary Stones, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Renal Calculi IntroductionDocument4 pagesRenal Calculi IntroductionirysatherfinestNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Venus L. BactolDocument14 pagesPresented By: Venus L. BactolVenus BactolNo ratings yet
- Kidney Stones: Jenny ZhaDocument16 pagesKidney Stones: Jenny ZhaJenny ZhaNo ratings yet
- Some Disorders of Excretory SystemDocument5 pagesSome Disorders of Excretory SystemANUBHAB SAHANo ratings yet
- Wilson'S Disease: DefinitionDocument4 pagesWilson'S Disease: DefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Vulvular Ulcers: 1) Septic Ulcers: Caused byDocument3 pagesVulvular Ulcers: 1) Septic Ulcers: Caused bySuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Femoral Triangle Anatomy and ContentsDocument4 pagesFemoral Triangle Anatomy and ContentsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument2 pagesWhooping CoughSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Weil's DiseaseDocument2 pagesWeil's DiseaseSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Fibromyoma of UterusDocument5 pagesFibromyoma of UterusSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Female External Genital OrganDocument6 pagesFemale External Genital OrganSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ECZEMA: CAUSES, TYPES & HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENTDocument5 pagesECZEMA: CAUSES, TYPES & HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENTSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Definition: An Ectopic Pregnancy Is One in Which The Fertilized Ovum IsDocument4 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Definition: An Ectopic Pregnancy Is One in Which The Fertilized Ovum IsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis: DefinitionDocument5 pagesDermatitis: DefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIADocument2 pagesECLAMPSIASuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- FemurDocument8 pagesFemurSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Femoral Nerve It Is Marked by Joining The Following Two PointsDocument3 pagesFemoral Nerve It Is Marked by Joining The Following Two PointsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Chole Lithia SisDocument1 pageChole Lithia SisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Depression 1Document5 pagesDepression 1Suhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Eczema SDocument7 pagesEczema SSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Conium Maculatum: Common Name: Prover: FamilyDocument4 pagesConium Maculatum: Common Name: Prover: FamilySuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Calcarea CarbinicaDocument6 pagesCalcarea CarbinicaSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Constitution: Constitution: Definition: Human Being Recieves Some Features of Mind & Body From TheDocument4 pagesConstitution: Constitution: Definition: Human Being Recieves Some Features of Mind & Body From TheSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Causticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionDocument6 pagesCausticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Cadaveric SpasmDocument3 pagesCadaveric SpasmSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DisordersDocument33 pagesAutoimmune DisordersSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- BoraxDocument4 pagesBoraxSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Aurum MetallicumDocument6 pagesAurum MetallicumSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction - : Complete Repertory To The Homoeopathic Materia Medica On Disease of The Eyes BerridgeDocument6 pagesIntroduction - : Complete Repertory To The Homoeopathic Materia Medica On Disease of The Eyes BerridgeSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Carbo VegetabilisDocument6 pagesCarbo VegetabilisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- BELLADONNADocument2 pagesBELLADONNASuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ANAEMIASDocument15 pagesANAEMIASSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The NoseDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The NoseSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Volume 47, Issue 41, October 7, 2016Document48 pagesVolume 47, Issue 41, October 7, 2016BladeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Assessing Listening Skills: Exercise 1: Match The Six Types of Listenning (1-6) To The Examples (A-F)Document4 pagesChapter 4: Assessing Listening Skills: Exercise 1: Match The Six Types of Listenning (1-6) To The Examples (A-F)Ánh Lã NgọcNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Skim The Following Job Advertisements. Then, Scan The Text That Follows andDocument2 pagesInstructions: Skim The Following Job Advertisements. Then, Scan The Text That Follows andVasu WinNo ratings yet
- Cases in OBLIGATIONS AND CONTRACTSDocument17 pagesCases in OBLIGATIONS AND CONTRACTSRommell Esteban ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Social, Humanitarian and Cultural Committee (SOCHUM)Document58 pagesSocial, Humanitarian and Cultural Committee (SOCHUM)Klara TomsicNo ratings yet
- Dade Girls SoccerDocument1 pageDade Girls SoccerMiami HeraldNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear RegressionDocument30 pagesMultiple Linear RegressionJonesius Eden ManoppoNo ratings yet
- Controller Spec SheetDocument4 pagesController Spec SheetLuis JesusNo ratings yet
- Types of Guidance and CounsellingDocument3 pagesTypes of Guidance and CounsellingJyoti Bodade100% (1)
- англійська 11 final altered PDFDocument192 pagesанглійська 11 final altered PDFАнна НазаренкоNo ratings yet
- Supervision Assigment 1Document18 pagesSupervision Assigment 1Wendimu Nigusie100% (3)
- Bovee, Arens 150-170Document32 pagesBovee, Arens 150-170Mădălina-Cristiana PaţachiaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Companies UK 2009Document21 pagesChemicals Companies UK 2009Dharmendra B MistryNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ASP)Document3 pagesQuestion Bank (ASP)Gurleen BabraNo ratings yet
- UoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Document45 pagesUoGx ECEg4155 Chapter 7 8Abdi ExplainsNo ratings yet
- Mitra 2018Document4 pagesMitra 2018rahulNo ratings yet
- A Dose of Emptiness PDFDocument304 pagesA Dose of Emptiness PDFEliza KarpNo ratings yet
- English Reviewer Subject-Verb Agreement Exercise 1Document3 pagesEnglish Reviewer Subject-Verb Agreement Exercise 1Honeybel EmbeeNo ratings yet
- A Street Car Named Desire (Penguin)Document18 pagesA Street Car Named Desire (Penguin)the_perfectionistNo ratings yet
- A CHAIN OF THUNDER: A Novel of The Siege of Vicksburg by Jeff ShaaraDocument13 pagesA CHAIN OF THUNDER: A Novel of The Siege of Vicksburg by Jeff ShaaraRandom House Publishing Group20% (5)
- ch-1 Phy MEASUREMENT AND MOTIONDocument2 pagesch-1 Phy MEASUREMENT AND MOTIONRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Geoboards in The ClassroomDocument37 pagesGeoboards in The ClassroomDanielle VezinaNo ratings yet
- 2015-10-26 Plaintiff's Letter To Defendant Regarding Discovery (Flores V DOJ) (FOIA Lawsuit)Document25 pages2015-10-26 Plaintiff's Letter To Defendant Regarding Discovery (Flores V DOJ) (FOIA Lawsuit)Progress QueensNo ratings yet
- Here The Whole Time ExcerptDocument18 pagesHere The Whole Time ExcerptI Read YA100% (1)
- Lasallian Core ValuesDocument1 pageLasallian Core ValuesLindaRidzuanNo ratings yet
- Corporate LendingDocument2 pagesCorporate LendingrubaNo ratings yet
- 15 Aluminium Packaging PDFDocument4 pages15 Aluminium Packaging PDFAchmadda FebiyonoNo ratings yet