Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in Analytics
Uploaded by
ramhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views52 pagesOriginal Title
2020012416543600013598_pertemuan 12 _ Future Trends_ Privacy and Managerial Considerations in Analytics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views52 pagesPertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in Analytics
Uploaded by
ramhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 52
Business Intelligence, Analytics, and Data
Science: A Managerial Perspective
Fourth Edition
Chapter 8
Future Trends, Privacy and
Managerial Considerations
in Analytics
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Learning Objectives (1 of 2)
8.1 Explore some of the emerging technologies that may
impact analytics, business intelligence (BI), and decision
support
8.2 Describe the emerging Internet of Things (IoT)
phenomenon, potential applications, and the IoT ecosystem
8.3 Describe the current and future use of cloud computing
in business analytics
8.4 Describe how geospatial and location-based analytics
are assisting organizations
Slide 8-2 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Learning Objectives (2 of 2)
8.5 Describe the organizational impacts of analytics
applications
8.6 List and describe the major ethical and legal issues of
analytics implementation
8.7 Identify key characteristics of a successful data science
professional
Slide 8-3 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
OPENING VIGNETTE
Analysis of Sensor Data Helps Siemens Avoid Train
Failures
Discussion Questions
1. In industrial equipment such as trains, what parameters
might one measure on a regular basis to estimate the
equipment’s current performance and future repair needs?
2. How would weather data be useful in analyzing a train’s
equipment status?
3. Estimate how much data you might collect in one month
using, say, 1,000 sensors on a train. Each sensor might
yield 1 KB data per second.
4. How would you propose to store such data sets?
Slide 8-4 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT is an area with explosive growth
• Connecting physical world to the Internet
• Social Network versus IoT
– human-to-human vs. machine-to-machine
• Enablers: sensors and sensing devices
• Example
– Self driving cars
– Fitness trackers
– Smartbin – trash detectors detecting fill levels
– Smart refrigerators, and other appliances
Slide 8-5
•
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Internet of Things (IoT)
• By 2020, besides computing and communication
devices (tablets, phones, and PCs), another 38B
things will be connected to the Internet
• Reasons for incredible growth in IoT:
– Hardware – smaller, affordable, more powerful
– Availability of BI tools – more capable and cheaper
– Emergence of new and innovative use cases
• There isn’t a universal agreement on the term IoT
– Web of Things
– Internet of Systems, …
Slide 8-6 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Application Case 8.1
SilverHook Powerboats Uses Real-Time Data Analysis to
Inform Racers and Fans
Questions for Discussion
1. What type of information might the sensors on a race boat
generate that would be important for the racers to know?
What about for the fans?
2. Which other sports might benefit from similar
technologies?
3. What technological challenges might you face in building
such systems?
Slide 8-7 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Application Case 8.2
Rockwell Automation Monitors Expensive Oil and Gas
Exploration Assets
Questions for Discussion
1. What type of information would likely be collected by an oil
and gas drilling platform?
2. Does this application fit the three V’s of Big Data (volume,
variety, velocity)? Why or why not?
3. Which other industries could use similar operational
measurements and dashboards?
Slide 8-8 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
IoT Technology Infrastructure
• IoT related technology components can be
divided into four major blocks:
1. Hardware
physical devices, sensors, and actuators
2. Connectivity
Collecting and sending sensory data to the cloud
3. Software
Integrating, and processing data for patterns
4. Applications
Creating context specific alerts, actionable insight
Slide 8-9 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Building Blocks of IoT Technology Infrastructure
Slide 8-10 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
RFID Sensors
• RFID: radio-frequency identification
• One of the earliest/disruptive sensor technologies
• Part of a family of automatic identification
technologies
– Including ubiquitous barcodes and magnetic strips
• The goal is to use radio-frequency waves to
accurately and quickly identify objects
• Use of RFID is led/promoted by large retailers
– Wal-Mart, Target, Dillard's
Slide 8-11 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
RFID Sensors
• How does RFID work?
– Tag – a circuit attached to the product to be identified
– Interrogator (i.e., reader) – with antennas and a computer
to detect objects, store the data, and take due actions
• Tags can be passive or active
– Passive tag – small, inexpensive, no power source
– Active tag – larger, more expensive, has power source
• Which one is better?
– Retail uses passive tags, others may use active tags
• RFID + Sensors can be used for perishable goods
Slide 8-12 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Data Representation in RFID
• Data representation for a given application domain
• For Retail: Electronic Product Code (EPC)
• RFID tags contain 96 bits of data
Slide 8-13 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Fog Computing
• Data produced by IoT is huge in size (problem)
• Fog computing is to address the issue by
– Proposing fog nodes to process the data close to IoT
– Fog nodes – any device including routers or switches
– Data Center/Cloud Fog Device Physical Device (i.e.,
sensors that generate
Slide 8-14 the data) Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Other IoT Considerations
• IoT Platforms – many large companies are in it
– Amazon AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT Suite, Predix IoT,
Platform by General Electric (GE), IBM Watson IoT
solutions, and Teradata Unified Data Architecture
• IoT Start-up Ecosystem
– Many start-up companies are emerging in the field of IoT
– Examples include Sigfox, 3D Robotics, Canary, Athos,
Greenwave, Jawbone, FreedomPop, Razer, and Ring
– Fitbit – one of the most successful IoT startups
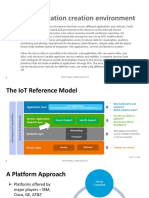
• See Figure 8.3 for a pictorial representation of IoT
Ecosystem
Slide 8-15 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem
Slide 8-16 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Managerial Considerations in the Internet
of Things
1. Organizational Alignment
2. Interoperability Challenges
3. Security
• Emerging growth of IoT and its potential to help us
achieve the vision of smart cities, smart grid,
smart anything
Slide 8-17 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Cloud Computing and Business Analytics
• A style of computing in which dynamically scalable and
often virtualized resources are provided over the
Internet.
• Users need not have knowledge of, experience in, or
control over the technology infrastructures in the cloud
that supports them.
• Cloud computing = utility computing, application service
provider grid computing, on-demand computing,
software-as-a-service (SaaS), …
– Cloud = Internet
– Related “-as-a-services”: infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS),
platforms-as-a-service (PaaS)
Slide 8-18 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Cloud Computing Example
• Web-based e-mail cloud computing application
– Stores the data (e-mail messages)
– Stores the software (e-mail programs)
– Centralized hardware/software/infrastructure
– Centralized updates/upgrades
– Access from anywhere via a Web browser
– e.g., Gmail
• Web-based general application = cloud application
– Google Docs, Google Spreadsheets, Google Drive,…
– Amazon.com’s Web Services
Slide 8-19 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Cloud Computing Example
• Cloud computing is used in
– e-commerce, BI, CRM, SCM, …
• Business model
– Pay-per-use
– Subscribe/pay-as-you-go
• Companies that offer cloud-computing services
– Google, Yahoo!, Salesforce.com
– IBM, Microsoft (Azure)
– Sun Microsystems/Oracle
Slide 8-20 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Cloud Computing and
Service-Oriented Thinking
• Service-oriented thinking is one of the
fastest-growing paradigms today
• Toward building agile data, information, and
analytics capabilities as services
• Service orientation + DSS/BI
• Component-based service orientation fosters
– Reusability, Substitutability, Extensibility,
Scalability, Customizability, Reliability, Low Cost
of Ownership, Economy of Scale,…
Slide 8-21 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Service-Oriented DSS/BI
Slide 8-22 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Variations of Service-Oriented Architecture
and the Cloud
• Data as a Service (DaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• …
• Why so many .aaS is emerging?
Slide 8-23 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Different Types of Cloud Offerings
Slide 8-24 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Essential Technologies for Cloud Computing
• Virtualization
– Creation of a virtual version of something like an
operating system or server
– Example: logical division of a hard drive to create two
separate hard drives in a computer
• Levels of virtualization
– Network virtualization
– Storage virtualization
– Server virtualization
• Relates to which cloud service is employed
Slide 8-25 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Cloud Deployment Models
• Private cloud
• Public cloud
• Hybrid cloud
• Which cloud model is good for you?
• Major cloud platform providers in analytics:
– Amazon Elastic Beanstalk
– IBM Bluemix
– Microsoft Azure
– Google App Engine
– OpenShift
Slide 8-26 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Representative Analytics as a Service Offering
• Teradata - Aster Analytics as a Service
• IBM Watson Analytics
• MineMyText.com
• SAS Visual Analytic and Visual Statistics
• Tableau
• Showflake
• Predix by General Electric
Most of these have free/restricted/trial offerings
Slide 8-27 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Illustrative Analytics Applications
Employing the Cloud Infrastructure
• MD Anderson Cancer Center Utilizes Cognitive
Computing Capabilities of IBM Watson to Give
Better Treatment to Cancer Patients
• Public School Education in Tacoma, Washington,
Uses Microsoft Azure Machine Learning to Predict
School Dropouts
• Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Provides
Personalized Proactive Healthcare Using
Microsoft Cortana Analytics Suite
Slide 8-28 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Illustrative Analytics Applications
Employing the Cloud Infrastructure
• Mankind Pharma Uses IBM Cloud Infrastructure
to Reduce Application Implementation Time by
98%
• Gulf Air Uses Big Data to Get Deeper Customer
Insight
• Chime Enhances Customer Experience Using
Snowflake
Slide 8-29 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Location-Based Analytics
• Geospatial Analytics
• Geocoding
– Visual maps
– Postal codes
– Latitude & Longitude
• Enables aggregate view of a large geographic
area
• Integrate “where” into customer view
Slide 8-30 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Location-Based Analytics
Slide 8-31 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Location-Based Analytics
• Location-based databases
• Geographic Information System (GIS)
– Used to capture, store, analyze, and manage the data
linked to a location
– Combined with integrated sensor technologies and
global positioning systems (GPS)
• Location Intelligence (LI)?
– Interactive maps that further drill down to
data/information details about any location
Slide 8-32 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Use of Location-Based Analytics
• Retailers – location + demographic details
combined with other transactional data can help …
– determine how sales vary by population level
– assess locational proximity to other competitors and their
offerings
– assess the demand variations and efficiency of supply
chain operations
– analyze customer needs and complaints
– better target different customer segments
–…
Slide 8-33 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
GIS Applications
• In addition to business/retail applications, GIS
based analytics are being used in
– Agricultural applications
– Crime analysis
– Disease spread prediction
• For more applications, look at
– esri.com (producer of ArcGIS)
– grindgis.com
• LI can be combined with weather and environmental data
to create a richer data/information infrastructure
Slide # of total
Slide 8-34 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Application Case 8.4
Indian Police Departments use Geospatial Analytics to Fight
Crime
Questions for Discussion
1. How can machine learning be incorporated in this case?
2. Can GPS tracking of field units help to further improve the
system? Or will it be too much to handle?
3. What type of analytics are used here (descriptive,
predictive, or prescriptive?)? Why?
4. Which other field can use a similar strategy?
Slide 8-35 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Application Case 8.5
Starbucks Exploits GIS and Analytics to Grow Worldwide
Questions for Discussion
1. What type of demographics and GIS information would be
relevant for deciding on a store location?
2. It has been mentioned that Starbucks encourages its
customers to use its mobile app. What type of information
might the company gather from the app to help it better
plan operations?
3. Will the availability of free Wi-Fi at Starbucks’ stores
provide any information to Starbucks for better analytics?
Slide 8-36 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
A Multimedia Exercise in Analytics
Employing Geospatial Analytics
• Go To Teradata University Network (TUN)
• Find the BSI Case video on “The Case of the
Dropped Mobile Calls”
• Watch the video via TUN or at YouTube
youtube.com/watch?v=4WJR_Z3exw4
• Also, look at the slides at
slideshare.net/teradata/bsi-teradata-the-case-of-the
-dropped-mobile-calls
• Discuss the case
Slide 8-37 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Real-Time Location Intelligence
• Many devices are constantly sending out their
location information
– Cars, airplanes, ships, mobile phones, cameras,
navigation systems, …
GPS, Wi-Fi, RFID, cell tower triangulation
• Reality mining?
– Real-time location information = real-time insight
– Path Intelligence (pathintelligence.com)
Footpath – movement patterns within a city or store
How to use such movement information
Slide 8-38 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Application Case 8.6
Quiznos Targets Customers for Its Sandwiches
Questions for Discussion
1. How can location-based analytics help retailers in
targeting customers?
2. Research similar applications of location-based analytics
in the retail domain.
Slide 8-39 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Analytics Applications for Consumers
• Explosive growth of the apps industry
– iOS, Android, Windows, Blackberry, Amazon, …
– Directly used by consumers (not businesses)
– Enabling consumers to become more efficient
– Interesting Examples
CabSense – finding a taxi in New York City
– Rating of street corners; interactive maps, …
ParkPGH – finding a parking spot
– Downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
– App industry is already 25B in size and growing
(wsj.com/apps)
Slide 8-40 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Issues of Legality, Privacy, and Ethics
• Legal issues to consider
– What is the value of an expert opinion in court
when the expertise is encoded in a computer?
– Who is liable for wrong advice (or information)
provided by an intelligent application?
– What happens if a manager enters an incorrect
judgment value into an analytic application?
– Who owns the knowledge in a knowledge base?
– Can management force experts to contribute
their expertise?
Slide 8-41 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Issues of Legality, Privacy, and Ethics
• Privacy - The right to be left alone and the right to be
free from unreasonable personal intrusions
– Collecting information about individuals
How much is too much?
– Mobile User Privacy
Location-based analysis/profiling
– Homeland Security and Individual Privacy
– Recent Issues in Privacy and Analytics
“What They Know” about you (wsj.com/wtk)
Rapleaf (rapleaf.com), X + 1 (xplusone.com), Bluecava
(bluecava.com), reputation.com, sociometric.com...
– Who owns our private data?
Slide 8-42 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Issues of Legality, Privacy, and Ethics
• Ethics in Decision Making and Support
– Electronic surveillance
– Software piracy
– Invasion of individuals’ privacy
– Use of proprietary databases
– Use of knowledge and expertise
– Accessibility for workers with disabilities
– Accuracy of data, information, and knowledge
– Protection of the rights of users
– Accessibility to information
– Personal use of corporate computing resources
– … more in the book
Slide 8-43 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Impacts of Analytics in Organizations
• Analytics revolution Cultural transformation
Slide 8-44 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Impacts of Analytics in Organizations
• New Organizational Units
– BI department
– Data science department
• Redesign of an Organization through the Use of
Analytics
– People analytics
– HR analytics
• Analytics Impact on Managers’ Activities,
Performance, and Job Satisfaction
– Data/fact/analytics driven decision
Slide 8-45 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Potential Impacts of Analytics on Managers
• Less expertise/experience is requirement
• Faster decision making (augmented with analytics)
• Less reliance on experts and analysts (data rules!)
• Power is being redistributed among managers
• Support for complex decisions makes them faster to
develop and be of better quality
• Information needed for high-level decision making is
expedited or even self-generated
• Automation of routine decisions or phases in the decision-
making process may eliminate some managers
Slide 8-46 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Impacts of Analytics in Organizations
• Industrial Restructuring
– AI, analytics, and cognitive computing can change the
industry in a fundamental way
• Automation’s Impact on Jobs
– Data science and AI will change the nature of human
jobs (another wave of automation is in the horizon)
• Unintended Effects of Analytics
– Social and long-term effects of the models
– “Weapons of Math Destruction: How Big Data
Increases Inequality and Threatens Democracy”
Slide 8-47 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Data Scientist as a Profession
“The Sexiest Job of the 21st Century”
Thomas H. Davenport and D. J. Patil
Harvard Business Review, October 2012
• Data Scientist = Big Data guru
– One with skills to investigate Big Data
• Very high salaries, very high expectations
• Where do Data Scientists come from?
– M.S./Ph.D. in MIS, CS, IE,… and/or Analytics
– There is not a specific degree program for DS!
– PE, PML, … DSP (Data Science Professional)
Slide 8-48 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Skills That Define a Data Scientist
Domain Expertise,
Problem Definition and
Decision Modeling
Data Access and
Communication and Management
Interpersonal (both traditional and
new data systems)
DATA
SCIENTIST
Curiosity and Programming,
Creativity Scripting and Hacking
Internet and Social
Media/Social Networking
Technologies
Slide 8-49 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
A Typical
Job Post
for Data
Scientist
Slide 8-50 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
Statements about Data Scientists
• Data scientists turn Big Data into big value, delivering
products that delight users and insight that informs
business decisions.
• A data scientist is not only proficient in working with
data, but also appreciates data itself as an invaluable
asset.
• By 2020 there will be 4.5 million new data scientist
jobs, of which only one-third will be filled because of
the lack of people available to fill them.
• Today’s data scientists are the quants of the financial
markets of the 1980s.
Slide 8-51 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
End of Chapter 8
• Questions / Comments
Slide 8-52 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education Ltd.
You might also like
- State of Devops 2021Document45 pagesState of Devops 2021Renato AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing Grade 9 ExamDocument7 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing Grade 9 ExamMa'am TabinasNo ratings yet
- 4.0 IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument44 pages4.0 IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesThushalie VyravanNo ratings yet
- Ict Chapter 5Document50 pagesIct Chapter 5Sean Misola Gacuya100% (2)
- Real-time Analytics through Edge/Fog Device CloudsDocument41 pagesReal-time Analytics through Edge/Fog Device CloudspeterindiaNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch05 KL CEDocument48 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch05 KL CEYounglife BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Configure and Verify A Site-To-Site IPsec VPN Using CLIDocument6 pagesConfigure and Verify A Site-To-Site IPsec VPN Using CLIMilošKovačevićNo ratings yet
- Unit:4 Iot Applications For Value CreationsDocument45 pagesUnit:4 Iot Applications For Value CreationsVishal Joshi100% (4)
- Chap 2 E-Commerce Infrastructure 30 Nov 2019Document20 pagesChap 2 E-Commerce Infrastructure 30 Nov 2019KY10NANo ratings yet
- 960701B Overview of OMNICOM Configuration PC SoftwareDocument10 pages960701B Overview of OMNICOM Configuration PC Softwareserie1984No ratings yet
- IoT Use Case EbookDocument11 pagesIoT Use Case EbookScott Poole100% (3)
- IoT Solution-Class PPT PDFDocument66 pagesIoT Solution-Class PPT PDFSuhil IrshadNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Analytics and Data Science A Managerial Perspective 4th Edition Sharda Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesBusiness Intelligence Analytics and Data Science A Managerial Perspective 4th Edition Sharda Solutions Manualzealantscavengebvpzfw100% (26)
- Lect4 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument39 pagesLect4 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesMerghani AbuelgasimNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis17 Ppt Ch05Document42 pagesLaudon Mis17 Ppt Ch05Ömer YağmurNo ratings yet
- S1.1 Laudon Mis17 PPT Ch05 2Document48 pagesS1.1 Laudon Mis17 PPT Ch05 2devilryder31No ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch05 KL CEDocument47 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch05 KL CEMohamedNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition: I T Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument18 pagesSixteenth Edition: I T Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesAlaa Al HarbiNo ratings yet
- Ece 3501-Iot Fundamentals: Module - 4Document50 pagesEce 3501-Iot Fundamentals: Module - 4Neelabro KonarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechWei TingNo ratings yet
- 1.3 FriessDocument16 pages1.3 FriessUgyenKpNo ratings yet
- Lec-2 BDA FundamentalsDocument28 pagesLec-2 BDA FundamentalsBushra ZainabNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0 Answer KeyDocument14 pagesIndustry 4.0 Answer KeyArunesh SNo ratings yet
- Technology Applications in IT Consulting IndustryDocument18 pagesTechnology Applications in IT Consulting IndustryTRISHAL ARORANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - IT Infrastructure and Emerging TechQiying LimNo ratings yet
- ECEN 5053-002: Developing The Industrial Internet of ThingsDocument50 pagesECEN 5053-002: Developing The Industrial Internet of ThingsChristina LenayNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Chapter 5 Designing For The Internet of ThingsDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank On Chapter 5 Designing For The Internet of ThingsPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Script for Case Study -3_4_2024Document3 pagesScript for Case Study -3_4_2024Anne DSNo ratings yet
- Iiot Components: Course Code: Csio4700 Course Name: Iot For IndustriesDocument19 pagesIiot Components: Course Code: Csio4700 Course Name: Iot For IndustriesVairavel ChenniyappanNo ratings yet
- Ds4015 Big Data Analytics QBDocument155 pagesDs4015 Big Data Analytics QBBARATHNo ratings yet
- Emerging Tech Trends in ComputingDocument32 pagesEmerging Tech Trends in ComputingMarvin PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cloud With Iot in Smart Parking: June 2017Document11 pagesCloud With Iot in Smart Parking: June 2017Lou LoulouNo ratings yet
- S1.1 Laudon - Mis17 - PPT - ch05Document48 pagesS1.1 Laudon - Mis17 - PPT - ch05devilryder31No ratings yet
- Digital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itFrom EverandDigital Technologies – an Overview of Concepts, Tools and Techniques Associated with itNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things IoT ApplicationsDocument10 pagesThe Internet of Things IoT Applicationstest2012No ratings yet
- Tapmi IT For Business and HRIS (HRS6600) Session 3Document16 pagesTapmi IT For Business and HRIS (HRS6600) Session 3Tv21 OrgNo ratings yet
- Laudon - Mis16 - PPT - ch05 - KL - CEDocument53 pagesLaudon - Mis16 - PPT - ch05 - KL - CEQumoriNo ratings yet
- AiprojectDocument21 pagesAiprojectKamlesh PariharNo ratings yet
- BUSHOR-1218 No. of Pages 10 The Internet of Things (IoT) : Applications, Investments, and Challenges For EnterprisesDocument10 pagesBUSHOR-1218 No. of Pages 10 The Internet of Things (IoT) : Applications, Investments, and Challenges For EnterprisesfreeretdocsNo ratings yet
- Iot Application Creation Environment: Krish Prabhu, Gian Lecture 5+7Document35 pagesIot Application Creation Environment: Krish Prabhu, Gian Lecture 5+7Surya Ganesh PenagantiNo ratings yet
- Iot Internet of ThingsDocument23 pagesIot Internet of ThingsNisha HiremathNo ratings yet
- Recent Machine Learning Applications To Internet of Things (Iot)Document19 pagesRecent Machine Learning Applications To Internet of Things (Iot)nagasai chegondiNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document20 pagesCH 11Samah AyadNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document5 pagesUnit 4studyexpress12No ratings yet
- A Big Data Analytics Architecture For The Internet of Small ThingsDocument36 pagesA Big Data Analytics Architecture For The Internet of Small ThingsNamratta SinghNo ratings yet
- 5 Things To Know About The IoT Platform Ecosystem PDFDocument7 pages5 Things To Know About The IoT Platform Ecosystem PDFvinodbalaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Internet of ThingsDocument8 pagesThesis Internet of Thingsjackieramirezpaterson100% (2)
- Scalable Methodology For Data Stream Analytics in Real-Time Internet of Things (IoT) ApplicationsDocument6 pagesScalable Methodology For Data Stream Analytics in Real-Time Internet of Things (IoT) Applicationsjava webNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Watson IoT Platform TamLNDocument24 pagesPresentation-Watson IoT Platform TamLNLa Van QuanNo ratings yet
- Sap Leonardo Iot and Industry 4.0: April 2021Document10 pagesSap Leonardo Iot and Industry 4.0: April 2021Ghislain KonéNo ratings yet
- IDC Marketscape PTCDocument9 pagesIDC Marketscape PTCcbqucbquNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IDocument32 pagesUNIT-IRavindranathNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks IoTDocument12 pagesWireless Networks IoTAmr HameedNo ratings yet
- IT, Culture, and The SocietyDocument17 pagesIT, Culture, and The SocietySean Misola GacuyaNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things Platform Approach 0614 1Document13 pagesInternet of Things Platform Approach 0614 1Soumitra DasNo ratings yet
- ICT Glossary - 2Document4 pagesICT Glossary - 2Mark Angelbert Angcon DeoNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Research PaperDocument5 pagesCloud Computing Research Paperbijesh_nair007No ratings yet
- Industrial Automation by IOTDocument5 pagesIndustrial Automation by IOTAsif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 10 eSCO-IoT-ch6-v4Document32 pages10 eSCO-IoT-ch6-v4Yahya HajaliNo ratings yet
- Ict TermsDocument8 pagesIct TermsAiza GungonNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.0: Will It Benefit India?Document11 pagesIndustry 4.0: Will It Benefit India?Raviraj PisheNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAo1SpYCo1YmTJeiGbHKH22nYKAL3GLgRtzpk4R3gRbHCAsTnCSMxfKm0SFBNYGz7keG7rfZN Y3QVo gdxiQyqG - 6KLsY2icnDocument14 pagesACFrOgAo1SpYCo1YmTJeiGbHKH22nYKAL3GLgRtzpk4R3gRbHCAsTnCSMxfKm0SFBNYGz7keG7rfZN Y3QVo gdxiQyqG - 6KLsY2icnIndianNo ratings yet
- (IJETA-V8I6P1) :yew Kee WongDocument7 pages(IJETA-V8I6P1) :yew Kee WongIJETA - EighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingDocument61 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Predictive Analytics II: Text, Web, and Social Media AnalyticsDocument5 pagesFourth Edition: Predictive Analytics II: Text, Web, and Social Media AnalyticsramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationDocument66 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationgabyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5 CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 5 CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsDocument52 pagesPertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationDocument66 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationgabyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsDocument52 pagesPertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5 CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 5 CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 9 - CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 9 - CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationDocument66 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationgabyNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingDocument61 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 9 - CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 9 - CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingDocument61 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 9 - CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 9 - CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5 CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 5 CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 5 CaseDocument5 pagesPertemuan 5 CaseramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationDocument66 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and VisualizationgabyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsDocument52 pagesPertemuan 12 - Future Trends - Privacy and Managerial Considerations in AnalyticsramhanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingDocument61 pagesFourth Edition: Descriptive Analytics II: Business Intelligence and Data WarehousingramhanNo ratings yet
- UTM 1 Edge DatasheetDocument4 pagesUTM 1 Edge DatasheetSoporte TijuanaNo ratings yet
- Release Notes Intel® Proset/Wireless Software 22.50.1: Supported Operating SystemsDocument3 pagesRelease Notes Intel® Proset/Wireless Software 22.50.1: Supported Operating SystemsSelçuk AlacalıNo ratings yet
- Upgrade IDU/ODU Software FibeAir IP-20Document7 pagesUpgrade IDU/ODU Software FibeAir IP-20Ardine MannuelaNo ratings yet
- Ccna Acl Lab: School of Information Studies Syracuse University Created by 4/22/2008 By: James Benninger Used in CCNADocument18 pagesCcna Acl Lab: School of Information Studies Syracuse University Created by 4/22/2008 By: James Benninger Used in CCNAFaby ReveloNo ratings yet
- User Manual For ZED Registration 20.04.2022 2022Document32 pagesUser Manual For ZED Registration 20.04.2022 2022Aneesh AneeshNo ratings yet
- Cloud Online Compiler Using Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCloud Online Compiler Using Cloud Computingshanmugaraja85No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Huawei Elte Solution For Airport PRDocument62 pagesToaz - Info Huawei Elte Solution For Airport PRpatrick vibilaNo ratings yet
- Sql4codesys enDocument3 pagesSql4codesys envonnetNo ratings yet
- Fort I ClientDocument4 pagesFort I ClientCarfin Febriawan Pratama PutraNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Plan TemplateDocument13 pagesSample Test Plan TemplateCialla MakaryanNo ratings yet
- Monitor apps with TAAM user guideDocument59 pagesMonitor apps with TAAM user guideKrish100% (1)
- NAS vs Server for Small Business: Which is BestDocument3 pagesNAS vs Server for Small Business: Which is Bestbogdanm67No ratings yet
- Naudio: Low Latency Audio Recording, Such As That Found in Digital Audio Workstation Software Used inDocument13 pagesNaudio: Low Latency Audio Recording, Such As That Found in Digital Audio Workstation Software Used indharshbtechNo ratings yet
- Rn2483 Lora Technology Module Command Reference User'S GuideDocument57 pagesRn2483 Lora Technology Module Command Reference User'S GuideFernando NancoNo ratings yet
- FYP-I Project ProposalDocument7 pagesFYP-I Project ProposalAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Liye - Info Netzwerk A1 1 PDF Download Minikeywordcom PRDocument2 pagesLiye - Info Netzwerk A1 1 PDF Download Minikeywordcom PRSpurgeon ClarksonNo ratings yet
- Sre Assignment 1 SolvedDocument5 pagesSre Assignment 1 SolvedFarjad AliNo ratings yet
- Emb Notes Unit 1Document50 pagesEmb Notes Unit 1mohanadevi chandrasekarNo ratings yet
- I Need Python Code For This. Write A Program That ...Document3 pagesI Need Python Code For This. Write A Program That ...viliame vuetibauNo ratings yet
- VulnVoIP (Vulnerable VoIP) SolutionsDocument10 pagesVulnVoIP (Vulnerable VoIP) SolutionsFelipe MeraNo ratings yet
- HP m880 User Guide Fabf3e1Document28 pagesHP m880 User Guide Fabf3e1Shareef ThabetNo ratings yet
- EMBEDDED LINUX BUILD AND DEBUGDocument44 pagesEMBEDDED LINUX BUILD AND DEBUGsubhashini kathiresanNo ratings yet
- Wiretapping End-to-End Encrypted VoIP Calls: Real-World Attacks On ZRTPDocument17 pagesWiretapping End-to-End Encrypted VoIP Calls: Real-World Attacks On ZRTPgsbabilNo ratings yet
- Threats Targeting Telecoms: DDoS, Exploits and Social EngineeringDocument18 pagesThreats Targeting Telecoms: DDoS, Exploits and Social EngineeringHarry MoleNo ratings yet
- CIS SynthesisDocument10 pagesCIS SynthesisChristian AribasNo ratings yet
- Aaa Accounting Through Aaa Local Authentication Attempts Max-FailDocument14 pagesAaa Accounting Through Aaa Local Authentication Attempts Max-Failobee1234No ratings yet