Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Posters
Uploaded by
api-480442981Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Posters
Uploaded by
api-480442981Copyright:
Available Formats
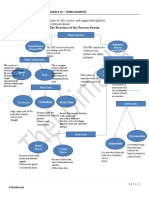
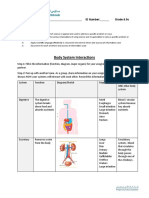
Nervous System Cardiovascular System Respiratory System Excretory and Digestive System
● Divided into two parts: Central Nervous System ● Excretory system is responsible for the
● The cardiovascular system uses a series of ● There are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: elimination of wastes produced by homeostasis
and Pheripheral System
veins and arteries to carry blood to and from the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of ● Digestive system breaks down food mechanically
● The central nervous system consisting of the brain
the heart respiration and absorbs its nutrients chemically
and spinal cord
● Transport of nutrients, oxygen, and hormones ● It transport air into the lungs and to facilitate the ● Can have stomach ache,
● The peripheral system which connects the central
to cells throughout the body and removal of diffusion of Oxygen into the bloodstream diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and
nervous system to the rest of the body.
metabolic wastes ● Rapid shallow breathing or loss of appetite
● It is responsible for coordinating
● It increased heart rate, make asthma symptoms worse
all of the body's activities
Anatomy palpitations, chest pain
Affected Body Systems Pathology Systemic consequences Signs & Symptoms
● Central Nervous System ● Pathology is the medical study of diagnosing ● Psychological therapy,,pharmacotherapy or a ● Overwhelming Fear
● Cardiovascular System disease combination of both ● Headaches
● Excretory and Digestive System ● The study of anxiety disorder shows that it is a ● The systematic consequence is to address negative ● Breathing problems
● Respiratory System normal response to stress thoughts and with the help of cognitive therapy ● Increased Blood Pressure
changing these negative thoughts into positive ● Muscle aches
Pathophysiology
Causes Risk factors
There is no single cause that will lead a person to develop an anxiety disorder but a number of risk factors may ● Trauma: If you endured abuse or trauma or witnessed traumatic events, you are more susceptible to developing an
contribute to it and make it more likely to occur. anxiety disorder at some point in life.
Life experiences such as traumatic events appear to trigger anxiety disorders in people who are already prone to anxiety. ● Illness: Serious illnesses can cause you to worry and significantly impact your thoughts about your future and if you
Inherited traits also can be a factor. Alternatively, anxiety can be caused from an underlying health issue. Examples will be ok or not
include: Heart disease, diabetes, thyroid problems, respiratory disorders, or even withdrawal from alcohol or other drugs. ● Stress: Big event or a buildup of smaller stressful situations may trigger anxiety like a death in the family, or
Also, it can be a side effect from certain medications. ongoing stress and worry about finances or work
● Personality: Certain personalities are more likely to develop an anxiety disorder.
● Other mental health disorders.: People with other mental health disorders, such as depression, often also have an
anxiety disorder.
Etiology ● Genetics: Anxiety disorders can run in families.
● Drugs or alcohol: Use, misuse or withdrawal can cause or worsen anxiety.
Upcoming treatments Current treatments: benefits and risks Prevention
Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation ● Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): ● A residential treatment center (RTC) ● Aware of life's stresses and understand your own ability to
○ A well-established, highly effective, and lasting treatment
(dTMS): stimulating larger, deeper brain ○ A live-in health care facility providing therapy for substance abuse,
cope with them
○ Patients learn skills during therapy sessions, but they must practice mental illness, or other behavioral problems.
regions; The procedure uses specialized repeatedly to see improvement. ● Diet and Exercise
○ Most centers focus on substance abuse
coils that reach about 4 centimeters ● Medication ● Complementary and alternative treatments: ● Symptoms management
beneath the surface of the skull ○ Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) ○ Stress and Relaxation techniques; Meditation; Yoga; Acupuncture
○ Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
● Getting adequate sleep
○ Can only reduce and help in long term
○ Benzodiazepines ● Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) ● Communication
○ Tricyclic Antidepressants ○ Creates a magnetic field to induce a small electric current in a specific ● Relaxation techniques
○ Ketamine part of the brain ● Interpersonal skills in dealing with difficult people and
○ Long-term use may require increased doses to achieve the same effect, ○ A safe, effective, and noninvasive option for people who have
situations or parenting skills training in dealing with your
Prevention &
which may lead to problems related to tolerance and dependence; depression that has not improved with medications
children. treatment
Canadian Mental Health Association. (2010). Social determinants of health. Retrieved from https://ontario.cmha.ca/provincial-policy/social-determinants/ Government of Canada. (July, 2016). Psychological health in the workplace. Retrieved from https://www.canada.ca/en/employment-social-development/services/health-safety/reports/psychological-health.html
Canada Mental Health Association. (October, 2004). Social anxiety disorder: An annual supplement to Health Reports.Statistics Canada Catalogue, no. 82-003. Retrieved from Government of Canada (May, 2017) Workplace Health and Well-being - Sample Workplace Health and Well-being Program Elements. Retrieved from
References https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/pub/11-008-x/2005001/article/7943 https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/psychosocial/sample_elements.html
eng.pdf?st=rHNnh2t4 Health quality Ontario. (n.d.). Evidence to Improve Care. Retrieved from http://www.hqontario.ca/Evidence-to-Improve-Care/Quality-Standards/View-all-Quality-Standards#back-to-top
Canada Mental Health Association. (n.d.). Mental illnesses in the workplace. Retrieved from https://ontario.cmha.ca/documents/mental-illnesses-in-the-workplace/ Team, T. M. (2017, December 12). Treatments for anxiety. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/info/anxiety/anxiety-treatments.php
Cherney, K. (July, 2018). Effects of anxiety on the body. Healthline. Timothy, J. L., (Ed). Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/anxiety/effects-on-body#1
You might also like
- Organ Systems of The Human Body and Their IntegrationDocument1 pageOrgan Systems of The Human Body and Their IntegrationUsman GulNo ratings yet
- New Anaphy Lesson 1Document5 pagesNew Anaphy Lesson 1Micaela BNo ratings yet
- Wearing On Her Nerves Case Study - Werner Williams Mccool Floyd AhmadDocument50 pagesWearing On Her Nerves Case Study - Werner Williams Mccool Floyd Ahmadapi-320365850100% (2)
- Science q3Document9 pagesScience q3Seiza MwaNo ratings yet
- 11 Human Body SystemDocument3 pages11 Human Body SystemCris EnriquezNo ratings yet
- 10 Biological Basis of Behavior PDFDocument6 pages10 Biological Basis of Behavior PDFHumanist English ManNo ratings yet
- Javan and Bryces Human Body ProjectDocument9 pagesJavan and Bryces Human Body Projectapi-347432027No ratings yet
- 2017-Physiology-and-Anatomy Massage TherapyDocument25 pages2017-Physiology-and-Anatomy Massage TherapyAlyssia SimpsonNo ratings yet
- CH 1 HomeostasisDocument67 pagesCH 1 Homeostasis360GamingNo ratings yet
- 6.ANS P2 Shortone DLVRDDocument11 pages6.ANS P2 Shortone DLVRDArooj FatimaNo ratings yet
- QIII LC-4 Part-IDocument23 pagesQIII LC-4 Part-Ifranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- SLM Q3 Week 1 1Document8 pagesSLM Q3 Week 1 1robilynestacionesherreraNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesNervous Systemflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- CouncellingDocument3 pagesCouncellingrumasadraunaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument1 pageNervous SystemhannaabededesNo ratings yet
- Intorduction To PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntorduction To PhysiologyHeswer RajNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument44 pagesNervous SystemSarathebestshowNo ratings yet
- (Template) Body SystemsDocument2 pages(Template) Body SystemsAri CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment of ClientDocument1 pagePhysical Assessment of ClientShaini ChristianNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemAdeelBaigNo ratings yet
- ANS RevisedDocument31 pagesANS Revisedr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Yellow and Blue Modern Art Festival Pamphlet Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesYellow and Blue Modern Art Festival Pamphlet Trifold BrochureMary Roselen MonayaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsDocument30 pagesWeek 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Oral Physioloy Lecture 3Document49 pagesOral Physioloy Lecture 3Habeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument73 pagesCoordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisThird WillowNo ratings yet
- Assignment Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesAssignment Autonomic Nervous Systemahmad72 raza72No ratings yet
- Ilhan Charyyarov Human Nerv SysDocument16 pagesIlhan Charyyarov Human Nerv SysIlhan CharyyarowNo ratings yet
- Ass Midterm PDFDocument2 pagesAss Midterm PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Bernadette Gonzales. ScienceDocument4 pagesBernadette Gonzales. ScienceBernadette GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 011 Organ SystemsDocument22 pages011 Organ SystemsAmada AvilésNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SysytemDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous SysytemDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- S1 Human Organism Part1Document4 pagesS1 Human Organism Part1cam broquelNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesThe Structure of The Nervous SystemThelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To PhysiologythrrishaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiDocument122 pagesAutonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Pathophysiology IntroductionDocument39 pagesPhysiology and Pathophysiology Introductionbasmala.a.zahranNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sports PhysiologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction of Sports PhysiologyRoop Inder ShergillNo ratings yet
- 2.when Glucose Level in The Blood Are High The Pancreas Releases Insulin Into The BloodDocument6 pages2.when Glucose Level in The Blood Are High The Pancreas Releases Insulin Into The BloodJoseph Dominic LagulosNo ratings yet
- Ccypi 3.0Document76 pagesCcypi 3.0GirishNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument26 pagesSistem Kontrol Saraf Dan Endokrin: Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology SummaryDocument1 pageHuman Physiology Summaryjoe_boyNo ratings yet
- Body System Interactions: Criterion DDocument4 pagesBody System Interactions: Criterion DReem AlmeheiriNo ratings yet
- LRPD EnglishDocument6 pagesLRPD EnglishKatherine Diaz CajaNo ratings yet
- BIO001Document2 pagesBIO001low keyNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 4Document1 pageHomeostasis 4api-535451383No ratings yet
- Q2WK1 - Body SystemsDocument27 pagesQ2WK1 - Body SystemsMary Grace GarrovilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HAP: by Dr. Mrs. Deepa K. Ingawale (Mandlik) Department of Pharmacology Poona College of Pharmacy, PuneDocument47 pagesIntroduction To HAP: by Dr. Mrs. Deepa K. Ingawale (Mandlik) Department of Pharmacology Poona College of Pharmacy, PunePrathi100% (2)
- Case Study Wearing On Her NervesDocument42 pagesCase Study Wearing On Her Nervesapi-460556390No ratings yet
- Body System WorksheetDocument2 pagesBody System Worksheetjoseluisvaldez012No ratings yet
- Sympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- NSDocument37 pagesNSVanessa Joy SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- ParasympatisDocument28 pagesParasympatisMeity ElvinaNo ratings yet
- Finished Evan Drew Human Body SystemDocument9 pagesFinished Evan Drew Human Body Systemapi-347109807No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- PPT, Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 pagesPPT, Anatomy and PhysiologyAzikah RohimahhNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Pathways of Communication: COMS 5483Document50 pagesNeuronal Pathways of Communication: COMS 5483Michael MerlinNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science Reviewer - PopoDocument10 pagesQ3 Science Reviewer - PopoXY PLAYZNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Case StudyDocument5 pagesMental Health Case Studyapi-480442981No ratings yet
- Environmental Plastic AssignmentDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Plastic Assignmentapi-480442981No ratings yet
- Global Health 2Document8 pagesGlobal Health 2api-480442981No ratings yet
- TechdataDocument16 pagesTechdataapi-480442981No ratings yet
- Suicide SlidesDocument11 pagesSuicide Slidesapi-480442981No ratings yet
- Digital Application Final 1Document11 pagesDigital Application Final 1api-480442981No ratings yet
- Stress Management InfographicDocument1 pageStress Management Infographicapi-480442981No ratings yet
- Slso Lst-Teacher Online LearningDocument5 pagesSlso Lst-Teacher Online Learningapi-467854007No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Clinical PsychologyDocument25 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Clinical PsychologyVibhasri GurjalNo ratings yet
- Ipa - Psych NursingDocument4 pagesIpa - Psych Nursingapi-402410951No ratings yet
- Autistic BurnoutDocument1 pageAutistic Burnoutmimi mosaNo ratings yet
- NLE Exam Drill 4 (Q Only 100)Document13 pagesNLE Exam Drill 4 (Q Only 100)Epaphras Joel Militar0% (1)
- Case Study AnalysisDocument3 pagesCase Study Analysisapi-241588828No ratings yet
- Conners 3Document4 pagesConners 3JamieMaza33% (3)
- Comprehensive Behavioral Intervention For TicsDocument2 pagesComprehensive Behavioral Intervention For TicsBettina SchettiniNo ratings yet
- Interact Handout 3Document2 pagesInteract Handout 3api-301978778No ratings yet
- Families in TransitionDocument6 pagesFamilies in TransitionDanielle SarnoNo ratings yet
- Anorexia Research Paper - Essay 1Document5 pagesAnorexia Research Paper - Essay 1api-329151535No ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Two Definitions of AbnormalityDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast Two Definitions of AbnormalityDipesh DIpeshNo ratings yet
- Geriatric AssessmentDocument51 pagesGeriatric AssessmentJustine Plaza100% (1)
- Discipline For Special Needs Students: Kerriebah Bedonie Briana Munoz Caitlynn MooreDocument15 pagesDiscipline For Special Needs Students: Kerriebah Bedonie Briana Munoz Caitlynn MooreKerriebah Alonzo HelenNo ratings yet
- Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule - Second Edition (ADOS-2)Document5 pagesAutism Diagnostic Observation Schedule - Second Edition (ADOS-2)shizuka samaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies (01-10)Document32 pagesCase Studies (01-10)Nomer EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Approach Counseling)Document2 pagesTheoretical Approach Counseling)vengattvd100% (3)
- Grp. 12 Learners With Difficulty With Self CareDocument10 pagesGrp. 12 Learners With Difficulty With Self CareSasa Arbilo100% (6)
- BEPbrochureDocument2 pagesBEPbrochureKeilah Leuschen WoodardNo ratings yet
- Prestasi Mahasiswa Program DoktoralDocument21 pagesPrestasi Mahasiswa Program Doktoraltasbihul anwarNo ratings yet
- Running Head: As Good As It Gets: An Analysis 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: As Good As It Gets: An Analysis 1Yassi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Emotional Painbody ChartDocument3 pagesEmotional Painbody ChartMilan Kolarevic100% (1)
- Substance Abuse and Psychiatric: Disordersin Prison InmatesDocument3 pagesSubstance Abuse and Psychiatric: Disordersin Prison InmatesNorberth Ioan OkrosNo ratings yet
- Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (Wfirs) InstructionsDocument3 pagesWeiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (Wfirs) InstructionsMariana LópezNo ratings yet
- Michigan Legislative Analysis - SCOPE OF PRACTICE FOR COUNSELORS 2019-HLA-4325-7B3BE14ADocument5 pagesMichigan Legislative Analysis - SCOPE OF PRACTICE FOR COUNSELORS 2019-HLA-4325-7B3BE14ABeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Who Is Minding The ChildrenDocument5 pagesWho Is Minding The Childrentheplatinumlife7364100% (1)
- 2015 Book PsychoeducationalAssessmentAnd PDFDocument371 pages2015 Book PsychoeducationalAssessmentAnd PDFCesar GaribaldiNo ratings yet
- ACT For Psychosis Recovery - A Practical Manual For Group-Based Interventions Using Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (PDFDrive)Document286 pagesACT For Psychosis Recovery - A Practical Manual For Group-Based Interventions Using Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (PDFDrive)Jhonatas Silva100% (2)
- Family Therapy Working With Challenging Family Dynamics in Effective MannerDocument13 pagesFamily Therapy Working With Challenging Family Dynamics in Effective MannerAdiba Sait100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Inclusive Education EssayDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 Inclusive Education Essayapi-369717940No ratings yet