100% found this document useful (1 vote)
303 views24 pagesUnderstanding Parabolas in Pre-Calculus
The document provides information about parabolas including:
(1) Defining a parabola as a set of points equidistant from a fixed point (focus) and line (directrix);
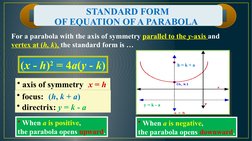
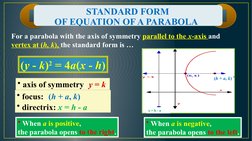
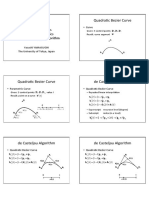
(2) Explaining the standard form equations of parabolas with the axis of symmetry parallel to the x- or y-axis;
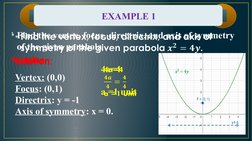
(3) Demonstrating how to graph parabolas using the vertex, focus, and directrix and solving practical problems involving parabolas.
Uploaded by
Jonel PasionaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
303 views24 pagesUnderstanding Parabolas in Pre-Calculus
The document provides information about parabolas including:
(1) Defining a parabola as a set of points equidistant from a fixed point (focus) and line (directrix);
(2) Explaining the standard form equations of parabolas with the axis of symmetry parallel to the x- or y-axis;
(3) Demonstrating how to graph parabolas using the vertex, focus, and directrix and solving practical problems involving parabolas.
Uploaded by
Jonel PasionaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Parabolas
- Learning Outcomes
- Definition of a Parabola
- Important Information about Parabolas
- Standard Form of Equation of a Parabola
- Graphing a Parabola in a Cartesian Plane
- Examples of Parabola Applications
- Situational Problem Involving Parabolas
- Applications of Parabolas
- References