0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views26 pagesChapter 3 RAC
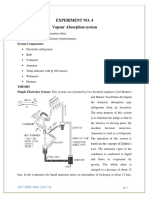
This document provides an overview of vapour absorption refrigeration systems. It discusses the basic components and working principle, comparing it to vapour compression systems. Vapour absorption uses heat rather than mechanical energy to power the system. The absorber, generator, pump and pressure reducing valve replace the compressor. Examples of domestic refrigerators using ammonia-hydrogen systems are described. Advantages include quiet operation without moving parts and ability to use low-grade heat sources, while disadvantages include larger size, higher costs and lower COP compared to compression systems.
Uploaded by
Sameer AhmadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views26 pagesChapter 3 RAC
This document provides an overview of vapour absorption refrigeration systems. It discusses the basic components and working principle, comparing it to vapour compression systems. Vapour absorption uses heat rather than mechanical energy to power the system. The absorber, generator, pump and pressure reducing valve replace the compressor. Examples of domestic refrigerators using ammonia-hydrogen systems are described. Advantages include quiet operation without moving parts and ability to use low-grade heat sources, while disadvantages include larger size, higher costs and lower COP compared to compression systems.
Uploaded by
Sameer AhmadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd