Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reymond Clacio - PPT Generator Principle
Uploaded by
Reymond Clacio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views18 pagesGENERATOR
Original Title
Reymond Clacio_ppt generator principle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGENERATOR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views18 pagesReymond Clacio - PPT Generator Principle
Uploaded by
Reymond ClacioGENERATOR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
GENERATOR PRINCIPLE
What is a generator? What is it used for? How
does it work? Does it have different types? If yes,
what are they? What are the different components
of a generator and what do they do? These are the
questions that should be answered before we buy a
generator? If you need a generator and are about to
buy one, we have good news for you, because we
are going to answer all these questions in this article
comprehensively and creatively.
What Is a Generator?
Generators are useful devices that provide electrical
power during a power cut-off and prevent discontinuity of
day and night affairs and activities or disruption in
operations in different conditions and places. All a generator
does is to convert the mechanical energy provided from an
external source, to electrical energy to provide enough
energy for other appliances. It works based on the Faraday
law of electromagnetic induction.
This law says that wherever a conductor is put among a
varying magnetic field, the electromagnetic flux is induced.
There are different electrical and physical configurations for
Generators. This diversity in the configuration is for use in
different applications. In the following sections, we will
elaborate on how a generator works, what different types it
has, and what parts a generator consists of. Read on to get
more acquainted with the world of this amazing device.
Types of Generators
The generators are divided into two
different and basic classes or categories which
are AC (Alternating Current) generator and DC
(Direct Current) generator.
AC Generator
The AC generators or as they are also called the
Alternator, are one of the most essential devices of
providing electrical power in several conditions in our life.
ACs work based on the principle of electromagnetic
induction. AC generators are classified into two categories:
induction generators and synchronous generators. As
there are no brushes in this type of generators,
maintenance is almost free. the size of ACs is smaller in
comparison to DCs. So, they are more commonly used.
And at last, what makes this type more popular is that the
losses of ACs are less than DCs.
DC Generator
This type of generator is commonly found in off-grid
applications. The DCs are classified into three main
categories according to the way their magnetic field is
developed in the stator: permanent-magnet generators,
separately-excite generators, and self-excited generators.
Some advantages of DCs are: they are designed plainly. They
are usually used for operating large motors and electrical
devices requiring direct control. DCs diminishes the
fluctuations described by smoothing the output voltage
through a regular set of coils around the armature for some
steady state applications.
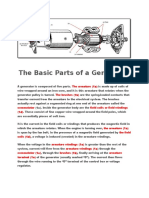
Components of Generators
So far, we have got familiar with the working principle and
different types of generators and gradually we are getting closer
to the answer to the question “what is a generator?” in this
section, we are about to make you acquainted with the main
parts of a generator. Apart from the mainframe, a generator
consists of 6 main components: the engine, the fuel system,
alternator, cooling, exhaust, and lubricating systems. We put
these 6 parts in 4 main categories. Keep reading to learn more
about these components.
1. The Engine
Maybe the most important part of every machine is the
engine. it is generally the part of the whole system that
converts the fuel into usable energy and helps it move or
perform its mechanical function. Thus, the engine is
sometimes called the machine’s prime mover. In a
generator, the engine fuel source can be gasoline, diesel,
natural gas, propane, bio-diesel, water, sewage gas, or
hydrogen. The engine uses one of these kinds of fuel to
create mechanical energy the generator will convert into
electricity. Some engines commonly used in the design of
generators include reciprocating, steam, turbine engines,
and microturbines.
2. Fuel System
All the Generators that are running on one
of the different types of fuel mentioned before
have a system that gathers and pumps the fuel
to the engine. The fuel system contains a tank
storing enough fuel to power a generator for an
equivalent number of hours. There is also a
pipe connecting to the tank and then to the
engine, and the return pipe connects the
engine to the fuel tank for the return of fuel.
There is a fuel pump whose job is to
move the fuel from the tank through a fuel
pipe and then to the engine. Another part of
the fuel system is the fuel filter whose job is
to filter any debris from the fuel before it
moves to the engine. The last component of
the fuel system is the fuel injector. The fuel
injector’s job is to atomize the fuel and then
inject the fuel directly into the combustion
chamber of the engine.
3. Alternator and Voltage Regulator
Maybe we can say that the main job of a
generator is up to the alternator. This
component turns the mechanical energy
produced by the engine into electrical current.
The alternator embodies the stator, a stationary
part of a set of coils, and the rotor or the
armature which creates a stable turning
electromagnetic field around the stator. Overall,
the alternator generates an electrical voltage
that must be regulated to produce a constant
current suitable for a practical use.
4. Cooling, Exhaust, and Lubricating Systems
There is a cooling system to prevent overheating
and regulate the temperature of the generator
components during the use. Some of the
generators use a fan, coolant, or both of them to
control the temperature of the generator at work.
As the combustion chamber of the generator
converts fuel, the generator will also create
exhaust..
The harmful gases emitted by the generator
during the use are dispelled by exhaust systems.
The last part is the lubricating system. As
Generators consists of many moving parts and
each of them requires oiling to move smoothly,
there should be a lubricating system which keeps
the generator well oiled and smooth
Conclusion
In this article, we tried to show you what exactly a
generator does. To answer the question of “what is a
generator?” we analyzed the working principle of a
generator and how it works. We explained the rules a
generator follows to turn the mechanical energy into
electrical power. After that, we reached to the different
types of generators and talked about two main types of
generators.
That’s all. Thank you
You might also like
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
- What Is A GeneratorDocument6 pagesWhat Is A GeneratorLeta NegasaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Generator A Simple Yet Useful GuideDocument8 pagesParts of Generator A Simple Yet Useful GuideClark Kent FuentebellaNo ratings yet
- Generadores de Corriente CONTINUA InglesDocument3 pagesGeneradores de Corriente CONTINUA InglesJoel ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Parts A Complete DescriptionDocument7 pagesDiesel Generator Parts A Complete DescriptionAli EndrisNo ratings yet
- AC Machine (Generator-Alternator) - WPS OfficeDocument88 pagesAC Machine (Generator-Alternator) - WPS OfficeJohnray HabolNo ratings yet
- Electric Generators: Types and ComponentsDocument5 pagesElectric Generators: Types and ComponentsReyes AlhynNo ratings yet
- InternDocument4 pagesInternSANTHOSHKUMAR VELMURUGAN (RA1911038010018)No ratings yet
- Types of AlternatorDocument8 pagesTypes of AlternatorOmar SelamiNo ratings yet
- The Engine: Sensitivity: LNT Construction Internal UseDocument3 pagesThe Engine: Sensitivity: LNT Construction Internal Usesowndarya balambikaNo ratings yet
- Generator WorkingDocument18 pagesGenerator WorkingchetanpsNo ratings yet
- How Generators Create ElectricityDocument7 pagesHow Generators Create ElectricityshivNo ratings yet
- How Alternators, Motors, Converters and Transformers WorkDocument4 pagesHow Alternators, Motors, Converters and Transformers WorkPEE JAYNo ratings yet
- How Does A Diesel Generator Create Electricity?Document3 pagesHow Does A Diesel Generator Create Electricity?ShreenivasNo ratings yet
- Revisi TugasDocument3 pagesRevisi Tugassyefira.anastasyaNo ratings yet
- AC generators:AC Generators Are Known As Single-Phase Generators and Are Limited To 25kWDocument9 pagesAC generators:AC Generators Are Known As Single-Phase Generators and Are Limited To 25kWJera ObsinaNo ratings yet
- Generator and AlternatorDocument8 pagesGenerator and Alternatorvirgilio mercadoNo ratings yet
- Denso Report FileDocument32 pagesDenso Report FileRahul Pandey75% (4)
- Electric Motor Voltage: Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Electric DrivesDocument17 pagesElectric Motor Voltage: Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Electric DrivesRAJOLI GIRISAI MADHAVNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument9 pagesIntroductiongalihwidiastoNo ratings yet
- Drive: Electric MotorDocument18 pagesDrive: Electric Motorsunny112811No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Standby GeneratorDocument26 pagesChapter 6 - Standby Generatorruben_robin67% (3)
- Indiction Generator TheoryDocument4 pagesIndiction Generator Theoryraghu_mnNo ratings yet
- PP Lab.Document16 pagesPP Lab.Sanjay C JNo ratings yet
- Electrical interview questions on motor principles and power electronicsDocument26 pagesElectrical interview questions on motor principles and power electronicsNavdeepNo ratings yet
- Diesel GeneratorDocument21 pagesDiesel GeneratoreiferjNo ratings yet
- Electric Drive: IntroductionDocument5 pagesElectric Drive: IntroductionThomas RussellNo ratings yet
- Ggenerator AlternatorDocument4 pagesGgenerator AlternatorShakir FadzliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1Justine James NuylesNo ratings yet
- Bing AwinDocument3 pagesBing Awinsyefira.anastasyaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Alternator?: Battery Voltage Regulator AlternatorDocument5 pagesWhat Is An Alternator?: Battery Voltage Regulator AlternatorNeverhhhNo ratings yet
- GeneratorDocument42 pagesGeneratorHAMMATION NITRO TRAXINo ratings yet
- M1 BasicsDocument15 pagesM1 BasicsSenpai GamingNo ratings yet
- How electrical drives precisely control motor speedDocument6 pagesHow electrical drives precisely control motor speedkaushik9595No ratings yet
- Electric Motor - Parts of Motor, Working of Electric Motor & UsesDocument7 pagesElectric Motor - Parts of Motor, Working of Electric Motor & UsesmanjuNo ratings yet
- How Generators Create ElectricityDocument6 pagesHow Generators Create ElectricityNaveen Babu DNo ratings yet
- DG SetDocument19 pagesDG SetSatyajit PandaNo ratings yet
- AC Motor, Servo Motor and Stepper MotorDocument12 pagesAC Motor, Servo Motor and Stepper MotorAhmedSayedNo ratings yet
- A Universal Motor Is UniversalDocument6 pagesA Universal Motor Is UniversalrodinooNo ratings yet
- Generating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasDocument4 pagesGenerating Electricity by Using Exhaust GasAnonymous j0aO95fgNo ratings yet
- Electrical-Group 3Document12 pagesElectrical-Group 3Lizabeth Pillos MarquezNo ratings yet
- What Is An AlternatorDocument16 pagesWhat Is An AlternatorSanrasni100% (1)
- Wa0006.Document14 pagesWa0006.5062 Pavankumar vepanjeriNo ratings yet
- The Basic Parts of A GeneratorDocument4 pagesThe Basic Parts of A GeneratorFionah Mae PraderoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterDocument35 pagesCharacteristics of Electric Drives: Subject Name: Electric Drives Class: 4 Year/ VII SemesterBabbu DograNo ratings yet
- Diesel (1) Az InternDocument6 pagesDiesel (1) Az InternrazviNo ratings yet
- Generators: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument6 pagesGenerators: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechanical EngineeringKeanu EspinaNo ratings yet
- AlternatorsDocument11 pagesAlternatorsIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light That Is Powered Through Speed Breaker Chapter - 1Document54 pagesAutomatic Street Light That Is Powered Through Speed Breaker Chapter - 1Anu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report DLW VaranasiDocument84 pagesSummer Training Report DLW VaranasiHemant MeenaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Electrical System PDFDocument31 pages11 - Electrical System PDFTanaji ShindeNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electrical & Electronics Unit II: Presented byDocument58 pagesAutomotive Electrical & Electronics Unit II: Presented bymharitmsNo ratings yet
- Charging System and ComponentsDocument58 pagesCharging System and ComponentsmharitmsNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electrical & Electronics Unit II: Presented byDocument58 pagesAutomotive Electrical & Electronics Unit II: Presented bymharitms100% (1)
- Motor Fundamentals PDFDocument12 pagesMotor Fundamentals PDFrajeshpalla4uNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor IT ReportDocument9 pagesElectric Motor IT ReportVincentNo ratings yet
- The Charging System Has Three Main Components: The Alternator, The Voltage Regulator, and The BatteriesDocument20 pagesThe Charging System Has Three Main Components: The Alternator, The Voltage Regulator, and The BatteriesMae CherryNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and WorkingDocument7 pagesUniversal Motor A Simple Guide To Construction Types and Workingmireyo1488No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNo ratings yet
- Clacio, Reymond Assignment1Document3 pagesClacio, Reymond Assignment1Reymond ClacioNo ratings yet
- Clacio, Reymond Method1act1Document1 pageClacio, Reymond Method1act1Reymond ClacioNo ratings yet
- Clacio, Reymond Ass2Document1 pageClacio, Reymond Ass2Reymond ClacioNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus, IDocument143 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus, IHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jni QseeDocument1 pageJni QseeReymond ClacioNo ratings yet
- Integral CalculusDocument408 pagesIntegral CalculusCharlyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Nauticat 38Document4 pagesNauticat 38f.sastreguaschNo ratings yet
- Om615 616 617 PDFDocument221 pagesOm615 616 617 PDFAnonymous wpUyixsj100% (1)
- Grader presentation-OPT-latestDocument34 pagesGrader presentation-OPT-latestJack SonNo ratings yet
- Refined EX1200-7 excavator optimized for efficiencyDocument13 pagesRefined EX1200-7 excavator optimized for efficiencyaung OoNo ratings yet
- Petroleum-Based and Bio-Derived Jet Fuel Efficiency Optimization Using Fuel Injection in A 34cc 4-Stroke Spark-Ignition EngineDocument9 pagesPetroleum-Based and Bio-Derived Jet Fuel Efficiency Optimization Using Fuel Injection in A 34cc 4-Stroke Spark-Ignition Enginemehdi siyahiNo ratings yet
- Mobile 1Document16 pagesMobile 1udantoNo ratings yet
- 330D Excavator Hydraulic System - Attachment: PUMP GPDocument2 pages330D Excavator Hydraulic System - Attachment: PUMP GPKJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- Rotary Blasthole Drill-MD6240Document8 pagesRotary Blasthole Drill-MD6240GARINo ratings yet
- SL 500 ManualDocument151 pagesSL 500 ManualpradenanNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Automobile Engineering Course DetailsDocument7 pagesLovely Professional University Automobile Engineering Course Detailsketanprasad56No ratings yet
- Final Period Long Quiz - ME 410 - 3101Document2 pagesFinal Period Long Quiz - ME 410 - 3101siva sachaphibulkijNo ratings yet
- Baotian Rambo 150cc BT151T 2fC2 OMANDocument23 pagesBaotian Rambo 150cc BT151T 2fC2 OMANSOFIA GHIMPUNo ratings yet
- Waukesha F11gsi - Valve Clearence - CompressionDocument2 pagesWaukesha F11gsi - Valve Clearence - Compressionnicol_sg100% (1)
- Carb 2Document29 pagesCarb 2Selva RamNo ratings yet
- 6,8dk-28 Instruction Manual (Operation)Document109 pages6,8dk-28 Instruction Manual (Operation)Ira PaschenkoNo ratings yet
- VAG K+CAN key device programs keys and bypasses immobilizersDocument4 pagesVAG K+CAN key device programs keys and bypasses immobilizersalmia tronics100% (1)
- UK Purchased Fm-Ul-Cul Approved Ratings KW/BHP: Fire Pump EnginesDocument11 pagesUK Purchased Fm-Ul-Cul Approved Ratings KW/BHP: Fire Pump Enginesluis vilcañaupaNo ratings yet
- A Maintenance Report On d6h LGP and 966cDocument2 pagesA Maintenance Report On d6h LGP and 966cBOMA DOUGLASNo ratings yet
- Better Every Call.: Engines and Commercial Mobile Generators For Fire and Emergency ApplicationsDocument16 pagesBetter Every Call.: Engines and Commercial Mobile Generators For Fire and Emergency ApplicationsvaisakhpillaiNo ratings yet
- 09 MaintenanceDocument58 pages09 MaintenanceJel SantanaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Market Potential of CNG Engine Oil FOR Gulf Oil Corporation Limited BY Neha 203Document68 pagesAssessing Market Potential of CNG Engine Oil FOR Gulf Oil Corporation Limited BY Neha 203Abhinav SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Paccar - PX-7 CM2350 (2013-17)Document17 pagesPaccar - PX-7 CM2350 (2013-17)solucionesdiesel2022No ratings yet
- Autocom 2017.01 - CARS - ENG PDFDocument460 pagesAutocom 2017.01 - CARS - ENG PDFCorban MihaiNo ratings yet
- 2015 QRG Lube FilterDocument215 pages2015 QRG Lube FilteraleksandrNo ratings yet
- YM351A YM357A: TractorDocument10 pagesYM351A YM357A: TractorLeo ArmandaNo ratings yet
- 146-140-SWE80-80H Service ManualDocument77 pages146-140-SWE80-80H Service Manualmin thet100% (2)
- Used Ford Ecosport Cars in Pune - Second Hand Ford Ecosport in PuneDocument1 pageUsed Ford Ecosport Cars in Pune - Second Hand Ford Ecosport in PuneARPIT GOHOKARNo ratings yet
- ASM User's Manual Covers 3 Roller Bending Machine SafetyDocument38 pagesASM User's Manual Covers 3 Roller Bending Machine SafetyPhuc Le HongNo ratings yet
- Premium Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Oil: Pertamina Meditran SX Ultra Gle SAE 15W-40 API CJ-4Document2 pagesPremium Heavy-Duty Diesel Engine Oil: Pertamina Meditran SX Ultra Gle SAE 15W-40 API CJ-4agnovNo ratings yet
- Hydraload Model Card en-GBDocument6 pagesHydraload Model Card en-GBAnonymous 1XBCMXNo ratings yet