Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System
Uploaded by
florie jane macayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System
Uploaded by
florie jane macayaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nervous System
The control system of the body
a complex network of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain and
spinal cord to various parts of the body.
It is considered as the body’s storage center of information and also the body’s control
system.
It is mainly responsible for controlling and coordinating all the organ systems by
sending messages from the brain through nerve signals.
It makes sure that all the parts of the body are working together efficiently.
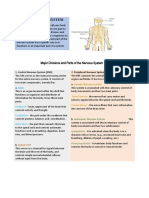
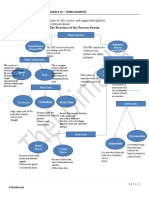
Major Divisions and Parts of the Nervous System
I.Central Nervous System (CNS) serves
as the main processing center
of the nervous system. It
consists of two main
components, namely;
A. Brain is an organ located within the skull that functions as organizer and
distributor of information for the body. It has three main parts:
1. Cerebrum is the large, upper part of the brain that controls activity and
thought.
2. Cerebellum is the part under the cerebrum that controls posture, balance,
and coordination.
3. Brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls automatic
functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure.
B. Spinal cord serves as a channel for signal between the brain and the majority of the body parts, and controls some simple
musculoskeletal reflexes even without the processing of the brain.
II. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects the central nervous system to the organs and limbs.
It has two main divisions:
A. Somatic Nervous System is associated with the voluntary control of body movements and has two main parts:
1. Spinal Nerves carry motor and sensory signals between the spinal cord and the body.
2. Cranial Nerves are nerve fibers that carry information into and out of the brain stem.
B. Autonomic Nervous System is associated with the involuntary control of body movements and has two subdivisions:
1. Sympathetic Nervous System is activated when the body is in a dynamic role or stress. (e.g., increased heart rate and
breathing, dilation of pupil, sweating)
2. Parasympathetic Nervous System maintains body functions and restores the body to normal or relaxed mode.
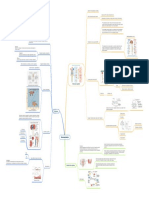
How Nervous System coordinates and regulates
feedback mechanisms to maintain
homeostasis?
The nervous system provides quick
responses in maintaining homeostasis
Homeostasis is maintained in the body by
regulating the body temperature, blood
pressure, pH, and glucose concentration.
The nervous system and endocrine system
are working together to maintain body’s
homeostasis. Homeostasis is the state
reached when each part of the body
functions in equilibrium with other parts.
This is attained through the regulation of
the bodily functions by the endocrine and
nervous systems. Feedback mechanisms
are used by most of body systems to
maintain homeostasis. When the brain
receives messages from the body about
an internal change in one of its systems, it
works to restore the system to its normal
state. The hypothalamus affects the
pituitary gland, also known as the master
gland, to secrete the right hormones. The
hormones will flow with the blood and
reach the specific organs to restore the
normal state of the body or homeostasis.
Molecules of hormones are received by
receptors of cells making this event a neuroendocrine coordination. The nerves that are found all over the body allows the
nervous system to monitor homeostasis of the body. While the endocrine system helps by secreting hormones into the
bloodstream and send them to specific organs. The levels of hormones in the body are controlled by feedback. It is important
that the amount of hormones in our body is kept at the right level. To achieve homeostasis, the nervous and endocrine systems
work with each other to maintain a normal range of many processes and substances in the body such as: • Temperature of the
body • Amount of water in the body • Amount of metabolic wastes in the cell • Blood calcium leve
You might also like
- An Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 pagesAn Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyZaid AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Mastering Mindfulness-Based EQ LeadershipDocument212 pagesMastering Mindfulness-Based EQ LeadershipJerry Forbes C100% (1)
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- B Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Document17 pagesB Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 2 (Week 3)Daisy Soriano PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Old Ideas: The Specificity Theory of PainDocument8 pagesOld Ideas: The Specificity Theory of Paingeloss23150% (2)
- Nursing Health Assessment and Pain (30 Items)Document17 pagesNursing Health Assessment and Pain (30 Items)Ik-ik MiralNo ratings yet
- Nds Lower Quarter Course Manual PDFDocument105 pagesNds Lower Quarter Course Manual PDFMskola Karlovac100% (1)
- NeuroSensory ExamsDocument26 pagesNeuroSensory Examsquidditch07100% (1)
- S.C.E.N.A.R.: Self-Controlled Energetic Neuro-Adaptive RegulatorDocument41 pagesS.C.E.N.A.R.: Self-Controlled Energetic Neuro-Adaptive RegulatorHoracio CastroNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 3: Earthquake Waves: ScienceDocument27 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 3: Earthquake Waves: ScienceCharity Bantigue100% (4)
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument53 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiKholid DamriNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3 Lesson 3Document3 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3 Lesson 3Hania PindatonNo ratings yet
- Science q3Document9 pagesScience q3Seiza MwaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Notes in Science 10: Unit 3Document3 pagesBiology: Notes in Science 10: Unit 3John Glenn E. L.No ratings yet
- Nervous Endocrine SystemsDocument44 pagesNervous Endocrine SystemsChristine Pinton BahianNo ratings yet
- Nervous System POWERPOINTDocument15 pagesNervous System POWERPOINTZhen Obelidor100% (1)
- Nervous System Science 10Document14 pagesNervous System Science 10Navy BunzzNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument65 pagesNervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisJoseph yvannNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 6 Reviewer For Science (3Q)Document19 pagesLesson 1 - 6 Reviewer For Science (3Q)maryayahdeleonNo ratings yet
- Case Study Wearing On Her NervesDocument42 pagesCase Study Wearing On Her Nervesapi-460556390No ratings yet
- SLM Q3 Week 1 1Document8 pagesSLM Q3 Week 1 1robilynestacionesherreraNo ratings yet
- Science Nervous SystemDocument1 pageScience Nervous SystemVirny Uno AceNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Recovery Lesson 1Document44 pagesLesson Title: Recovery Lesson 1Benjamin WatsonNo ratings yet
- E1.1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesE1.1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyhzntrpNo ratings yet
- Major Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellDocument6 pagesMajor Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellAllysa Mae MoraNo ratings yet
- QIII LC-4 Part-IDocument23 pagesQIII LC-4 Part-Ifranzpersonal810No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous SystemJoana RoxasNo ratings yet
- Wearing On Her Nerves Case Study - Werner Williams Mccool Floyd AhmadDocument50 pagesWearing On Her Nerves Case Study - Werner Williams Mccool Floyd Ahmadapi-320365850100% (2)
- The Structure of The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesThe Structure of The Nervous SystemThelNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science Reviewer - PopoDocument10 pagesQ3 Science Reviewer - PopoXY PLAYZNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesNervous System Flyer PDFKawaii GlamourNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Module 3Document32 pagesQuarter 3 Module 3Herbert DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 10 Third QuarterDocument9 pagesReviewer Science 10 Third QuarterKim TzukiNo ratings yet
- At The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninDocument8 pagesAt The Base of The Brain Stimulates Growth and Controls The Functions of Other Glands Below The Voice Box Thyroxin, CalcitoninAubrey Jen MañasNo ratings yet
- 10 Biological Basis of Behavior PDFDocument6 pages10 Biological Basis of Behavior PDFHumanist English ManNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Handout - Nervous and EndocrineDocument2 pagesScience 10 Handout - Nervous and EndocrineAngelica MartinNo ratings yet
- 11 Functional Organization of Nervous TissueDocument37 pages11 Functional Organization of Nervous TissueEdinaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Parts & Functions)Document30 pagesNervous System (Parts & Functions)Sharlene Cecil PagoboNo ratings yet
- CouncellingDocument3 pagesCouncellingrumasadraunaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 NeurologicalProcessesDocument3 pagesUnit3 NeurologicalProcessesMay Anne BañagaNo ratings yet
- Module - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of BehaviorDocument11 pagesModule - Wk5&6 - The Biological Foundation of Behavioraudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- Introduction Ana and PhysioDocument54 pagesIntroduction Ana and PhysioAffie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesNervous Systembarrymapandi0% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument42 pagesNervous Systembrandonbrandino624No ratings yet
- Bio Pse U1 L3Document16 pagesBio Pse U1 L3AlalafsaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Systemanaliane azucenaNo ratings yet
- WK 2 Handout 3 - Parts of The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesWK 2 Handout 3 - Parts of The Nervous SystemLaura HullNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument6 pagesReviewer For Anatomy and Physiology Lectureden mNo ratings yet
- Bio HHW Tip ChartDocument6 pagesBio HHW Tip ChartasdfghNo ratings yet
- Gayu OhotosDocument20 pagesGayu OhotosasdfghNo ratings yet
- Wepik Maintaining Balance The Role of Homeostasis in The Nervous System 20240226024838MLkDDocument29 pagesWepik Maintaining Balance The Role of Homeostasis in The Nervous System 20240226024838MLkDIel FedericoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesThe Nervous SystemCathy C DNo ratings yet
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADocument5 pagesNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Document15 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Zahra Alexä DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SytemDocument24 pagesNervous SytemShaine MalunjaoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Science 10 Activity 1Document2 pagesQuarter 3 Science 10 Activity 1Czarina GrandeNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesActivity 5 Nervous SystemKolynNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 4Document1 pageHomeostasis 4api-535451383No ratings yet
- Activity-Sheet 7-MC Bio 4-ArcigaDocument2 pagesActivity-Sheet 7-MC Bio 4-ArcigaArciga, Sheena Mae BienNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument27 pagesCoordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve Homeostasiskate corveraNo ratings yet
- SCIE 10-Q3-Negative and Positive Fedback MechanismDocument25 pagesSCIE 10-Q3-Negative and Positive Fedback MechanismJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Science Pointers To ReviewDocument8 pagesScience Pointers To ReviewAudrielle RejesusNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science - Chapter 10 - Response & CoordinatiionDocument32 pagesCambridge Science - Chapter 10 - Response & CoordinatiionDK01No ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument1 pageScience NotesAshley Babe ServianoNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesCentral Nervous SystemamazenokutendamNo ratings yet
- Week3 Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument26 pagesWeek3 Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve Homeostasisperlasirisalthea22No ratings yet
- GEO 204 - Stars and ConstellationsDocument20 pagesGEO 204 - Stars and Constellationsflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 InteractionsDocument18 pagesMODULE 5 Interactionsflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- UNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument16 pagesUNIT4 Uniformly Accelerated Motionflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Crosswise Copy and AnswerDocument32 pagesCrosswise Copy and Answerflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - MicroscopeDocument5 pagesModule 2 - Microscopeflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Living Things Other Than Plants and AnimalDocument14 pagesLiving Things Other Than Plants and Animalflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Unit 1: Subject Standards/Content and OST AlignmentDocument17 pagesCells: Unit 1: Subject Standards/Content and OST Alignmentflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document51 pagesModule 1florie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument17 pagesCELLflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Things You Usually Consider Whenever You Plan To Have A Picnic?Document54 pagesWhat Are The Things You Usually Consider Whenever You Plan To Have A Picnic?florie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- 1 EnergyDocument32 pages1 Energyflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Atom g8Document21 pagesAtom g8florie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- Soalan SainsDocument6 pagesSoalan SainsMohamad HattaNo ratings yet
- Myopathy: Figure 35-1Document14 pagesMyopathy: Figure 35-1Izabella MihályNo ratings yet
- Urmium Eng - 1 - CTYDocument50 pagesUrmium Eng - 1 - CTYnguyenthequang03No ratings yet
- Speed Dating CardsDocument15 pagesSpeed Dating Cardsapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Axo GenDocument28 pagesAxo GenTao LevyNo ratings yet
- Review Questions and Answers For Veterinary Technicians e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesReview Questions and Answers For Veterinary Technicians e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFdonna.crow358100% (39)
- Ini SarafDocument6 pagesIni SarafIvanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Spinal Segmental Sensitization As A New Concept of Pain and Employ Its Treatment StrategiesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Spinal Segmental Sensitization As A New Concept of Pain and Employ Its Treatment Strategiesheaven6938No ratings yet
- Effect of Effleurage Techniques To Inten 82ec4d7d PDFDocument7 pagesEffect of Effleurage Techniques To Inten 82ec4d7d PDFeka istiyaniNo ratings yet
- 1184bns 1Document14 pages1184bns 1Daniela GanchasNo ratings yet
- Ning Wang EnglishDocument5 pagesNing Wang EnglishAngela PagliusoNo ratings yet
- Probable Vasovagal Reaction Following Cystocentesis in Two CatsDocument4 pagesProbable Vasovagal Reaction Following Cystocentesis in Two CatsBruno Félix MendesNo ratings yet
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation and Its Use For Sports Training Programs: A ReviewDocument32 pagesElectrical Muscle Stimulation and Its Use For Sports Training Programs: A ReviewMiguel Martín Del CampoNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Nervous SystemPractice Test and KeyDocument13 pagesCH 8 Nervous SystemPractice Test and KeyvpcpharmdNo ratings yet
- SEMON, Richard The Mneme PDFDocument318 pagesSEMON, Richard The Mneme PDFCassio Barbieri100% (2)
- Nervous Systemchapt 28Document58 pagesNervous Systemchapt 28Emerito PerezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations and Supply Chain Management 3rd Edition Bozarth Test BankDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Operations and Supply Chain Management 3rd Edition Bozarth Test BankCaseyBrownaoqn100% (55)
- 4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Document63 pages4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Hoang Nhu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Research Papers Fangruida Discovery and PapersDocument113 pagesResearch Papers Fangruida Discovery and PapersRs BriceNo ratings yet
- Physioanatomical Aspect of Vamana Karma PDFDocument5 pagesPhysioanatomical Aspect of Vamana Karma PDFSiddharth RoyNo ratings yet
- Manual HandlingDocument39 pagesManual HandlingAnkurNo ratings yet
- Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 14th Ed - ExportedDocument12 pagesGuyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 14th Ed - Exportedhassnfiras04No ratings yet