Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2c. Egg Membranes
Uploaded by
Manisha Bisht0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pagesegg membranes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentegg membranes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pages2c. Egg Membranes
Uploaded by
Manisha Bishtegg membranes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
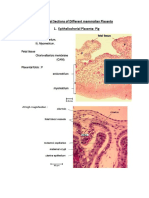
EGG MEMBRANES
• Egg membrane The layer of material that covers an animal
egg cell. Primary membranes develop in the ovary and
cover the egg surface in addition to the normal plasma
membrane. The primary membrane is called the vitelline
membrane in insects, molluscs, birds, and amphibians,
the chorion in tunicates and fish, and the zona pellucida in
mammals. Insects have a second thicker membrane, also
called the chorion. Secondary membranes are secreted by
the oviducts and parts of the genital system while the egg
is passing to the outside. They include the jelly coat of
frogs' eggs and the albumen and shell of birds' eggs.
• The egg membranes are classified into three
types. They are
• 1. primary membranes
• 2. Secondary membranes and
• 3. Tertiary membrane.
I. primary membranes
• The membranes secreted by egg cytoplasm (ooplasm)
constitute the primary membrane. They are closely attached
to the surface of the egg. The primary membranes are named
differently in the different animals. They are
• a. Plasma Membrane: It is the membrane covering the egg
immediately It over it, is found in all the eggs in structure, It
resembles the plasma membrane of a cell.
• b. Vitelline Membrane: it is closely attached to the plasma
membrane of egg. Commonly found in Egg of Amphioxus.
molluscs. Echinoderms, amphibians birds etc It is very thin
and and transparent. It is formed of mucopolysacharide and
fibrous protein. The space formed between it and the plasma
membrane is called perivitelline space filled with a fluid called
perivitelline fluid.
• c. Chorion:It is found in the eggs of lower chordates like fishes
(styela). It is a product of surface ooplasm
• d. Zona Radiata The egg of the shark Scyllium canicula, has
two primary membrane produced by the surface ooplasm.
The outer membrane is the vitetline membrane and the inner
membrane has a radiating appearance and hence called zona
radiata.The eggs of teleost fishes are also covered by zona
radiata.
• e. Zona Pellucida All mammalian eggs are surrounded by a
membrane called zona pellucida is also named as zone
radiata. It is so named because it gives a striated appearance
under the microscope'
• The striations are due to the presence of microvilli and
macrovilli (desmosomes) in this zone. The microvilli are
produced by the surface of the egg and macrovilli are
produced by Follicle cells. They protrude into the zona
pellucida
II. Secondary Membranes
• The secondary membranes are produced by the follicle cells
(cells found around the developing oocytes) of the ovary.
These membranes are usually tough and jmpermeable' The
secondary membranes are as follows
• a. Chorion
• This is a common outer covering in the eggs of insects,
ascidians and cyclostomes (Myxine). It is found outside the
vitelline membrane. As the chorion is tough and impermeable
it is provided with one or more openings called micropyles
through which the sperms enter the egg
• b. Corona Radiata It is found in mammalian eggs. This
membrane is formed of a layer of follicle cells. The cells are
radially arranged around the zona pellucida
III. Tertiary Membranes
• The tertiary membranes are produced by the oviduct.
• a. White Albumen
• It is found in the egg of hen. It is found outside the vitelline membrane. It is
formed of three layers-an inner less dense albumen, a middle dense
albumen and an outer less dense albumen. The albumen is formed of
water and protein
• b. Shell Membrane: The shell membrane is formed around the albumen in
the egg of hen. It is a double membrane. The two membranes adhere closely
and are separated by an air space at the blunt end of the egg. This
membrane is formed of keratin.
• c. Shell: The shell is the outer covering of land animals eggs. It is formed of
calcium carbonate. Lt is white or brown in colour.
• It contains as many as 7000 minute pores. These pores are 0.04 to 0.05 mm
in diameter. They are filled with a proteinous substance called collagen.
• d. Jelly Coat:The amphibian eggs are surrounded by a gelatinous covering
called jelly coat
• e. Mermaid's Purse
• It is the egg case of some cartilaginous fishes. It is a
protective hard shell secreted by the shell glands
present in the oviduct. The shape of the purse varies
from group to group.
• Generally, it is rectangular in shape. The corners of the
shell are drawn out into four long twisted elastic
filaments which serve to attach the eggs to sea weeds.
In dog-fish Chiloscyllium, development is completed
within this purse
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Developmental Biology: Fundamental Processes of DevelopmentDocument9 pagesDevelopmental Biology: Fundamental Processes of DevelopmentManisha BishtNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Historical Section of PlacentaDocument5 pagesHistorical Section of PlacentaManisha BishtNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 2b. Types of Egg and CleavageDocument55 pages2b. Types of Egg and CleavageManisha BishtNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Globin Gene & Molecular Clock PDFDocument36 pagesGlobin Gene & Molecular Clock PDFManisha BishtNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Evidences of Evolution PDFDocument69 pagesEvidences of Evolution PDFManisha Bisht100% (1)
- Evolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManDocument39 pagesEvolution:: The Origin and Evolution of ManManisha Bisht100% (4)
- GSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFDocument27 pagesGSM Rtu Controller Rtu5011 v2 PDFAbdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- WikipediaDocument29 pagesWikipediaradhakodirekka8732No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Head and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalDocument29 pagesHead and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalSudhir NairNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- HSE Inspection Report-07Document32 pagesHSE Inspection Report-07najihahNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- PRIMARY Vs Secondary Vs TertiaryDocument1 pagePRIMARY Vs Secondary Vs TertiaryIshi Pearl Tupaz100% (1)
- 2-Amino-5-Aryl-2-Oxazolines.: (,ee TableDocument7 pages2-Amino-5-Aryl-2-Oxazolines.: (,ee TableChristopher HowellNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Student EssaysDocument41 pagesStudent EssaysAsif RahmanNo ratings yet
- BasicsDocument1 pageBasicsRishi Raj100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- FFL/ A: Tutorial On Reed-Solomon Error Correction CodingDocument144 pagesFFL/ A: Tutorial On Reed-Solomon Error Correction Codingbatman chamkadarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Lithium Dongjin 48v100ahDocument5 pagesLithium Dongjin 48v100ahmk7718100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- AI LabDocument17 pagesAI LabTripti JainNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Vocabulary: ExileDocument5 pagesVocabulary: ExileWael MadyNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Migloo's Day Info SheetDocument4 pagesMigloo's Day Info SheetCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Legal NoticeDocument3 pagesLegal NoticeT Jayant JaisooryaNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- CHAPTER 5 Ground ImprovementDocument47 pagesCHAPTER 5 Ground ImprovementBeman EasyNo ratings yet
- RCU II Open Protocol Communication Manual FV 9 10 31 08 PDFDocument17 pagesRCU II Open Protocol Communication Manual FV 9 10 31 08 PDFAndrés ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine MusicDocument11 pagesContemporary Philippine MusicmattyuuNo ratings yet
- Train Collision Avoidance SystemDocument4 pagesTrain Collision Avoidance SystemSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pega DevOps Release Pipeline OverviewDocument200 pagesPega DevOps Release Pipeline OverviewArun100% (1)
- Police Log September 24, 2016Document14 pagesPolice Log September 24, 2016MansfieldMAPoliceNo ratings yet
- State Magazine, May 2001Document38 pagesState Magazine, May 2001State MagazineNo ratings yet
- Zencrack Installation and ExecutionDocument48 pagesZencrack Installation and ExecutionJu waNo ratings yet
- (FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Document160 pages(FORD) Manual de Propietario Ford Ranger 1998Marly Salas GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Problem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature and RadiationDocument39 pagesDual Nature and RadiationWedger RealmeNo ratings yet
- Media EthicsDocument11 pagesMedia EthicsSreekanth Reddy100% (2)
- Piezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Document38 pagesPiezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Encardio RiteNo ratings yet
- Medicine Colloquium Exam - 2015 ADocument41 pagesMedicine Colloquium Exam - 2015 ArachaNo ratings yet
- E. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarDocument3 pagesE. What Was The Chinese POW Death Rate in WW2 and The Second Sino-Japanese WarPamela SantosNo ratings yet
- ACO 201 - (Section) - Spring 2021Document8 pagesACO 201 - (Section) - Spring 2021George BeainoNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)