Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 Applications and Case Studies
Uploaded by
HotdesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 Applications and Case Studies
Uploaded by
HotdesCopyright:
Available Formats
Applications
and Case Studies
Applications and Case Studies 2-1
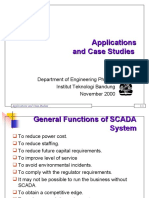
General Functions of SCADA System
To reduce power cost.
To reduce staffing.
To reduce future capital requirements.
To improve level of service
To avoid environmental incidents.
To comply with the regulator requirements.
It may not be possible to run the business without
SCADA.
To obtain a competitive edge.
To replace an existing aging system.
Applications and Case Studies 2-2
SCADA Performance Indicators
Immediate alarm of lost production.
Problem localization to minimize time to repair.
Remote alarm to avoid equipment damage and lost
production.
Automatic shutdown on detection of serious problem.
Identification of field operational problems.
Optimization of production.
Applications and Case Studies 2-3
SCADA & Corporate IT Integration
Applications and Case Studies 2-4
Changing Attitudes to Successful Oil/Gas
Field Automation
Acceptance of automation by field operations
personnel is essential to its success!
Remotely monitors the performance of oil/gas wells.
Making it possible to remotely control the flow of
oil/gas at each well.
Substantially reduces the number of necessary
operator visits to the well sites.
Changes the operator roles.
Safety and protection of the personnel & environment
are improved.
Applications and Case Studies 2-5
Oil/Gas Field Automation
Improving the flow balance for the field.
Automating well-test procedure increases production limits.
Production control suitable for the spot market.
Consistent oil/gas delivery.
Field operators are responsible for 50% more sites.
Saves operators from unnecessary travel to sites.
Reducing their costs for road clearing and maintenance.
Increases billing accuracy and reduces the billing cycle.
Enable to analyze well performance for maintenance scheduling
and for resource reserve analysis.
Applications and Case Studies 2-6
Application Areas of SCADA System
Well-head control, custody transfer, automatic well-
testing.
Production monitoring and control, gathering facilities,
enhanced oil recovery.
Tank farm/terminals – tanker loading/unloading,
fire/gas protection, alarms/shutdown/interlocking, etc.
Pipeline – pump or compressor control, surge control,
alarm and shutdown protection, metering, etc.
Applications and Case Studies 2-7
Applications and Case Studies 2-8
Gas Lift System Related Information
Oil volumes – produced
Oil volumes – inventory
Gas compressor status
Alarm summary (active)
Analog data summary
Well head status, pressure, oil/gas flow rate
Applications and Case Studies 2-9
Sucker Rod Pump Data Acquisition
Alarm Analog Signal
• Pump on/off • Rod load
• Power failure • Motor current
• RTU battery voltage • Well-head pressure
low • Beam-position
• Well-head pressure • Vibration level
• Vibration
Applications and Case Studies 2-10
Applications and Case Studies 2-11
Well-head Monitoring and Control
Well-head pressure.
Well-head temperature.
Well-head valve position.
Well throttling control.
Hydraulic Emergency Shut Down System.
Remote stop control.
Applications and Case Studies 2-12
Applications and Case Studies 2-13
Process Variables for Well-Head Management
1.Inlet gas lift pressure
2.Gas lift injection differential pressure
3.Casing-head pressure
4.Casing-head temperature
5.Tubing-head pressure
6.Tubing-head Temperature
7.Nozzle outlet differential pressure
8.Well outlet discharge pressure.
Applications and Case Studies 2-14
Leak Detection of Liquid Pipeline
Rate of change of pressure.
Rate of change of flow.
Static volume balance.
Transient modeling system.
Visual (Line walking, aerial surveillance, etc.)
Applications and Case Studies 2-15
Leak Detection of Gas Pipeline
Pressure drop detectors at block valves.
Rate of change of pressure at block valves.
Mass/volume balance.
Transient modeling system.
Acoustic.
Portable gas detectors, buried detector.
Applications and Case Studies 2-16
Integration Improvement of
Flow Computer – SCADA System
Makes a cost effective larger SCADA System.
Applicable communication protocols: Modbus or
Fieldbus.
OPC client/server may be the effective standard
interface.
Expensive, specialized host software packages will
no longer be required to retrieve and display flow
computer data.
Material/energy flow balance can be monitored
easily.
Applications and Case Studies 2-17
TANK FARM SYSTEM
Applications and Case Studies 2-18
EQUIPMENT MONITORING
SYSTEM
Functions:
Continuous Protection Against Catastrophic Failure.
Early Detection of Machine Abnormalities.
Accurate Diagnosis of Problem.
Assessment of Level of Severity.
Accurate Prediction of Future Machine Condition Versus
Time (including time to failure).
Generation of Feedback Information for Control of
Machine Operational Characteristics.
Equipment health monitoring and failure prediction has been a
key technology area for over 15 years.
Applications and Case Studies 2-19
SAFETY INSTRUMENTED SYSTEMS
A failure of some part of automation system may
cause injury to:
- member of public
- member of worker
- equipment
- environment
All process should be equipped with a safety
instrumented system.
Applications and Case Studies 2-20
Design Philosophy of Safety Systems
SHOULD BE ABLE TO OVERRIDE NORMAL
CONTROL SYSTEM.
SHOULD NOT SHARE COMPONENTS WITH
NORMAL CONTROLS.
SHOULD BE AS SIMPLE AS POSSIBLE.
Applications and Case Studies 2-21
MTU #1
MTU #2
Shutdown LC
Logic 202
RTU #2 RTU #1
LY
202
LS LS
203 203
Very complex safety system
Applications and Case Studies 2-22
RTU
S S
R
IAS
LS
203
INLET
SCRUBBER
SCADA system with local loop override
Applications and Case Studies 2-23
FROM RTU
S S
R R
IAS
PSL
FT
208
SCADA system with local shutdown
Applications and Case Studies 2-24
PIPELINE PROTECTION
SYSTEM
Applications and Case Studies 2-25
Valve with Satellite Communication Interface
for Pipeline Safety System
Applications and Case Studies 2-26
Applications and Case Studies 2-27
Well Details
Applications and Case Studies 2-28
Well Production Revenue
Applications and Case Studies 2-29
INTEGRATED SAFETY SYSTEM
Applications and Case Studies 2-30
GAS PLANT SCADA SYSTEM
Applications and Case Studies 2-31
SCADA System dependent AREAS
(Corporate Resource Planning)
Business Environment
Inventory Management
Process Modeling
Analysis, Control and Measurements
Planning
Applications and Case Studies 2-32
Corporate Resource Planning
Applications and Case Studies 2-33
Benefits of CRP
Increases Availability
Increases Productivity
Proactive Monitoring & Control
Continuous Process Improvement
Business Performance Monitoring & Control
Applications and Case Studies 2-34
Future Issues
Open, non-proprietary systems are expected to
prevail for remote monitoring and control.
The software should facilitate communications with all
types of field equipment as well as other computer
systems within the company.
A standard communication protocol is required to
support the standard configuration of future
automation system (Fieldbus protocol).
Web browser will be one user interface tools.
Field – Office data integration becomes a crucial
need.
Applications and Case Studies 2-35
Trends in SCADA and Internet
By 2001, projections show the Internet to have over
200 million hosts and 2 billion people interconnected.
More industries are executing more financial
transactions, online banking, and sharing vast
amounts of information.
More companies are developing a number of
software that can exploit the interconnectedness of
the Internet.
MMI allows a user the ability to connect to a SCADA
system from a remote site to control a process.
IT managers and system analysts should have a
greater understanding on potential misuses of this
communication medium.
Applications and Case Studies 2-36
You might also like
- Offshore Electrical Engineering ManualFrom EverandOffshore Electrical Engineering ManualRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- ScadaDocument13 pagesScadamdayyub50% (6)
- B2B Streamlined Bill Sample - Phone Bill Template FormDocument9 pagesB2B Streamlined Bill Sample - Phone Bill Template FormBrendon DrewNo ratings yet
- SCADAPack Product BrochureDocument16 pagesSCADAPack Product BrochureAqua Technology Group100% (1)
- Manage Critical Infrastructure Remotely with ClearSCADADocument32 pagesManage Critical Infrastructure Remotely with ClearSCADAKu LOa100% (1)
- 16 Samss 507 PDFDocument27 pages16 Samss 507 PDFnadeemNo ratings yet
- fSCADA SPECIFICATIONDocument66 pagesfSCADA SPECIFICATIONArunTomarNo ratings yet
- 23 Samss 030Document31 pages23 Samss 030nadeem shaikh100% (1)
- List of PowerGrid ManualsDocument3 pagesList of PowerGrid ManualsAnonymous 2l8XJIVNo ratings yet
- SCADA RTU Interface GuideDocument59 pagesSCADA RTU Interface Guideshivam.nagar100% (1)
- Saep 136 PDFDocument30 pagesSaep 136 PDFRami ElloumiNo ratings yet
- 23 Samss 030Document33 pages23 Samss 030siddiq alviNo ratings yet
- AR Table MappingDocument19 pagesAR Table MappingVenkatesan Ramamoorthy100% (2)
- SAEP-136 - Saudi Aramco Management of Electric Equipment Obsolescence Program PDFDocument26 pagesSAEP-136 - Saudi Aramco Management of Electric Equipment Obsolescence Program PDFQA QC100% (2)
- Sabp y 856Document38 pagesSabp y 856Hassan Mokhtar100% (1)
- 34 Samss 841Document68 pages34 Samss 841naruto256No ratings yet
- Subsea Production Control Systems: 1 ForewordDocument25 pagesSubsea Production Control Systems: 1 ForewordBSFNo ratings yet
- 1810 (W 100 CFi - W 120 CFi - W 130 CFi) PDFDocument1 page1810 (W 100 CFi - W 120 CFi - W 130 CFi) PDFadrianNo ratings yet
- 34 Samss 851Document82 pages34 Samss 851Eagle SpiritNo ratings yet
- 052KP 01 New 24" Gas Transmission Pipeline To Alkhalij Power Generation Station Control /ESD and Operating Philosophy 052KP 01 PHL IN 001, Rev.01Document26 pages052KP 01 New 24" Gas Transmission Pipeline To Alkhalij Power Generation Station Control /ESD and Operating Philosophy 052KP 01 PHL IN 001, Rev.01Jabel Oil Services Technical DPTNo ratings yet
- Norsok U-Cr-005 Subsea Production Control SystemsDocument25 pagesNorsok U-Cr-005 Subsea Production Control SystemscristianoclemNo ratings yet
- 34 Samss 846Document35 pages34 Samss 846naruto256No ratings yet
- IELTS Handbook 2007Document22 pagesIELTS Handbook 2007srikwaits4u100% (15)
- Working With Time - Lab Solutions Guide: Index Type Sourcetype Interesting FieldsDocument10 pagesWorking With Time - Lab Solutions Guide: Index Type Sourcetype Interesting FieldsPreet GadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Appendix G - TRS 09082B - Inverter System Interface To Plant Computer (KIT) Rev 0Document14 pagesAppendix G - TRS 09082B - Inverter System Interface To Plant Computer (KIT) Rev 0pthakur234No ratings yet
- Relay Testing and CommissioningDocument28 pagesRelay Testing and CommissioningKailash PanthaNo ratings yet
- CT-Analyzer - User Manual2 PDFDocument240 pagesCT-Analyzer - User Manual2 PDFHotdesNo ratings yet
- IMPLEMENTING SCADA FOR GAS PIPELINE MONITORINGDocument14 pagesIMPLEMENTING SCADA FOR GAS PIPELINE MONITORINGnwabukingzNo ratings yet
- SAES-J-505 Combustible Gase & H2S DetectionDocument16 pagesSAES-J-505 Combustible Gase & H2S DetectionanburishiNo ratings yet
- Overview of SCADA Application in Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesOverview of SCADA Application in Thermal Power PlantAndrew IvanusNo ratings yet
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Un Sistema Fotovoltaico Universidad de EcuadorDocument17 pagesDiseño de Un Sistema Fotovoltaico Universidad de EcuadorCamila gomez thomasNo ratings yet
- Illustration 7Document18 pagesIllustration 7Jeh UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Application& Case Studies of SCADADocument36 pagesApplication& Case Studies of SCADAFrenky IndraNo ratings yet
- SCADA SpecificationcDocument51 pagesSCADA Specificationcshiraz.ncecNo ratings yet
- Soiling Index Measurement Solution: Cr-Pvs1Document3 pagesSoiling Index Measurement Solution: Cr-Pvs1Francisco José Fontelles ObelenisNo ratings yet
- What is SCADA? Understanding Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionDocument7 pagesWhat is SCADA? Understanding Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionVinitaVartakNo ratings yet
- 34 Samss 846Document37 pages34 Samss 846Artur UzeevNo ratings yet
- Introduction to SCADA Systems FundamentalsDocument20 pagesIntroduction to SCADA Systems FundamentalsНурсултан БекзулдаNo ratings yet
- Materials System SpecificationDocument26 pagesMaterials System SpecificationArtur UzeevNo ratings yet
- SCADA Systems Made Simple: ExecutiveDocument13 pagesSCADA Systems Made Simple: ExecutivePrince Israel EboigbeNo ratings yet
- Section (4B) - SCS PDFDocument17 pagesSection (4B) - SCS PDFMohamed Ben mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Compiled Syllabus SEM VI IC MSE II 2017-1Document7 pagesCompiled Syllabus SEM VI IC MSE II 2017-1Shubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Gather meter information with SCADA technologyDocument3 pagesGather meter information with SCADA technologyYayan Putra AmanerNo ratings yet
- Real TimeDocument18 pagesReal Timeknisa amrNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Scada in Gas PipelineDocument50 pagesImplementation of Scada in Gas PipelinenwabukingzNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - Data Logger and SensorsDocument24 pagesCatalogue - Data Logger and SensorsShaileshnartiNo ratings yet
- Study and Analysis of Systems For Monitoring in Power SubstationsDocument3 pagesStudy and Analysis of Systems For Monitoring in Power SubstationsIsrael DanielNo ratings yet
- AptdDocument28 pagesAptdrudresh singhNo ratings yet
- Final Draft - 25 KV Traction SCADA - SPECIFICATION Final DraftDocument66 pagesFinal Draft - 25 KV Traction SCADA - SPECIFICATION Final Draftmott macNo ratings yet
- 411 2CDC110004C0210 (2015 Catalogue)Document424 pages411 2CDC110004C0210 (2015 Catalogue)Hisham MostafaNo ratings yet
- New Equipmentfor Transformers Online MonitoringDocument7 pagesNew Equipmentfor Transformers Online MonitoringalbertianusmNo ratings yet
- 723 Plus DigitalDocument4 pages723 Plus DigitalproesantNo ratings yet
- SE WhitePaper Letter SCADAOverview V005Document13 pagesSE WhitePaper Letter SCADAOverview V005aromero888No ratings yet
- Sco Ibms-Technical SpecificationDocument116 pagesSco Ibms-Technical SpecificationShameel PtNo ratings yet
- Monitoring underground ventilation with VUMA networkDocument6 pagesMonitoring underground ventilation with VUMA networkallison ramirezNo ratings yet
- KROHNE Gerhard Geiger Principles of Leak Detection 2012Document68 pagesKROHNE Gerhard Geiger Principles of Leak Detection 2012Alvaro Luiz SmiderleNo ratings yet
- Ge DGCM Field Rtu CatalogDocument12 pagesGe DGCM Field Rtu CatalogyogacruiseNo ratings yet
- DuctWatch IR Gas Detector Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesDuctWatch IR Gas Detector Instruction ManualGustavo silvaNo ratings yet
- My Top Skills:-: Short BioDocument7 pagesMy Top Skills:-: Short BiosanchayanNo ratings yet
- A SCADA System For On-Line Battery Early Faults PrecautionDocument5 pagesA SCADA System For On-Line Battery Early Faults Precautionabbas.fadhail5dNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Safety Functions - Shutdown SystemsDocument17 pagesLecture 5 Safety Functions - Shutdown SystemsLazarescu ElenaNo ratings yet
- Ready-To-Connect: Solutions For Smart Transformer SubstationsDocument6 pagesReady-To-Connect: Solutions For Smart Transformer SubstationsMallampati RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Improve The Reliability of Safety Instrumented SystemsDocument12 pagesImprove The Reliability of Safety Instrumented SystemsABRAHAM ESTRADANo ratings yet
- 5B. - Steam Turbine Control - Petrotech PDFDocument4 pages5B. - Steam Turbine Control - Petrotech PDFJaviStg1100% (1)
- Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)Document20 pagesRemote Terminal Unit (RTU)HotdesNo ratings yet
- Notice To IELTS Candidates: Rules and RegulationsDocument0 pagesNotice To IELTS Candidates: Rules and RegulationsEmin ÖksüzNo ratings yet
- Information For Candidates May 2006 PDFDocument8 pagesInformation For Candidates May 2006 PDFsamaloutNo ratings yet
- 01 Scada System OverviewDocument33 pages01 Scada System OverviewHotdesNo ratings yet
- Field Device Guide: Sensors, Actuators, and Measurement FundamentalsDocument26 pagesField Device Guide: Sensors, Actuators, and Measurement FundamentalsHotdesNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) GuideDocument42 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller (PLC) GuideHotdesNo ratings yet
- Singapore Downloads Student Handbook Exams IeltsDocument24 pagesSingapore Downloads Student Handbook Exams Ieltsuthomas_babuNo ratings yet
- Singapore Downloads Student Handbook Exams IeltsDocument24 pagesSingapore Downloads Student Handbook Exams Ieltsuthomas_babuNo ratings yet
- Shell Diala BrochureDocument2 pagesShell Diala BrochureFritz D P HasugianNo ratings yet
- EZCAD User ManuaL PDFDocument154 pagesEZCAD User ManuaL PDFHotdesNo ratings yet
- Shell Diala BrochureDocument2 pagesShell Diala BrochureFritz D P HasugianNo ratings yet
- EZCAD User ManuaL PDFDocument154 pagesEZCAD User ManuaL PDFHotdesNo ratings yet
- Shell Diala BrochureDocument2 pagesShell Diala BrochureFritz D P HasugianNo ratings yet
- Shell Diala BrochureDocument2 pagesShell Diala BrochureFritz D P HasugianNo ratings yet
- Shell Diala BrochureDocument2 pagesShell Diala BrochureFritz D P HasugianNo ratings yet
- A Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!Document16 pagesA Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!HotdesNo ratings yet
- Fluke Norma 5000 - User Guide PDFDocument76 pagesFluke Norma 5000 - User Guide PDFHotdesNo ratings yet
- Fluke Norma 5000 - Star Point AadpterDocument4 pagesFluke Norma 5000 - Star Point AadpterHotdesNo ratings yet
- Franeo 800 Brochure EnuDocument12 pagesFraneo 800 Brochure Enu159753No ratings yet
- CT Analyzer User ManualDocument154 pagesCT Analyzer User ManualRodrigoNo ratings yet
- A Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!Document16 pagesA Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!HotdesNo ratings yet
- A Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!Document16 pagesA Clear Path To Electrical Power Excellence!HotdesNo ratings yet
- AsiaSat 5G Interference Rejection Bandpass Filter Leaflet - 0Document1 pageAsiaSat 5G Interference Rejection Bandpass Filter Leaflet - 0hennrynsNo ratings yet
- Foxit Reader Quick Start GuideDocument41 pagesFoxit Reader Quick Start GuideMedina BekticNo ratings yet
- RQ2203056Document1 pageRQ2203056suryaNo ratings yet
- CC Unit4Document8 pagesCC Unit4Harsh RajputNo ratings yet
- Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules For Gigabit Ethernet ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules For Gigabit Ethernet ApplicationsCarlos Eduardo Flores SilvaNo ratings yet
- Stiffness by Definition and Direct Stiffness MethodsDocument56 pagesStiffness by Definition and Direct Stiffness MethodsSmartEngineerNo ratings yet
- MEITRACK - MVT600-User-Guide-V2.0 Sensor de Combustible ResistenciaDocument22 pagesMEITRACK - MVT600-User-Guide-V2.0 Sensor de Combustible ResistenciaManuel Flores CorderoNo ratings yet
- Payan: Axle Jack PAYAN P/N: 2012Document38 pagesPayan: Axle Jack PAYAN P/N: 2012gmailNo ratings yet
- Valtek Handwheels and Limit Stops (Flow Serve)Document12 pagesValtek Handwheels and Limit Stops (Flow Serve)dharmendrabholeNo ratings yet
- How+to+Cobiax+ +SL+ (Slim+Line) FINALDocument4 pagesHow+to+Cobiax+ +SL+ (Slim+Line) FINALmohamed turkiNo ratings yet
- Elec Cold Test - Smdb-Roof AtkinsDocument2 pagesElec Cold Test - Smdb-Roof AtkinsNabilBouabanaNo ratings yet
- ON Semiconductor Logic Date Code and Traceability MarkingDocument20 pagesON Semiconductor Logic Date Code and Traceability MarkingxuanquyvtNo ratings yet
- Using Event Log Using Syslog - Moxa Technologies Managed Ethernet Switch - Extender User Manual (Page 96)Document1 pageUsing Event Log Using Syslog - Moxa Technologies Managed Ethernet Switch - Extender User Manual (Page 96)Boudam BoudjemaNo ratings yet
- Final AssignmentDocument4 pagesFinal AssignmentAssignment HandleNo ratings yet
- E and C Data PrivacyDocument24 pagesE and C Data PrivacyTeofilus Evan RuselNo ratings yet
- Application Controls: Batch Processing Application AuditDocument34 pagesApplication Controls: Batch Processing Application AuditYanYan YumulNo ratings yet
- API 5L Grade X52 Pipe Chemical Composition and Mechanical PropertiesDocument1 pageAPI 5L Grade X52 Pipe Chemical Composition and Mechanical PropertiesMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 2Document7 pagesInformation Sheet 2Candice SumayangNo ratings yet
- PRPL - Assignment 2 - Software Analysis DocumentDocument4 pagesPRPL - Assignment 2 - Software Analysis DocumentDzaki HNo ratings yet
- Hearing Handicap Inventory - Screening Version (HHIE-S) : InstructionsDocument2 pagesHearing Handicap Inventory - Screening Version (HHIE-S) : InstructionsYERLY ISABEL PINOCHET CARMONANo ratings yet
- Urban Design Long HuaDocument5 pagesUrban Design Long HuaVuong AnhNo ratings yet
- Models - Heat.conical Dielectric ProbeDocument28 pagesModels - Heat.conical Dielectric ProbeDenis JaissonNo ratings yet
- Evaluacion Lin100final 2021Document2 pagesEvaluacion Lin100final 2021Lioney Ortiz TorrezNo ratings yet
- VAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services)~onlineapp02~150~8013TDocument1 pageVAHAN 4.0 (Citizen Services)~onlineapp02~150~8013Tmdneyaz9831No ratings yet