Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8051 TIMER PROGRAMMING
Uploaded by
leevasusan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views39 pagesThe document discusses timers and counters in 8051 microcontrollers. It covers the modes and registers for timers 0 and 1, including TMOD and TCON. It explains how to program the timers in modes 1 and 2 to generate delays or count external events. Mode 1 is a 16-bit timer that reloads on overflow, while mode 2 is an 8-bit timer that auto-reloads. GATE allows starting and stopping timers by external hardware. Counters use the same programming but are clocked from external pins instead of software.
Original Description:
Original Title
module 4_part 1_final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses timers and counters in 8051 microcontrollers. It covers the modes and registers for timers 0 and 1, including TMOD and TCON. It explains how to program the timers in modes 1 and 2 to generate delays or count external events. Mode 1 is a 16-bit timer that reloads on overflow, while mode 2 is an 8-bit timer that auto-reloads. GATE allows starting and stopping timers by external hardware. Counters use the same programming but are clocked from external pins instead of software.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views39 pages8051 TIMER PROGRAMMING
Uploaded by
leevasusanThe document discusses timers and counters in 8051 microcontrollers. It covers the modes and registers for timers 0 and 1, including TMOD and TCON. It explains how to program the timers in modes 1 and 2 to generate delays or count external events. Mode 1 is a 16-bit timer that reloads on overflow, while mode 2 is an 8-bit timer that auto-reloads. GATE allows starting and stopping timers by external hardware. Counters use the same programming but are clocked from external pins instead of software.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
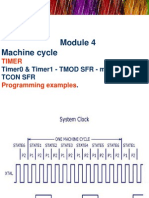
MODULE 4
• 8051 Timers/Counters-Modes and Applications
• Serial Data Transfer-SFRs of serial
port,working,Programming the 8051 to transfer data
serially
• Introduction to ARM-ARM family,ARM 7 register
architecture,ARM programmer-s model
• System Software-Assembler, Interpreter, Compiler,
Linker, Loader, Debugger.
Dept . Of ECE SSET
8051 TIMER
PROGRAMMING
Dept . Of ECE SSET
8051 Timers
The 8051 has two timers/counters, they can be
used as
Timers to generate a time delay
Event counters to count events happening
outside the microcontroller
Both Timer 0 and Timer 1 are 16 bits wide
Since 8051 has an 8-bit architecture, each 16-
bits timer is accessed as two separate registers
of low byte and high byte
Dept . Of ECE SSET
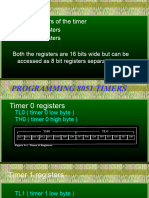
Timer 0 & 1 Registers
•Accessed as low byte and high byte
• The low byte register is called
TL0/TL1
• The high byte register is called
TH0/TH1
• Accessed like any other register
MOV TL0,#4FH
MOV R5,TH0
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
TMOD Register
Both timers 0 and 1 use the same register,
called TMOD (timer mode), to set the
various timer operation modes
• TMOD is a 8-bit register
• The lower 4 bits are for Timer 0
• The upper 4 bits are for Timer 1
• In each case, the lower 2 bits are
used to set the timer mode
• The upper 2 bits to specify the
operation
DeptOf ECE SSET
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
GATE
Timers of 8051 do starting and stopping by either
software or hardware control.
• In using software to start and stop the timer
where GATE=0
• The start and stop of the timer are
controlled by way of software by the TR
(timer start) bits TR0 and TR1
• The SETB instruction starts it, and it is
stopped by the CLR instruction
• These instructions start and stop the
timers as long as GATE=0 in the TMOD
register
Dept . Of ECE SSET
GATE (cont.)
• The hardware way of starting and stopping the
timer by an external source is achieved by making
GATE=1 in the TMOD register
Dept . Of ECE SSET
TCON Register (1/2)
• Timer control register: TCON
• Upper nibble for timer/counter, lower nibble for
interrupts
• TR (run control bit)
• TR0 for Timer/counter 0; TR1 for Timer/counter 1.
• TR is set by programmer to turn timer/counter on/off.
• TR=0: off (stop)
• TR=1: on (start)
(MSB) (LSB)
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
Timer 1 Timer0 for Interrupt
Dept . Of ECE SSET
TF (timer flag, control flag)
• TF0 for timer/counter 0; TF1 for
timer/counter 1.
• TF is like a carry. Originally, TF=0. When TH-TL
roll over to 0000 from FFFFH, the TF is set to
1.
• TF=0 : not reach
• TF=1: reach
(MSB) (LSB)
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
Timer 1 Timer0 for Interrupt
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Mode 1 Programming
• The following are the characteristics and
operations of mode1:
• It is a 16-bit timer
• It allows value of 0000 to FFFFH to be
loaded into the timer’s register TL and TH
• After TH and TL are loaded with a 16-bit
initial value, the timer must be started
• This is done by SETB TR0 for timer 0 and
SETB TR1 for timer 1
• After being started, it starts to count up
• It counts up until it reaches its limit of FFFFH
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Mode 1 Programming (cont.)
When it rolls over from FFFFH to 0000, it sets high a
flag bit called TF (timer flag)
Each timer has its own timer flag: TF0 for timer 0, and
TF1 for timer 1
This timer flag can be monitored
When this timer flag is raised, one option would be to
stop the timer with the instructions CLR TR0 or CLR
TR1, for timer 0 and timer 1, respectively
In order to repeat the process
TH and TL must be reloaded with the original value
TF must be reloaded to 0
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Steps to Mode 1 Program
1) Load the TMOD value register
2) Indicating which timer (timer 0 or timer 1) is to be
used and which timer mode (1 or 2) is selected
3) Load registers TL and TH with initial count value
4) Start the timer
5) Keep monitoring the timer flag (TF)
6) With the JNB TFx,target instruction to see if it is
raised
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Steps to Mode 1 Program (cont.)
7) Get out of the loop when TF becomes high
8) Stop the timer
9) Clear the TF flag for the next round
10) Go back to Step 2 to load TH and TL again
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Finding the Loaded Timer Values
• To calculate the values to be loaded into the TL
and TH registers:
• Assume XTAL = 11.0592 MHz
• Divide the desired time delay by 1.085 us
• Perform 65536 – n, where n is the decimal
value we got in Step1
• Convert the result of Step2 to hex, where
yyxx is the initial hex value to be loaded
into the timer’s register
• Set TL = xx and TH = yy
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
CPL P1.5 ; Comp. P1.5 to get Hi, Lo
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Write a 8051 program to toggle only the bit P1.5
continuously every 5 ms.Use Timer 0,mode 1(16-
bit) to create the delay.
• # include <reg51.h>
• void T0M1Delay(void)
• sbit mybit=P1^5
• Void main(void)
{
While(1)
{
mybit= ֘ mybit;
T0M1Delay();
}
}
• Void T0M1Delay(void)
•{
• TMOD=0x01; //timer 0,mode1(16 bit )
• TL0=0x00;
• TH0=0xEE;
• TR0=1;
• While(TF0==0);
TR0=0;
TF0=0;
}
CPL P2.3 ; Comp. P2.3 to get Hi, Lo
CLR TF1 ; Clear timer 1 flag
SJMP AGAIN ;Reload timer
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Mode 2 Programming
• The following are the characteristics and
operations of mode 2:
• It is an 8-bit timer
• It allows only values of 00 to FFH to be
loaded into the timer’s register TH
• After TH is loaded with the 8-bit value, the
8051 gives a copy of it to TL
• Then the timer must be started
• This is done by the instruction SETB TR0 for
timer 0 and SETB TR1 for timer 1
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Mode 2 Programming (cont.)
• After the timer is started, it starts to count up by
incrementing the TL register
• It counts up until it reaches its limit of FF
• When it rolls over from FFH to 00, it sets high the TF (timer
flag)
• When TF is set to 1, TL is reloaded automatically with the
original value kept by the TH register
• To repeat the process, we must simply clear TF and let it go
without any need by the programmer to reload the original
value
Mode 2 Programming (cont.)
• Mode 2 can auto-reload, in contrast with mode 1 in which the
programmer has to reload TH and TL
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Steps to Mode 2 Program
• Load the TMOD value register
• Indicating which timer (timer 0 or timer 1) is to be used,
and the timer mode (mode 2) is selected
• Load the TH registers with the initial count value
• Start timer
• Keep monitoring the timer flag (TF)
• With the JNB TFx,target instruction to see whether it is
raised
• Get out of the loop when TF goes high
• Clear the TF flag
• Go back to Step 4
• Since mode 2 is auto-reload
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Counter Programming
• Timers can also be used as counters
• Counting events happening outside the 8051
• A pulse outside of the 8051 increments the TH,
TL registers
• TMOD and TH, TL registers are the same as for
the timer
• Programming the timer also applies to
programming it as a counter
• Except the source of the frequency
• The C/T bit in the TMOD registers decides the
source of the clock for the timer
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Counter Programming (cont.)
• When C/T = 1, the timer is used as a counter and gets its pulses
from outside the 8051
• The counter counts up as pulses are fed from pins 14 and 15
• These pins are called T0 (timer 0 input) and T1 (timer 1 input)
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Dept . Of ECE SSET
TCON Register
� TCON (timer control) register is an 8-bit register
Dept . Of ECE SSET
TCON Register (cont.)
� TCON register is a bit-addressable register
Dept . Of ECE SSET
Case of GATE = 1
� The start and stop of the timer are done externally through pins
P3.2 and P3.3 for timers 0 and 1, respectively
� Allows to start or stop the timer externally at any time via a simple
switch
Dept . Of ECE SSET
You might also like
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller 8051 Programming in CDocument22 pagesMicrocontroller 8051 Programming in CM.K50% (2)
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For: Arm Assembly LanguageDocument129 pagesSolutions Manual For: Arm Assembly Languagemohammed IrheemNo ratings yet
- Timers, Serial, InterDocument107 pagesTimers, Serial, Inters sreehari,No ratings yet
- Lecture-6 (Microprocessors and Microcontrollers)Document25 pagesLecture-6 (Microprocessors and Microcontrollers)KhuleedShaikhNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504751_2024-03-18_Reference-Material-IDocument53 pagesWINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504751_2024-03-18_Reference-Material-IDivya JagwaniNo ratings yet
- 8051 TimerDocument36 pages8051 TimerSanthosh CricketNo ratings yet
- MPMC - Module - 3 - Part-2Document55 pagesMPMC - Module - 3 - Part-2atharv atreNo ratings yet
- Configure and Use 8051 Timers and CountersDocument40 pagesConfigure and Use 8051 Timers and Countersআশিক পালোয়ানNo ratings yet
- 6 8051 TimersDocument45 pages6 8051 TimersharinkhedetNo ratings yet
- Iv TimersDocument48 pagesIv TimersanishthNo ratings yet
- Timers, Serial CommunicationDocument19 pagesTimers, Serial CommunicationVyshnav PNo ratings yet
- Timers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Document51 pagesTimers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Sureka N Assistant Professor - ECENo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504751_2024-03-27_Reference-Material-IDocument73 pagesWINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504751_2024-03-27_Reference-Material-IDivya JagwaniNo ratings yet
- Parul Institute of Engineering & Technology: Subject Code:-151001 Name of Subject: - Microcontroller and InterfacingDocument35 pagesParul Institute of Engineering & Technology: Subject Code:-151001 Name of Subject: - Microcontroller and InterfacingSiva CharanNo ratings yet
- Timers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Document57 pagesTimers, Serial Port & Interrupts in 8051Kadher Naina MohamedNo ratings yet
- 8051 Timer CounterDocument98 pages8051 Timer CounterpremNo ratings yet
- MICROCONTROLLER NOTES Unit 6Document13 pagesMICROCONTROLLER NOTES Unit 6SOMESH B SNo ratings yet
- Basics of Interrupts.: Steps Taken by Processor While Processing An InterruptDocument10 pagesBasics of Interrupts.: Steps Taken by Processor While Processing An InterruptAmy OliverNo ratings yet
- 8051 Timers Used as Timers, Counters or Both with Mode 1 and Mode 2 ProgrammingDocument4 pages8051 Timers Used as Timers, Counters or Both with Mode 1 and Mode 2 ProgrammingQWENo ratings yet
- Module - 4: 8051 Timers and Serial PortDocument37 pagesModule - 4: 8051 Timers and Serial PortPramod PatilNo ratings yet
- 8051 TIMER & Interrupt PROGRAMMING IN ASSEMBLY AND CDocument63 pages8051 TIMER & Interrupt PROGRAMMING IN ASSEMBLY AND CMehran PashaeiNo ratings yet
- Timer CountersDocument70 pagesTimer CountersnNo ratings yet
- 8051 Timer Programming in Assembly and C: ObjectivesDocument17 pages8051 Timer Programming in Assembly and C: Objectivessohail aminNo ratings yet
- Programming Timers on the 89S52 MicrocontrollerDocument48 pagesProgramming Timers on the 89S52 MicrocontrollerManjunath ShimogaNo ratings yet
- Counter/Timer Programming in The 8051Document40 pagesCounter/Timer Programming in The 8051Ashmiya leninNo ratings yet
- Lec4 8051 Timers CountersDocument10 pagesLec4 8051 Timers CountersOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- 9-Timer Programming-01-02-2023Document60 pages9-Timer Programming-01-02-2023BRO CUBIESNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller & Its Applications: TimersDocument14 pagesMicrocontroller & Its Applications: Timersmukundiyer_300No ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller - Timer ProgrammingDocument16 pages8051 Microcontroller - Timer ProgrammingABHISHEK DWIVEDI (RA2111043010082)No ratings yet
- Real Timer ControlDocument94 pagesReal Timer ControlSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- 6-Timer Programming-09-02-2024Document60 pages6-Timer Programming-09-02-2024someshwaranmNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 NotesDocument46 pagesModule - 4 NotesManjuanthNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Lec - 8051 - Part2 2Document76 pagesWeek 5 - Lec - 8051 - Part2 2basit qureshiNo ratings yet
- Generate 8051 Timer DelayDocument8 pagesGenerate 8051 Timer Delaymuralimunraj100% (1)
- Module 4 MC 18EC46 Timer CounterDocument19 pagesModule 4 MC 18EC46 Timer Counterkirthi bharadwajNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504752_2024-03-18_Reference-Material-I (1)Document32 pagesWINSEM2023-24_BECE320E_ETH_VL2023240504752_2024-03-18_Reference-Material-I (1)lakshit.choudhary2021No ratings yet
- 8051 CH9 950217Document103 pages8051 CH9 950217Amardeep PotdarNo ratings yet
- Unit-III 8051 Timers, Interrupts and Serial Communication: TH/TL (Timer High/ Timer Low)Document19 pagesUnit-III 8051 Timers, Interrupts and Serial Communication: TH/TL (Timer High/ Timer Low)Rushikesh NandeNo ratings yet
- 8051 Timers and Serial Port GuideDocument16 pages8051 Timers and Serial Port GuidePate VishnuNo ratings yet
- Timers and Counters Interfacing With 8051Document12 pagesTimers and Counters Interfacing With 8051Faizan RajNo ratings yet
- Timer Serial and InterruptDocument20 pagesTimer Serial and InterruptAyan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Timers and CounterDocument5 pagesDifference Between Timers and CounterAmit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ec522 8051 10Document63 pagesEc522 8051 10Anurag BansalNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document68 pagesWeek 7Swapnil Sen100% (1)
- TimerDocument29 pagesTimerhanhdoducNo ratings yet
- 8051 TimersDocument55 pages8051 TimersAbhiroop ReddyNo ratings yet
- TimersDocument17 pagesTimers87krishna331No ratings yet
- 8051 Timers Mode ProgrammingDocument16 pages8051 Timers Mode ProgrammingjaltitiNo ratings yet
- 8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CDocument101 pages8051-CH9-TimePmg in Assem & CshivaspyNo ratings yet
- Timer/Counter Guide for AVR MicrocontrollersDocument66 pagesTimer/Counter Guide for AVR Microcontrollersdoddysuryo100% (1)
- 4.9 Timers - Counters in 8051Document11 pages4.9 Timers - Counters in 8051Smarajit MishraNo ratings yet
- 5 Timer (Part 1)Document29 pages5 Timer (Part 1)dbhargavreddyNo ratings yet
- PIC TimersDocument16 pagesPIC TimersSmita PatilNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Typed NotesDocument34 pagesUnit 5-Typed NotesAparna durairajNo ratings yet
- Timer Programming: The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and CDocument62 pagesTimer Programming: The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and CAnab MalikNo ratings yet
- It Is A 16 Bit Timer. Therefore It Allows The Value 0000 ToDocument6 pagesIt Is A 16 Bit Timer. Therefore It Allows The Value 0000 ToSuman KumarNo ratings yet
- Timers - Counters in 8051Document16 pagesTimers - Counters in 8051rajesh koneNo ratings yet
- 8051 Timers Programming in CDocument12 pages8051 Timers Programming in CDr. Ritula ThakurNo ratings yet
- 5 Timer (Part 1)Document29 pages5 Timer (Part 1)lsuwdaa100% (1)
- Module 3 NAND and NOR LogicDocument19 pagesModule 3 NAND and NOR LogicleevasusanNo ratings yet
- ECL 202 Analog Circuits and Simulation Lab: Course Information & Course PlanDocument10 pagesECL 202 Analog Circuits and Simulation Lab: Course Information & Course PlanleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Module1 QPDocument1 pageModule1 QPleevasusanNo ratings yet
- LayoutDocument22 pagesLayoutleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Part 2 - Serial Data TransferDocument52 pagesModule 4 - Part 2 - Serial Data TransferleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 NAND and NOR LogicDocument19 pagesModule 3 NAND and NOR LogicleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor bellows system for crystal growthDocument4 pagesSemiconductor bellows system for crystal growthleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Harris Module2Document137 pagesChapter 5 Harris Module2leevasusanNo ratings yet
- Basic Operation of ComputerDocument13 pagesBasic Operation of ComputerleevasusanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Question BankDocument2 pagesMODULE 1 Question BankleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Multistage Amplifier Frequency Response: No Zeroes Exactly One "Dominant" Pole (Document10 pagesMultistage Amplifier Frequency Response: No Zeroes Exactly One "Dominant" Pole (leevasusanNo ratings yet
- Finfet: Fin Field Effect TransistorDocument12 pagesFinfet: Fin Field Effect TransistorleevasusanNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter4Document36 pages14 Chapter4Sk Sariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Survey On IoTDocument17 pagesSurvey On IoTleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Boe Final Manual IisemDocument44 pagesBoe Final Manual Iisemkaran_bhalla22No ratings yet
- EP2105983A1 AbstractDocument3 pagesEP2105983A1 AbstractleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Voltage RegulatorsDocument13 pagesVoltage RegulatorsleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - EdcDocument48 pagesModule 6 - EdcleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Voltage RegulatorsDocument13 pagesVoltage RegulatorsleevasusanNo ratings yet
- 15EC102L Electronics Engineering PracticesDocument64 pages15EC102L Electronics Engineering PracticesleevasusanNo ratings yet
- BEDocument81 pagesBEWatan SahuNo ratings yet
- Aic Modified 1Document80 pagesAic Modified 1leevasusanNo ratings yet
- EE 010 408 Electronic Circuits LabDocument1 pageEE 010 408 Electronic Circuits LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Analogelectronics 150608164354 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument58 pagesAnalogelectronics 150608164354 Lva1 App6891 PDFrijilpoothadiNo ratings yet
- Design of The MIPS ProcessorDocument24 pagesDesign of The MIPS Processorwelcome to my worldNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Arduino: Atmega8 Atmega168 Atmega8 Atmega168Document1 pageEvolution of Arduino: Atmega8 Atmega168 Atmega8 Atmega168LeunamezNo ratings yet
- CEG 2131 - Fall 2006 - FinalDocument16 pagesCEG 2131 - Fall 2006 - FinalAmin DhouibNo ratings yet
- Verilog Code For Counter With Testbench PDFDocument1 pageVerilog Code For Counter With Testbench PDFBien MedinaNo ratings yet
- ARM Cortex-A12 Block DiagramDocument1 pageARM Cortex-A12 Block Diagram文帅宋No ratings yet
- An Efficient Methodology For Achieving Optimal Power and Speed in AsicDocument22 pagesAn Efficient Methodology For Achieving Optimal Power and Speed in Asickumarbsnsp50% (2)
- SDMK RSUD DATOE BINANGKANG 2018 DesDocument596 pagesSDMK RSUD DATOE BINANGKANG 2018 DesArlinto SimbalaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument2 pagesLogATS TLNo ratings yet
- Ram and Its Types: Multiplexing DemultiplexingDocument3 pagesRam and Its Types: Multiplexing Demultiplexingusman100% (1)
- The CPU & Storage: Hardware 1Document58 pagesThe CPU & Storage: Hardware 1laelaNo ratings yet
- 8086 Addressing Modes ExplainedDocument30 pages8086 Addressing Modes ExplainedFiza ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & Computer Architecture IntroductionDocument50 pagesMicroprocessor & Computer Architecture Introductionanon_999010792No ratings yet
- The - Format Is Usually Used To Store Data.: A) BCD B) Decimal C) Hexadecimal D) OctalDocument27 pagesThe - Format Is Usually Used To Store Data.: A) BCD B) Decimal C) Hexadecimal D) OctalSuchit KumarNo ratings yet
- E MMC v4.41 and v4.5: Architecture For High Speed Architecture For High SpeedDocument38 pagesE MMC v4.41 and v4.5: Architecture For High Speed Architecture For High SpeedNoss DakoNo ratings yet
- Midterm1 SolDocument5 pagesMidterm1 SolLiaqat Hussain BhattiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Embedded SystemDocument75 pagesUnit 2 - Embedded Systemsujith100% (4)
- CH04 COA11eDocument48 pagesCH04 COA11eShi TingNo ratings yet
- d36978004 S5000vsa Tps v1 0Document84 pagesd36978004 S5000vsa Tps v1 0enforcer2008No ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Interfacing Course OverviewDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor and Interfacing Course OverviewEr Umesh ThoriyaNo ratings yet
- Simple OS Assignment ReportDocument24 pagesSimple OS Assignment ReportNguyen Trong Tin50% (2)
- EC8691 Notes PDFDocument136 pagesEC8691 Notes PDFKeerthana Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- 8 Bit Microcontroller: Vishal V.Panchbhai, Asst. Prof. E & T DeptDocument41 pages8 Bit Microcontroller: Vishal V.Panchbhai, Asst. Prof. E & T DeptSagar DhapkeNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer Initialization and OperationDocument19 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer Initialization and OperationNaganarasaiah GoudNo ratings yet
- Coa - 2nd Sessional (Ece)Document1 pageCoa - 2nd Sessional (Ece)Dr. Mohd ShahidNo ratings yet
- MachinesDocument2 pagesMachinesmohamedNo ratings yet
- Memory Management in OSDocument76 pagesMemory Management in OSratanNo ratings yet
- Stack OrganizationDocument33 pagesStack OrganizationNikhita VNo ratings yet
- 23 Canlas Melson Ziolo PDocument20 pages23 Canlas Melson Ziolo PMelson CanlasNo ratings yet
- 8086 Interrupt: Interrupt Vector Table - IVTDocument2 pages8086 Interrupt: Interrupt Vector Table - IVTkaram hayderNo ratings yet