Professional Documents
Culture Documents
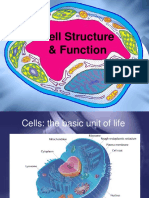
Cells
Cells
Uploaded by
Lalitha Rajesh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views34 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views34 pagesCells
Cells
Uploaded by
Lalitha RajeshCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 34
Cells
• Cells are the building blocks of life
• Cells take in raw materials to make new molecules
• Who named cells?
• Robert Hooke, English Scientist (1667)
How can we see cells?
• Microscope
• A camera can be fitted to these microscopes
• The pictures are called micrographs
• Light micrographs are color images
• Electron micrographs are black and white, can be artificially coloured
What is cell comprised of?
Cell wall
• Plant cell has cell wall
• Cell wall is made of cellulose
• It protects cell from injury and give fixed shape to the cell
• Cell wall is fully permeable
• Absent in animal cells
• Aerobic respiration happen
• Food energy
• Energy used for growth and reproduction
Ribosomes
• These are small round structures
• They are attached to ER or lie freely in the cytoplasm
• Functions:
• They are needed for synthesizing proteins
• They attach to ER and make proteins
• Ribosomes in cytoplasm make proteins that are used by cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
• Also called as Golgi body
• It is shaped like a disc
• It consists of a stack of flattened spaces surrounded by membranes
• Vesicles fuse with one side of Golgi body and gets pinched off from
opposite side
• Functions:
• It chemically modifies substances made by ER
• Stores and packages these substances in vesicles for secreting it out of
cells
Chloroplasts
• Chloroplasts are oval structures found in plant cells
• They contain a green pigment called chlorophyll
• Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis
es
Specialised cells, tissues, organs and systems
• There are many different types of cells
• The cells differ in size, shape and functions
• Human body have nerve cells, liver cells, skin cells, etc.
• Plants have xylem cells, phloem cells, root hair cells, etc.
• New cells are produced by cell division
• New cells produce or loose some structures to carry out certain
functions
• This process of development is called differentiation
Cell structure related to cell function
Tissues, organs and systems
T.S. of a leaf
T.S. of stem
1. Stomachgland tissue, muscular tissue, nervous tissue
• Nervous tissue detects presence of food in stomach
• Gland tissuesecrete enzymes to digest food
• Muscular tissue contracts to break food and mix with digestive
enzymes
• 2. Leaf mesophyll, xylem, phloem tissue
• Work together
• Xylemtransports water and mineral salts from roots to leaf
• Mesophyll carries out photosynthesis
• Phloem transports prepared food away from leaf
Organ system
• Comprise of several organs working together
• Animalsdigestive system, circulatory system, respiratory system,
transport system
• Plantsroot system and shoot system
Organism
• Various system make entire organism
You might also like
- Liquor Prices in PunjabDocument3 pagesLiquor Prices in Punjabishare digital100% (1)
- 1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Document9 pages1Q Reviewer General Biology 1Ruby May Regala100% (9)
- Shostakovich String Quartet 8 Verison MusescoreDocument35 pagesShostakovich String Quartet 8 Verison MusescoreJoão Corrêa100% (1)
- Art Nouveau and Art DecoDocument34 pagesArt Nouveau and Art Decoabuwafi122No ratings yet
- 9 IGCSE Cell Stucture & Function RevisionDocument35 pages9 IGCSE Cell Stucture & Function RevisionpixelhoboNo ratings yet
- Cell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceDocument48 pagesCell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Siva PrasadDocument28 pagesCells and Tissues: Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDocument62 pagesCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument43 pagesCell StructureKexinNo ratings yet
- Cells & Cell Organelles: Doing Life's WorkDocument36 pagesCells & Cell Organelles: Doing Life's WorkBB TestNo ratings yet
- Cell and TransportDocument77 pagesCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- Cell Class 9 Cbse Biology - CompleteDocument42 pagesCell Class 9 Cbse Biology - Completenayshajain63No ratings yet
- Class Lec. 3 & 4, Cell & Associated StudiesDocument25 pagesClass Lec. 3 & 4, Cell & Associated StudiesQasimNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument40 pagesThe CellNutnicha SiangpleangNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organelles: Patterns in NatureDocument39 pagesCells and Organelles: Patterns in NaturekdjskfsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Vicky BiologiaDocument2 pagesVicky BiologiaVictoria Menéndez SimonuttiNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument22 pagesCell StructureAbdullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Cells and OrganismDocument29 pagesCells and OrganismMohammed FazilNo ratings yet
- Life Is: CellularDocument48 pagesLife Is: Cellularekapratista26No ratings yet
- PPT - CellDocument75 pagesPPT - CellTarun BisenNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - Cell StructureDocument19 pagesClass 1 - Cell StructureSukanta SabatNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study NotesDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study Noteschedza FordNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESDocument19 pagesLower Secondary BIOLOGY NOTESmamboian01No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Notes - CellsDocument42 pagesChapter 7 Notes - CellsKyungmin OñaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & Functionuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- Class - Ix - Cell OrganellesDocument22 pagesClass - Ix - Cell OrganellesshamshadNo ratings yet
- CellDocument50 pagesCellmasuma.bvbvnird21No ratings yet
- EARTHSCI L7 Cell Theory and TimelineDocument31 pagesEARTHSCI L7 Cell Theory and Timeline2023200285No ratings yet
- Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument33 pagesCells: The Building Blocks of LifeLorenz Dadis AlonosNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Ferdinand V. Escalante, LPT Vvinzons Pilot High School Ppt3 7/01/19Document59 pagesCell Biology: Ferdinand V. Escalante, LPT Vvinzons Pilot High School Ppt3 7/01/19MaKenJi EscalanteNo ratings yet
- 638dba179fd2e400bf4af02f - ## - The Fundamental Unit of Life: Class Notes - SprintDocument45 pages638dba179fd2e400bf4af02f - ## - The Fundamental Unit of Life: Class Notes - SprintShivam RajNo ratings yet
- 1&2. Basic Unit of Life - CellsDocument59 pages1&2. Basic Unit of Life - CellsRaffyChuaNo ratings yet
- Cells - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument42 pagesCells - The Basic Unit of LifeAnum TariqNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument14 pagesCell Structure and OrganizationFatita XoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Introduction To Cells: Prepared By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, FwacnDocument55 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Introduction To Cells: Prepared By:-Mr. Saihou Sanneh RN, RM, BSN&RH, Fwacnflex gyNo ratings yet
- Pre Found BioDocument334 pagesPre Found BioAARYAN SURESH V. X DNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellcmizalpccfuNo ratings yet
- Imunoglobulinele Si RiuDocument25 pagesImunoglobulinele Si RiuAna-Maria ȘtefanNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifellamaNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Skeleton. Ms Mutembedza: The CellDocument24 pagesCells, Tissues and Skeleton. Ms Mutembedza: The Celltadiwanashe alvinNo ratings yet
- CELLS1ADRIANADISOR1Document3 pagesCELLS1ADRIANADISOR1A AbsbsbNo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument2 pagesWhat Is A CellJohn HughesNo ratings yet
- Botany Lesson 4Document21 pagesBotany Lesson 4hillaryNo ratings yet
- Bio 05Document24 pagesBio 05Usama Ehsan ButtNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell-Structure, Function, OrganisationDocument16 pages2.1 Cell-Structure, Function, OrganisationTHARISHINI A/P THANABALASINGAM A18KT0305No ratings yet
- Morphology and Physiology: CellsDocument57 pagesMorphology and Physiology: CellsDiana Mae Caigas SimbeNo ratings yet
- E18f338b CellsDocument42 pagesE18f338b CellsMohammad Abdullah KNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of AnimalsDocument27 pagesCell and Tissue of AnimalsUtami100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionDocument94 pagesLecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesChapter 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionsakurashahidNo ratings yet
- PPTs Cell OrganellesDocument40 pagesPPTs Cell OrganellesFatima KhalidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument55 pagesWeek 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument2 pagesThe Cellrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cytology: Cell Components and Cell CycleDocument21 pagesCytology: Cell Components and Cell CycleKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument37 pagesCell Structure & FunctionAtika Ayu KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument32 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsTheresa Filomena B BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function (JIGSAW)Document15 pagesCell Structure and Function (JIGSAW)Milimo JingsawNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument13 pagesPlant and Animal CellsMolan JenaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesLESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsSophia CamachoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chapter 3-Movement of SubstancesDocument37 pagesChapter 3-Movement of SubstancesLalitha RajeshNo ratings yet
- Unit III TabletsDocument89 pagesUnit III TabletsLalitha RajeshNo ratings yet
- Protein Diversity 1Document4 pagesProtein Diversity 1Lalitha RajeshNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure Similarity: Mlesnick@stanford - EduDocument8 pagesProtein Structure Similarity: Mlesnick@stanford - EdualsreshtyNo ratings yet
- viếtDocument5 pagesviếtNhư Dương Thị QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Pr118 20220130 MNL Yyz InboundDocument9 pagesPr118 20220130 MNL Yyz InboundIdentifyNo ratings yet
- Recruiting Made SimpleDocument14 pagesRecruiting Made SimpleUnderRecruited PrepsNo ratings yet
- Festivals and Theater Arts of China IIDocument4 pagesFestivals and Theater Arts of China IIlalaine misolesNo ratings yet
- FreelanderDocument51 pagesFreelandermrdavid070% (1)
- Evo - February 2017Document180 pagesEvo - February 2017Kiran KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Sensors and IoT 1Document39 pagesSensors and IoT 1Kani mozhiNo ratings yet
- Soc DetailsDocument11 pagesSoc DetailssreeNo ratings yet
- OCS AA Orientation PPT 2Document16 pagesOCS AA Orientation PPT 2Axel LaheraNo ratings yet
- 27 Ways To Boost Your Metabolism and Torch FatDocument3 pages27 Ways To Boost Your Metabolism and Torch Fathima_bindu_89No ratings yet
- Pioneer - Deh 1500r, Deh 1530r, Deh 1510 PDFDocument74 pagesPioneer - Deh 1500r, Deh 1530r, Deh 1510 PDFRichárd MucsiNo ratings yet
- Minor Project PresentationDocument17 pagesMinor Project PresentationC.E. Ishmeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Led TV: ServiceDocument43 pagesLed TV: ServicesunnyNo ratings yet
- Love of My LifeDocument8 pagesLove of My LifeDani PutraNo ratings yet
- Bollywood ProducersDocument10 pagesBollywood ProducersRathinder Rathi0% (1)
- PDF Photobooth Manual 2023Document24 pagesPDF Photobooth Manual 2023api-725597460No ratings yet
- Daloy Dancers MoaDocument4 pagesDaloy Dancers MoaDinarSantosNo ratings yet
- Pilihlah Salah Satu Jawaban Yang Paling Tepat! Questions 1 To 4. Questions 5 To 7. DirectionsDocument8 pagesPilihlah Salah Satu Jawaban Yang Paling Tepat! Questions 1 To 4. Questions 5 To 7. DirectionsAgung WidyonoNo ratings yet
- Bi ShumDocument7 pagesBi ShumBeshara KehdiNo ratings yet
- Renu Yarn List: Type Quality Brightness Country of Origin MOQDocument4 pagesRenu Yarn List: Type Quality Brightness Country of Origin MOQSharif0721No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Ingles B1+Document4 pagesQuiz 1 Ingles B1+juan vargasNo ratings yet
- 02.0 PP II IV Music Since 1900Document6 pages02.0 PP II IV Music Since 1900Marisa KwokNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.Document16 pagesSubject-Verb Agreement: Lesson No.mariamNo ratings yet
- General Instruction Manual HamiltonDocument100 pagesGeneral Instruction Manual HamiltonDonato AndriaNo ratings yet
- MUSIC Quarter 1 Module 1Document9 pagesMUSIC Quarter 1 Module 1eonaarwen camorroNo ratings yet
- Student's Book P. 24, Ex. 1Document5 pagesStudent's Book P. 24, Ex. 1RUSLAN DORONNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Kelas 7Document5 pagesSoal PTS Kelas 7Hj. ArisahNo ratings yet