0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views20 pagesAutoCAD Drawing Tools Overview
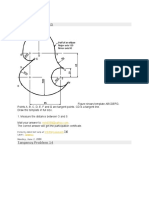
This document describes how to use various drawing tools in AutoCAD including the Arc, Ellipse, Polygon, and Rectangle tools. It also introduces the AutoSnap and Object Snap (Osnap) systems for ensuring accuracy when constructing drawings, as well as the Dynamic Input (DYN) system for displaying coordinate information. Examples are provided for constructing geometric shapes using different tools and snapping methods.
Uploaded by
Fasil GetachewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views20 pagesAutoCAD Drawing Tools Overview
This document describes how to use various drawing tools in AutoCAD including the Arc, Ellipse, Polygon, and Rectangle tools. It also introduces the AutoSnap and Object Snap (Osnap) systems for ensuring accuracy when constructing drawings, as well as the Dynamic Input (DYN) system for displaying coordinate information. Examples are provided for constructing geometric shapes using different tools and snapping methods.
Uploaded by
Fasil GetachewCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd