Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Waves and Spectrum: Wetlands
Uploaded by
Mikela Delatore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views26 pagesWetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. They serve important functions such as providing habitat for many species and improving water quality. Wetlands can be found on every continent except Antarctica and come in many forms, including swamps, marshes, and bogs. They are declining worldwide due to development and drainage for agriculture. Protection and restoration of remaining wetlands is important for biodiversity and environmental health.
Original Description:
Original Title
Electromagnetic_Spectrum
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. They serve important functions such as providing habitat for many species and improving water quality. Wetlands can be found on every continent except Antarctica and come in many forms, including swamps, marshes, and bogs. They are declining worldwide due to development and drainage for agriculture. Protection and restoration of remaining wetlands is important for biodiversity and environmental health.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views26 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Spectrum: Wetlands
Uploaded by
Mikela DelatoreWetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. They serve important functions such as providing habitat for many species and improving water quality. Wetlands can be found on every continent except Antarctica and come in many forms, including swamps, marshes, and bogs. They are declining worldwide due to development and drainage for agriculture. Protection and restoration of remaining wetlands is important for biodiversity and environmental health.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Wetlands
Jed P. Campomayor
Electromagnetic Waves and ALPINE SKI HOUSE
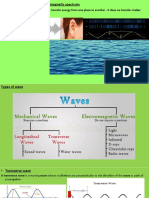
Electromagnetic Waves
• EM Waves are transverse
waves without a medium.
• They can travel through
empty space.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 2
Electromagnetic Waves
• They travel as vibrations in electrical and magnetic
fields.
• Have some magnetic and some electrical properties to
them.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 3
Electromagnetic Waves
• When an electric field changes, so does the magnetic
field.
• The changing magnetic field causes the electric field to
change.
• When one field vibrates, so does the other.
• The result will be an electromagnetic wave.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 4
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
• They transfer energy from one place to another.
• They are transverse waves.
• They can travel through vacuum.
• They travel through vacuum with the speed of light = 3.0
x 108 m/s.
• The speed is given by v = f (frequency) x λ (wavelength).
• They obey the laws of reflection and refraction.ALPINE SKI HOUSE 5
Wetlands
Jed P. Campomayor
Properties of Waves ALPINE SKI HOUSE
Parts of a Wave
Crest
Rest Position
Trough
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 7
Properties of Waves
• Amplitude
• Wavelength
• Frequency
• Period
• Speed
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 8
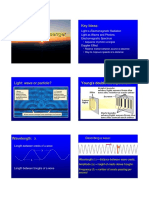
Properties of Waves
• Amplitude
• Refers to the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on
the medium from its rest position.
• The distance from the rest to crest.
• Wavelength
• The distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave.
• Measured in the direction of the wave.
• The longer the wavelength, lower the frequency and vice versa.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 9
Crest
Wavelength
Rest Position
Amplit
ude
Trough
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 10
Properties of Waves
• Frequency
• The number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given amount
of time.
• The SI unit for wave frequency is the hertz (Hz).
• Period
• The time it takes to complete one cycle.
• The SI unit for wave is seconds.
• The higher the frequency of a wave, the lower the wave period.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 11
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 12
Properties of Waves
• Speed
• The distance a wave travels in each amount of time,
such as the number of meters it travels per second.
• Speed = Wavelength x Frequency
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 13
Wetlands
Jed P. Campomayor
Electromagnetic Spectrum ALPINE SKI HOUSE
Electromagnetic Spectrum
• Name for the range of EM waves when placed in order of
increasing frequency.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 15
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 16
Radio Waves
• Have the longest wavelengths
and lowest frequencies of all
the EM waves.
• Transmits sound and pictures
in radio and television.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 17
Radio Waves
• Global Positioning
Systems (GPS) measure
the time it takes for a
radio wave to travel
form several satellites
to the receiver,
determining the
distance to each
satellite. ALPINE SKI HOUSE 18
Radio Waves
• Magnetic Resonance
Imaging (MRI) uses
short wave radio waves
with a magnet to create
an image.
• Used to look at organs
and structures of the
body.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 19
Microwaves
• Microwaves are radio waves of very short wavelengths. ( from
10-3m to 10-1m).
• Uses:
Satellite Communications Microwave Ovens Radar
Communications
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 20
Infrared Radiation
• Waves just beyond the red end of the visible light spectrum.
• Wavelengths range from 10-7m to 10-3m.
• Uses:
Remote Intruder Alarms Radiant Heater
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 21
Visible Light
• Visible light is part of the EM spectrum that the human eye can
detect.
• The various wavelength of light are classified by colors.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 22
Visible Light
• Uses:
Optical Fibres for medical and Lasers for medical and
Telecommunication uses. Telecommunication uses
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 23
Ultraviolet Radiation
• Wavelengths range from 10-8m to 10-7m.
• Main source is sunlight.
• Uses
Sunbeds Sterilization Flourescence Effect
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 24
X-Rays
• Wavelengths range from 10-13m to 10-8m.
• Uses
Medical/Dental Inspection Airport Security Radiation Therapy
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 25
Gamma rays
• Results of the decay of radioactive nuclei.
• Wavelengths range from 10-10m to less than 10-14m.
• Can cause serious damage when absorbed by living tissue.
• Causes mutations.
• Highest frequency = highest energy
• Uses include sterilization, radiation therapy.
ALPINE SKI HOUSE 26
You might also like
- 10 Electromagnetic RadiationDocument21 pages10 Electromagnetic Radiationapi-2352694010% (1)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum No PasswordDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum No Passwordprashanth_k443No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum No PasswordDocument23 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum No Passwordsachin_varshney_13No ratings yet
- Unit 2 EM WaveDocument5 pagesUnit 2 EM Wavevenkata karthikNo ratings yet
- Building Science 2A: Lecture 5: Light and The Electromagnetic Spectrum Dr. MN. Mthethwa and Lawrence OgunsanyaDocument24 pagesBuilding Science 2A: Lecture 5: Light and The Electromagnetic Spectrum Dr. MN. Mthethwa and Lawrence OgunsanyaLawrence OgunsanyaNo ratings yet
- Fa18 Awp Lec01Document41 pagesFa18 Awp Lec01Muhammad SohaibNo ratings yet
- sp19 Awp Lec01 PDFDocument41 pagessp19 Awp Lec01 PDFMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- ElectromagneticspectrumDocument19 pagesElectromagneticspectrumAbhishek gargNo ratings yet
- IR Training - LIDIDocument52 pagesIR Training - LIDInigussu temesganeNo ratings yet
- Assign. Physics (Autosaved)Document17 pagesAssign. Physics (Autosaved)zakir4532rtewNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: Udma, Kasaragod, Mob: 9961985448)Document4 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: Udma, Kasaragod, Mob: 9961985448)parveezNo ratings yet
- Interference Diffraction PolarizationDocument45 pagesInterference Diffraction Polarizationloharnikhil309No ratings yet
- PHY 102 EM Spectrum NewDocument31 pagesPHY 102 EM Spectrum NewTimothy PromiseNo ratings yet
- AWP Unit 5 Sky Wave PropagationDocument48 pagesAWP Unit 5 Sky Wave Propagationjenath1100% (1)
- 7.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument26 pages7.1 Electromagnetic Spectrumstevenlego85No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation: DR Judy JaysDocument29 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation: DR Judy Jaysfojide7482No ratings yet
- EM Waves and Spextrum PDFDocument45 pagesEM Waves and Spextrum PDFJoanna SeproNo ratings yet
- S2Q2 PhysicsDocument9 pagesS2Q2 PhysicsJillian BautistaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves Have Many Uses.: How Can You Make Radio Waves?Document8 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Have Many Uses.: How Can You Make Radio Waves?lauraNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic TheoryDocument41 pagesThe Electromagnetic TheorySabnahis Batongbuhay ExtensionNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerAphrodite UnderwoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Electromagnetic Spectrum & LightDocument71 pagesChapter 18: Electromagnetic Spectrum & Lightapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Inam BEET 4833 CHP4-TYPES OF ANTENNAS Wire Antennas Part ADocument13 pagesInam BEET 4833 CHP4-TYPES OF ANTENNAS Wire Antennas Part AKishen KunalanNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - UPHDocument20 pagesEM Waves - UPHSHIVA THAVANI100% (1)
- Transducer TutorialDocument33 pagesTransducer TutorialokosNo ratings yet
- Electromag DemoDocument28 pagesElectromag DemoJuliana NepembeNo ratings yet
- CEGE046 / GEOG3051 Principles & Practice of Remote Sensing (PPRS) 2: Radiation (I)Document42 pagesCEGE046 / GEOG3051 Principles & Practice of Remote Sensing (PPRS) 2: Radiation (I)MadanNo ratings yet
- Light and Illumination: Sunder Deep College of ArchitectureDocument21 pagesLight and Illumination: Sunder Deep College of ArchitectureRohit LodhiNo ratings yet
- Illumination 2k17Document88 pagesIllumination 2k17M. kashif karimNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum PowerpointDocument20 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum PowerpointCarl AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Waves PowerpointDocument68 pagesWaves PowerpointMadana R naikNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument59 pages8.2 Electromagnetic SpectrumHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- 2 Intro - To - Ultrasonics 03092013 OKDocument43 pages2 Intro - To - Ultrasonics 03092013 OKferyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesjosephrandalldeiparineNo ratings yet
- Magnetostriction and Applications of Ultrasonic Waves: 15Z204 - Materials ScienceDocument17 pagesMagnetostriction and Applications of Ultrasonic Waves: 15Z204 - Materials Sciencesumedha moharanaNo ratings yet
- Types of Antenna FinalDocument48 pagesTypes of Antenna Finaljohn dikoNo ratings yet
- Light The Messenger: Key IdeasDocument4 pagesLight The Messenger: Key IdeasabdishakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Electromagnetic Radiation: Section 1Document33 pagesChapter: Electromagnetic Radiation: Section 1Alex SmnNo ratings yet
- Technician License Course: Propagation and AntennasDocument52 pagesTechnician License Course: Propagation and AntennasGur PreetNo ratings yet
- Waves: Mechanical and ElectromagneticDocument56 pagesWaves: Mechanical and ElectromagneticJohn andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Hssreporter Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesHssreporter Electromagnetic Wavesamir suhailNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument37 pagesSpectrosKiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument44 pagesElectromagnetic Waves & The Electromagnetic SpectrumsdawsgsdgsNo ratings yet
- Christine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIDocument82 pagesChristine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIRyuji ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1.unit - 1 - Interference PPT - NewDocument60 pages1.unit - 1 - Interference PPT - Newprithviraj gavhaneNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document38 pagesPresentation 1Kiruthick DonNo ratings yet
- Wilhelm Röntgen: Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesWilhelm Röntgen: Electromagnetic WavesSophie LizardoNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Year 11 PhysicsDocument18 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum: Year 11 PhysicsStephen HillNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave PropagationDocument135 pagesRadio Wave PropagationMarvin IlaoNo ratings yet
- 08 U2T3 - Light and Sound 1.1Document28 pages08 U2T3 - Light and Sound 1.1Loh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- UltrasonicDocument51 pagesUltrasonicpreeti vermaNo ratings yet
- EM Waves - Science Q2Document5 pagesEM Waves - Science Q2Pard LouNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic WavesAchilles Toring100% (1)
- Module 2 - Radiative TransferDocument37 pagesModule 2 - Radiative TransferAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves: - Transverse Waves Without A Medium!Document29 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: - Transverse Waves Without A Medium!Rosli Ab GhaniNo ratings yet
- General Wave PropertiesDocument29 pagesGeneral Wave PropertiesEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument39 pagesElectromagnetic WavesHarjoot BrarNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) SpectrosDocument23 pagesFourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrospreeti VermaNo ratings yet
- Elec RAdDocument26 pagesElec RAdariba khanNo ratings yet
- DELATORE - STM25 - Physics 1 - Problem Set 2Document5 pagesDELATORE - STM25 - Physics 1 - Problem Set 2Mikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Delatore - STM25 - Physics - Da1Document5 pagesDelatore - STM25 - Physics - Da1Mikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Plate Boundaries & Processes and LandformsDocument25 pagesPlate Boundaries & Processes and LandformsMikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Reproductive System and Its DiseasesDocument45 pagesLESSON 1 - Reproductive System and Its DiseasesMikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Part 2Document24 pagesElectromagnetism Part 2Mikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Practical Uses of The EM SpectrumDocument33 pagesPractical Uses of The EM SpectrumMikela Delatore100% (1)
- LESSON 6 - Genetic DisordersDocument14 pagesLESSON 6 - Genetic DisordersMikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- Sequences: Arithmetic SequenceDocument9 pagesSequences: Arithmetic SequenceMikela DelatoreNo ratings yet
- 1756 Pa75 PDFDocument24 pages1756 Pa75 PDFDiogo FiaesNo ratings yet
- HVDC ControlDocument74 pagesHVDC ControlKaran SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 2 - A Student AnsDocument87 pages2 Chapter 2 - A Student Ansfullmetal Aesir100% (1)
- PI-200, PI-400, PI-750, XI41B: Models / ModelosDocument31 pagesPI-200, PI-400, PI-750, XI41B: Models / ModelosRolando MaasNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis & DesignDocument13 pagesStructural Analysis & DesignChamil Mahagamage100% (1)
- Ipho 1977Document9 pagesIpho 1977Lâm Văn Sa HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFDocument52 pagesElectrical Machines II Atif Iqbal PDFSantosh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- The Orbits of The Planets in Our Solar SystemDocument2 pagesThe Orbits of The Planets in Our Solar SystemMarko ŠtimacNo ratings yet
- Unit I Electrical Properties of Materials PDFDocument39 pagesUnit I Electrical Properties of Materials PDFSankar RamNo ratings yet
- Switchgear: Presented by Ajay Kumar Nikunj EMP NO-100326Document24 pagesSwitchgear: Presented by Ajay Kumar Nikunj EMP NO-100326SamNo ratings yet
- Electricity Tariff Rates of Nepal Electricity Authority: Category A: Domestic ConsumersDocument3 pagesElectricity Tariff Rates of Nepal Electricity Authority: Category A: Domestic Consumersmarab12No ratings yet
- OLTC UCG - VUCG 1ZSE 5492-105 Technical GuideDocument84 pagesOLTC UCG - VUCG 1ZSE 5492-105 Technical Guidearmandoa71565No ratings yet
- List of Worldwide AC Voltages and FrequenciesDocument3 pagesList of Worldwide AC Voltages and FrequencieskrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- STATCOM-ET - 10june-6aug ReportDocument37 pagesSTATCOM-ET - 10june-6aug ReportVamsi SwapnaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Science - CompleteDocument19 pagesGrade 10 - Science - CompleteLucille Gacutan AramburoNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Bridge: 2 Principle of OperationDocument3 pagesKelvin Bridge: 2 Principle of OperationDen AdenNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument46 pagesGeneral ScienceJosepino JosepinoNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion 5.48 MBDocument56 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion 5.48 MBLakshyaNo ratings yet
- 12.1 and 12.2 Quiz 1Document1 page12.1 and 12.2 Quiz 1DoraemonNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Pendulum Operated Water PumpDocument16 pagesDesign and Development of Pendulum Operated Water PumpMayugam Infotech100% (1)
- Padilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMDocument25 pagesPadilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMKurt Allen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Mgb2 SlideDocument25 pagesMgb2 SlideIntikhabNo ratings yet
- GrowlersDocument1 pageGrowlersZoran LazicNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Term 4 Control - Test - 2021 Exams 2Document11 pagesGR 11 Term 4 Control - Test - 2021 Exams 2PhilNo ratings yet
- Wind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Document13 pagesWind Code Evaluation Caribbean Islands (Caricom) : Name of Document: Caribbean Uniform Building Code (Cubic)Jayant LakhlaniNo ratings yet
- Question AnwerDocument23 pagesQuestion AnwerOnsoti NyaberaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Combined)Document16 pagesLab Manual Combined)Chris Thye0% (1)
- Clamp Meters Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsDocument4 pagesClamp Meters Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsTEUKUNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Vector Calculus - QBDocument2 pagesModule 3 - Vector Calculus - QBSaathvik BhatNo ratings yet
- Rotor Rso Reflectometer TYPE TDR100 and TDR100RBDocument38 pagesRotor Rso Reflectometer TYPE TDR100 and TDR100RBDevas ShuklaNo ratings yet