Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Computers Work
Uploaded by
maha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesHow Computers Work
Uploaded by
mahaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
How Computers Work
•The Four Basic Operations
•The Boot Process
•Hardware Components & Their Functions
•Differences in Portable Devices
The Four Basic Computer
Operations
Input – Getting data from the
outside world into the computer
Processing – Manipulating the
information
Output – Presenting data from the
computer to the outside
Storage – Efficiently and
inexpensively holding data for later
use.
Hardware to Provide
Four Functions
The Boot Process
1. The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
setup program loads and runs
2. The Power-On-Self-Test (POST) runs
3. The Operating System loads
4. System Configuration
5. System utilities load
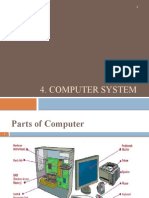
PC Components
Case
Processor
Power Supply
Motherboard
Memory
Hard Drives
Removable Media Drives
Video, Audio Functionality
Monitor
Mouse, Keyboard
The Processor
Single core vs. Dual core
Intel vs. AMD
Trade-off between price and speed
• The newest, fastest processors are
always overpriced. Best "bang for the
buck" is with the next step down.
System Memory
How much?
• Single core or dual core processor
• Types of applications
What kind?
• Types
SDRAM
DDR SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM
• Motherboard and CPU must support.
Choosing a Power Supply
Enough power for high class video
cards
Special connectors available for SATA
Hard Drives and PCI-E video cards
Motherboard may have a 20-pin or
24-pin main connector
Storage
Hard Drives
• How much, based on applications used
• What type (SATA or PATA)?
Optical Drives
• CD Burner, DVD-ROM, DVD Burner
(Single Layer or Dual Layer)
• How many? Two really make copying
disks easy.
Floppy Drive?
Hard Drives
IDE (ATA)
• EIDE – ATA2 aka Fast ATA
• ATA3 – Ultra ATA - Improved interface,
hard drives can report status
information to the MB.
• Two devices per channel (or cable)
SATA – Serial ATA
• One device per channel
SCSI – Many devices can be daisy-
chained.
Choosing a Motherboard
Supports the chosen Processor
Storage connectors ( PATA [aka
IDE], SATA150, SATA 3.0)
Memory type and amount
Built-ins (Video, Audio, LAN)
Graphic Card support (PCI-e, AGP)
PCI Expansion slots
RAID support
Factors in Choosing a Case
4 Form Factors
• Desktop
• Mid-Size Tower
• Full-Size Tower
• Little, Teeny, Tiny Cases (VSFF)
External and Internal Drive Bays
Front (Top) Panel Multi-Media
Connectors
Cooling System (can also add-on)
Display
Made up of two components
• Monitor
• Video card or circuitry
Monitors
CRT
• Cheaper
• Takes up more desktop real estate
• Can tire your eyes
Flat Panel
• More expensive
• Saves space
• Sharper Image
Video Cards
PCI
• Fits in a standard expansion slot
• General purpose video
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
• AGP 2X/4X, AGP 4X/8X, AGP Pro 4X/8X
PCI Express (PCIe)
• PCIe x1, PCIe x4, PCIe x8, PCIe x16
Replacing a Video Card
Make sure you don't buy too much
card for the monitor.
It doesn't matter if the original video
was built-in to the motherboard.
Installing a video card and loading
drivers "takes over" from the old
video.
Get a card the motherboard supports.
You might also like
- Hardware Components Inside a Computer CaseDocument33 pagesHardware Components Inside a Computer CaseRIZALDY CANTONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2Document44 pagesChapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2abinissri rajamuniswaranNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument41 pagesMotherboardjoseph rey ybiosaNo ratings yet
- Hardware and Software DependenciesDocument160 pagesHardware and Software DependenciesLuis SandovalNo ratings yet
- HardwareDocument152 pagesHardwareMegha SanghaviNo ratings yet
- Motherboard TerminologyDocument8 pagesMotherboard TerminologyshockkrewNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of System UnitDocument48 pagesParts and Function of System UnitIvy ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Motherboardppt41 160905161959Document39 pagesMotherboardppt41 160905161959Adrian Yan Yan DelaraNo ratings yet
- H55 HD - 20200717Document5 pagesH55 HD - 20200717Choy SkieNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Document82 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Pastor Roy Onyancha CyberNo ratings yet
- PC SupportDocument13 pagesPC Supportokuhlelolly6No ratings yet
- Simatic Ipc847d-En WebDocument5 pagesSimatic Ipc847d-En WebEmir DelicNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - IcsDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - Icsruzanna abu bakarNo ratings yet
- Expansion Cards and System Interfaces-SNDocument18 pagesExpansion Cards and System Interfaces-SNoceanmae.2020No ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument87 pagesComputer HardwareLutfiNo ratings yet
- ISA to USB: A Guide to Common Motherboard Components and TechnologiesDocument13 pagesISA to USB: A Guide to Common Motherboard Components and TechnologiessklatzNo ratings yet
- IT Chapter 1Document10 pagesIT Chapter 1Alice HovsepyanNo ratings yet
- (Black Meets Black: Older PC'S) : Notes On PC Assembly Make SAFETY Your First PriorityDocument8 pages(Black Meets Black: Older PC'S) : Notes On PC Assembly Make SAFETY Your First Prioritycyrene_20100% (2)
- PC Assembling WorkshopDocument51 pagesPC Assembling Workshopkitty8200No ratings yet
- Hardrives: Supporting Hard DrivesDocument84 pagesHardrives: Supporting Hard DrivesJehu MwangiNo ratings yet
- Major Hardware Components of A Computer SystemDocument21 pagesMajor Hardware Components of A Computer SystemgiameaeeNo ratings yet
- Toshiba ManualDocument9 pagesToshiba ManualMelissa FincherNo ratings yet
- Szakmai Angol HandoutDocument12 pagesSzakmai Angol Handoutnigger buflákNo ratings yet
- Selection Criteria MotherboardDocument12 pagesSelection Criteria Motherboardshahshehin4No ratings yet
- Total HardwareDocument7 pagesTotal HardwarejaieasathNo ratings yet
- 2 Computer Components With Their FunctionsDocument58 pages2 Computer Components With Their FunctionsPatrick L. RondinaNo ratings yet
- Chap8-10 - Storage Device Supporting Hard Drives 1Document30 pagesChap8-10 - Storage Device Supporting Hard Drives 1CoNnie AwangNo ratings yet
- Motherboard - 11Document58 pagesMotherboard - 11jmkcbeNo ratings yet
- Selecting Criteria of A MotherboardDocument3 pagesSelecting Criteria of A MotherboardDa NishNo ratings yet
- Hardware IntroDocument53 pagesHardware IntroParthasarathy SowrirajanNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- It User Fundamentals: Instructor: Sanam FayazDocument19 pagesIt User Fundamentals: Instructor: Sanam FayazAIJAZ ALI ABDUL LATIFNo ratings yet
- Intel® Desktop Board DQ45CBDocument4 pagesIntel® Desktop Board DQ45CBJosé Luis Neme PeredaNo ratings yet
- Technology ICT: By: Aljohn D. EsplanaDocument58 pagesTechnology ICT: By: Aljohn D. EsplanaAljohn Duran EsplanaNo ratings yet
- PC ComponentsDocument57 pagesPC ComponentsbronxkieNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument8 pagesMotherboardSudarsan JaganathanNo ratings yet
- PowerMac G4 MDD SpecsDocument2 pagesPowerMac G4 MDD Specslongcoat000No ratings yet
- M Oads, Processors, RamDocument32 pagesM Oads, Processors, RamMirhesen HuseynzadeNo ratings yet
- A+ Guide To Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5eDocument66 pagesA+ Guide To Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5edtyguhgyftrdfygNo ratings yet
- System UnitDocument24 pagesSystem UnitWindy Rose Gamao DeliquiñaNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Using The Correct Specifications As Specified in The Operating SystemDocument21 pagesOperating System: Using The Correct Specifications As Specified in The Operating SystemJason EchevariaNo ratings yet
- HARDWAREDocument45 pagesHARDWARES Naresh RaoNo ratings yet
- Bab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1Document30 pagesBab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1haniNo ratings yet
- satellite_A10-S129Document9 pagessatellite_A10-S129Cesar JakobyNo ratings yet
- PC ComponentsDocument56 pagesPC ComponentsAmit Bikram GogoiNo ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument39 pagesThe MotherboardGenevev Reyes100% (1)
- Lesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Document57 pagesLesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Kaye CorNo ratings yet
- Asrock - G41m-LeDocument2 pagesAsrock - G41m-Lenaveend111No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of A Computer System: Hardware & SoftwareDocument37 pagesFundamentals of A Computer System: Hardware & SoftwareJason SebastianNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- Parts of Motherboard: Reporters: Ebajo, Bonete, and SatorinasDocument11 pagesParts of Motherboard: Reporters: Ebajo, Bonete, and SatorinasHirai MomoNo ratings yet
- Technical Lesson 1Document63 pagesTechnical Lesson 1PAUL GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseDocument39 pagesMotherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseSachin DhamiNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing NC IIDocument21 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing NC IIShe Ma RieNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: - Chip SetDocument19 pagesMotherboard: - Chip SetAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- FM2A68M-DG3Document66 pagesFM2A68M-DG3kotoed163No ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- All About The: Present SimpleDocument13 pagesAll About The: Present SimplemahaNo ratings yet
- Cte I Computer PartsDocument30 pagesCte I Computer Partsapi-240796577No ratings yet
- Parts of a Computer System ExplainedDocument18 pagesParts of a Computer System ExplainedmahaNo ratings yet
- Cte I Computer PartsDocument30 pagesCte I Computer Partsapi-240796577No ratings yet
- How Computers WorkDocument16 pagesHow Computers WorkmahaNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Hardware and Software ExplainedDocument14 pagesBasic Computer Hardware and Software ExplainedMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet
- How Computers WorkDocument16 pagesHow Computers WorkmahaNo ratings yet
- Using Python On A Macintosh - Python 3.9.5 DocumentationDocument3 pagesUsing Python On A Macintosh - Python 3.9.5 DocumentationIoanna DiamNo ratings yet
- Expert Veri Ed, Online, Free.: Custom View Settings Question #65Document2 pagesExpert Veri Ed, Online, Free.: Custom View Settings Question #65KRISHANU DASNo ratings yet
- EchoLife EG8145V5 Datasheet 01 (R20C00, 7dB)Document3 pagesEchoLife EG8145V5 Datasheet 01 (R20C00, 7dB)nicolas poloNo ratings yet
- Debugging Guide: Enable InspectorDocument4 pagesDebugging Guide: Enable Inspectorvalle rajendranNo ratings yet
- SSS 1 3RD Term Lesson NoteDocument29 pagesSSS 1 3RD Term Lesson NoteOyinade AdeoluNo ratings yet
- OS LAbDocument5 pagesOS LAbUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Catalyst 9200 Series Switches StackWiseDocument24 pagesCisco Catalyst 9200 Series Switches StackWisehydro-testNo ratings yet
- Seminar3 enDocument7 pagesSeminar3 enandreiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Linux 6.3 Release NotesDocument9 pagesOracle Linux 6.3 Release NotesalkischrNo ratings yet
- Word Protection and SecurityDocument13 pagesWord Protection and Securityalamelulakshmi515No ratings yet
- Armstrong Web Services Listings 1-5Document12 pagesArmstrong Web Services Listings 1-5franco091084No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing MAKAUTDocument21 pagesCloud Computing MAKAUTDr-Rahul Kumar GhoshNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Student Lab Manual v5.0Document118 pagesCCNA 3 Student Lab Manual v5.0Nolton100% (3)
- RH-29 SB-007 Version 1Document7 pagesRH-29 SB-007 Version 1TepadoNo ratings yet
- g25s Snapdragon APQ8096 SBC Brochure R1.0Document2 pagesg25s Snapdragon APQ8096 SBC Brochure R1.0r.veenaaNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic & Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument39 pagesDigital Logic & Computer Organization and ArchitectureMamta BorleNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2003-2008 R2: Active Directory Disaster RecoveryDocument21 pagesWindows Server 2003-2008 R2: Active Directory Disaster RecoveryChakibMedchakibNo ratings yet
- BDSCP Module 08 MindmapDocument1 pageBDSCP Module 08 MindmappietropesNo ratings yet
- Standard Access-List Example On Cisco RouterDocument1 pageStandard Access-List Example On Cisco RouterSamuel HOUNGBEMENo ratings yet
- Book 1Document2 pagesBook 1asdasasdasdasddNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 2003 Setup (0001)Document2 pagesMicrosoft Office 2003 Setup (0001)Asif SadiqNo ratings yet
- Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) - 4.0 AC-A09 - Gi ConfigurationDocument33 pagesGateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) - 4.0 AC-A09 - Gi Configurationsling3100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Tools and Methodology For Citrix XenApp 5 EnvironmenDocument62 pagesTroubleshooting Tools and Methodology For Citrix XenApp 5 EnvironmenErin José Mendoza NadjarNo ratings yet
- M.2 SSD vs. SATA SSD? Which One Is The Best?Document3 pagesM.2 SSD vs. SATA SSD? Which One Is The Best?Sing PengNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise Lorejo JomreyDocument3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise Lorejo JomreyJimboy LorejoNo ratings yet
- Log File2Document19 pagesLog File2Sergio OchoaNo ratings yet
- SX3000sbc Maintenance GuideDocument15 pagesSX3000sbc Maintenance GuideRu AlexNo ratings yet
- ASUS F7SR Chapter 05-v1.0Document56 pagesASUS F7SR Chapter 05-v1.0Jeovando BatistaNo ratings yet
- Vision LF CNC Operacion y Manual PartesDocument180 pagesVision LF CNC Operacion y Manual Parteswilly1234512No ratings yet
- IBM Tivoli Monitoring Troubleshooting Guide V6.3 PDFDocument370 pagesIBM Tivoli Monitoring Troubleshooting Guide V6.3 PDFEricNo ratings yet