Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbial Disease of The Eye
Microbial Disease of The Eye
Uploaded by
Joanne Espinosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesConjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that can be caused by viral, bacterial, or allergic reactions. Common symptoms include redness, irritation, watering eyes, and discharge. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea that can be caused by fungi, parasites, or exposure to water. It can lead to scarring if deep layers of the cornea are involved. Cytomegalovirus retinitis is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the retina and can lead to blindness in immunocompromised individuals. Bacterial meningitis is a serious infection that occurs when bacteria enter the central nervous system, often through the bloodstream or respiratory tract
Original Description:
Microbial Disease of the Eye
Original Title
Microbial Disease of the Eye
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that can be caused by viral, bacterial, or allergic reactions. Common symptoms include redness, irritation, watering eyes, and discharge. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea that can be caused by fungi, parasites, or exposure to water. It can lead to scarring if deep layers of the cornea are involved. Cytomegalovirus retinitis is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the retina and can lead to blindness in immunocompromised individuals. Bacterial meningitis is a serious infection that occurs when bacteria enter the central nervous system, often through the bloodstream or respiratory tract
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views15 pagesMicrobial Disease of The Eye
Microbial Disease of The Eye
Uploaded by
Joanne EspinosaConjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva that can be caused by viral, bacterial, or allergic reactions. Common symptoms include redness, irritation, watering eyes, and discharge. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea that can be caused by fungi, parasites, or exposure to water. It can lead to scarring if deep layers of the cornea are involved. Cytomegalovirus retinitis is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the retina and can lead to blindness in immunocompromised individuals. Bacterial meningitis is a serious infection that occurs when bacteria enter the central nervous system, often through the bloodstream or respiratory tract
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
MICROBIAL DISEASE OF THE EYE
Presentation by: Joanne Espinosa
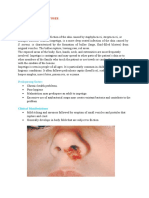
CONJUNCTIVITIS / PINK EYE / MADRAS EYE
• It is the inflammation of the conjunctiva which consist of
the outermost layer of the eye and the inner surface of the
eyelids
• Conjunctivitis most commonly caused by a viral infection
or less commonly a bacterial infection or by allergic
reaction.
SYMPTOMS
• An inflamed, red eye (hyperaemia)
• Irritation (chemosis)
• Watering of the eyes (epiphora)
3 TYPES OF PINK EYE
• VIRAL STRAINS most common and start from one eye
where it cause lot of tears and watery discharge and
within few days, the other eye gets involved
• BACTERIAL STRAINS usually infect one eye but can
show up in both. Your eye will put out lot of pus and
mucus
• ALLERGIC TYPES produce tearing, itching and redness
in both eyes. You might also have an itchy, runny nose
KERATITIS
- is a condition in which the eye cornea, the front part of the eye becomes
inflamed
• Superficial keratitis involves the superficial layers (epithelium) of the cornea.
After healing, this form of keratitis does not leave a scar.
• Deep keratitis involves deeper involves deeper layers of the cornea and the
natural course leaves a scar upon healing that impairs vision if it occurs on or
near the visual axis.
• This can be reduced or avoided with the use of topical corticosteroid eye
drops.
• FUNGAL KERATITIS occurs when part of a tree or plant such as twig injures
the ye, so those people who work with plants are more at risk
• Exposing the eyes to water – such as when swimming or in a hot tub – is at
high risk of keratitis.
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS RETINITIS
• Also known as CMV Retinitis is an inflammation of the
retina of the eye that can lead to blindness. Caused by
human cytomegalovirus, it occurs predominantly in
people whose immune system has been compromised.
• ACANTHAMOEBISASIS
• Acanthmaoebiasis is caused by a protozoan parasite.
Acanthmaoeba is a very common organism within
freshwater and marine environments worldwide. While it
usually doesn’t cause an infection, when it does, it can
damage your vision.
• Acanthamoeba is transmitted through direct contact with
the parasite and the cornea of the eye. Poor contact lens
care is a major risk factor for developing
acanthamoebiasis.
LOIASIS
• Loiasis is caused by a helminth parasite
• You can acquire the infection through the bite of an
infected fly. Once inside the body, the parasite continues
to develop and can migrate to various tissues. It also
produce larvae called microfilariae.
• Both the adult worm and its larvae can cause eye pain,
impaired eye movement, and vision problems including
sensitivity to light.
MICROBIAL DISEASE OF THE NERVOUS
SYSTEM
BACTERIAL MENINGITIS
• is one of the most serious forms of meningitis.
• Bacteria that cause meningitis often gain access to the
CNS through the bloodstream after trauma or a result of
the action of bacterial toxins.
• Bacteria may also spread from structures in the upper
respiratory tract such as oropharynx, nasopharynx,
sinuses and middle ear.
• Patients with head wounds or cochlear implants are also
at risk for developing meningitis.
TETANUS
• Is a non-communicable disease characterized by
uncontrollable muscle spasms (contraction) caused by
the action of TeNT.
• It generally occurs when C. tetani infects the wounds and
produces TeNT, which rapidly binds to neural tissue,
resulting in an intoxication of neurons.
• Generalized tetanus that occurs in a newborn is called
neonatal tetanus.
• Generalized tetanus that occurs in a newborn is called neonatal tetanus.
• Localized tetanus occurs when TeNT only affects the muscle groups close to
the injury site.
• Cephalic tetanus is a rare, localized form of tetanus generally associated with
wounds on the head or face.
• In rare cases, it has occurred in cases of otitis media (middle ear infection).
Cephalic tetanus often results in patients seeing double images, because of
the spasms affecting the muscles that control eye movement.
• Neonatal tetanus typically occurs when the stump of the umbilical cord is
contaminated with spores of C.tetani after delivery.
• After the end of first week of life, infected infants become irritable, feed poorly
and develop rigidity with spasms.
• TETANUS TOXOID (TT) VACCINE is available for
protection and prevention of tetanus. One dose is
recommended fof adolescents and adults as TT booster
every 10 years.
BOTULISM
• Is a rare but frequently fatal illness caused by intoxication
by BoNT. It can occur either as a result of an infection
C.botulinum in which case the bacteria produce BoNt in
vivo or as the result of direct introduction of BoNT into
tissue.
• BOTULINUM TOXIN is often intentionally injected into
people to treat their conditions.
HANSEN’S DISEASE (LEPROSY)
• Is caused by a long, thin, filamentous rod-shaped bacteria Myobacterium
leprae, an obligate intracellular pathogen.
• Hansen’s disease affects the PNS, leading to permanent damage and loss of
appendages or other body parts.
• Hansen’s disease is communicable but not highly contagious.
• Person to person transmission occurs by inhalation into nasal mucosa or
prolonged and repeated contact with infected skin.
• TUBERCULOID HANSEN’S DISEASE is marked by the presence of
relatively few, flat blanched skin lesions with small nodules at the edge and
few bacteria present in the lesion.
• Individuals who are unable to contain the infection may later develop
LEPROMATOUS HANSEN’S DISEASE. This is a progressive form of
disease characterized by nodules filled with acid fast bacilli and
macrophages.
You might also like
- MeningitisDocument6 pagesMeningitisCheena DolormenteNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument32 pagesTetanusVinotheran MichaelNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases With Rashes LastDocument46 pagesViral Diseases With Rashes LastHasan kahhalehNo ratings yet
- Senior Research Microbiologist Molecular Biologist in Philadelphia PA Resume Michele OtteDocument2 pagesSenior Research Microbiologist Molecular Biologist in Philadelphia PA Resume Michele OtteMicheleOtteNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument13 pagesImpetigoTasya SyafhiraNo ratings yet
- Source of Infections 1. Endogenous SourceDocument6 pagesSource of Infections 1. Endogenous SourceDeepu VijayaBhanuNo ratings yet
- Impetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImpetigo, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- ImpetigoDocument24 pagesImpetigoIvan Sitohang100% (2)
- Case Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument14 pagesCase Study of Community Acquired PneumoniaRachelNo ratings yet
- Syndromic Management of STDsDocument13 pagesSyndromic Management of STDsMeenachi SNo ratings yet
- Tetanus DR Moses KazevuDocument13 pagesTetanus DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Neonatal InfectionDocument19 pagesNeonatal InfectionLekshmi ManuNo ratings yet
- Eye DiseaseDocument31 pagesEye DiseaseTsegaye YalewNo ratings yet
- Viral Infection On HumansDocument29 pagesViral Infection On HumansMashimallowNo ratings yet
- 10 Contact DiseasesDocument26 pages10 Contact DiseasesMunazzaNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument18 pagesMeningitisAteeq RahmanNo ratings yet
- Contact Lens-Associated Microbial KeratitisDocument39 pagesContact Lens-Associated Microbial Keratitisณัช เกษมNo ratings yet
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliDocument30 pagesVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliAsad FrazNo ratings yet
- Tinea Cruris Imp Points With ReferencesDocument35 pagesTinea Cruris Imp Points With ReferencesSyed Saqib AliNo ratings yet
- Infectious DermatosesDocument41 pagesInfectious DermatosesJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Eyelid, Conjunctiva and CorneaDocument19 pagesPathology of Eyelid, Conjunctiva and CorneaX And ZNo ratings yet
- Microbio Nervous System LectureDocument15 pagesMicrobio Nervous System LecturesweetiepotamusNo ratings yet
- Neonatal InfectionsDocument18 pagesNeonatal InfectionsSanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- Tinea Barbae Is A Rare Dermatophytic Infection That Is Limited To The Bearded Areas of The FaceDocument3 pagesTinea Barbae Is A Rare Dermatophytic Infection That Is Limited To The Bearded Areas of The FaceMardiah Nurul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Tinea Barbae Is A Rare Dermatophytic Infection That Is Limited To The Bearded Areas of The FaceDocument5 pagesTinea Barbae Is A Rare Dermatophytic Infection That Is Limited To The Bearded Areas of The Facemardiah nurulNo ratings yet
- BacteriologyDocument39 pagesBacteriologyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis 1Document28 pagesConjunctivitis 1Nrs Sani Sule MashiNo ratings yet
- KeratitisDocument16 pagesKeratitisHarmin AliminNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology: Aureus and GABHS 10% of The Time. Methicillin-Resistant S Aureus (MRSA) HasDocument8 pagesEpidemiology: Aureus and GABHS 10% of The Time. Methicillin-Resistant S Aureus (MRSA) HasPutra YdpaNo ratings yet
- Derma 2Document40 pagesDerma 2tyleree3No ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The Different Organ SystemsDocument10 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Different Organ SystemsRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- Red Eye With Normal VisionDocument58 pagesRed Eye With Normal VisionDiskaAstariniNo ratings yet
- DPT PresentationDocument36 pagesDPT PresentationTanviNo ratings yet
- Brain InfectionDocument8 pagesBrain Infectionsistla naveenNo ratings yet
- Traumatic UlcersDocument25 pagesTraumatic UlcersHina MahessarNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria: EpidemiologyDocument3 pagesDiphtheria: EpidemiologyItstineeNo ratings yet
- Session 24 Tetanus and RabiesDocument26 pagesSession 24 Tetanus and RabiesJohn MoshaNo ratings yet
- NAME:-Puspendu Maity. ROLL: - 16101717014. Reg. No: - 171611210014. Subject: - Corneal Ulcer. Semester: - 7 SemesterDocument15 pagesNAME:-Puspendu Maity. ROLL: - 16101717014. Reg. No: - 171611210014. Subject: - Corneal Ulcer. Semester: - 7 SemesterKumar jit MaityNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDocument75 pagesOphthalmology: by Dr. Laraib Jameel RPHDhivya SekarNo ratings yet
- Open Infections 2Document76 pagesOpen Infections 2Jehad AlzubairNo ratings yet
- Shs.317.lec-03 Skin Infections PDFDocument48 pagesShs.317.lec-03 Skin Infections PDFHashir AliNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument14 pagesMicroorganismsDima MasadehNo ratings yet
- CORYNEBACTERIUMDocument22 pagesCORYNEBACTERIUMHamidreza RahmaniNo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document48 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Nauli PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- TrachomaDocument24 pagesTrachomabenedicta ahiaborNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 CNSDocument13 pagesPBL 3 CNSAbdullah SohailNo ratings yet
- Eye Pain and DischargeDocument53 pagesEye Pain and DischargeJitendra ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On The Topic TetanusDocument16 pagesA Seminar On The Topic TetanusRajat PadhanNo ratings yet
- Session 39 MeningitisDocument25 pagesSession 39 MeningitisJohn MoshaNo ratings yet
- Ocular Manifestations in TB, Leprosy and SyphilisDocument62 pagesOcular Manifestations in TB, Leprosy and SyphilisAnumeha JindalNo ratings yet
- Eye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDocument63 pagesEye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- VARICELLA PowerpointDocument28 pagesVARICELLA PowerpointMelina SagalaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading: Update On The Management of Infectious KeratitisDocument35 pagesJournal Reading: Update On The Management of Infectious KeratitisninataniaaaNo ratings yet
- Brain InfectionDocument8 pagesBrain Infectionsistla naveenNo ratings yet
- Airborne Transmission: Nurul Aqmar Mohd Nor Hazalin Phc454 - Pharmaceutical MicrobiologyDocument27 pagesAirborne Transmission: Nurul Aqmar Mohd Nor Hazalin Phc454 - Pharmaceutical MicrobiologySuhaila Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Diphtheria ReportDocument13 pagesDiphtheria ReportAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY QuinterDocument177 pagesDERMATOLOGY QuinterstaceyatienoomaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis, Opthalmia Neonatarum & HIV/AIDSDocument15 pagesNeonatal Sepsis, Opthalmia Neonatarum & HIV/AIDSSAKSHI RANANo ratings yet
- Common Infections BDS4124Document25 pagesCommon Infections BDS4124NouraHabiba28No ratings yet
- The CorneaDocument60 pagesThe CorneaSarahNo ratings yet
- wk11 INFECTIOUS DISORDER PART TWODocument52 pageswk11 INFECTIOUS DISORDER PART TWOclaire yowsNo ratings yet
- Erbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Document13 pagesErbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Kubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Erbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Document14 pagesErbil Polythecnic University Soran Technical Insititute Midwifery Dipartment First Stage (M)Kubra ĖdrisNo ratings yet
- Mrsia Tally BoardDocument186 pagesMrsia Tally BoardMichael Dave MonoyNo ratings yet
- Potensi Virus Nipah Sebagai Wabah Baru Di Indonesia: June 2021Document15 pagesPotensi Virus Nipah Sebagai Wabah Baru Di Indonesia: June 2021aditya maltaNo ratings yet
- Eradication Guide Mycoplasma HyopneumoniaeDocument12 pagesEradication Guide Mycoplasma Hyopneumoniaenick224100% (1)
- Chicken-Pox Concept MapDocument4 pagesChicken-Pox Concept MapElle0% (1)
- Session 1 Part 2Document216 pagesSession 1 Part 2AmalNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Food Safety HazardsDocument2 pagesCauses and Prevention of Food Safety HazardsMulubrhan OkbaiNo ratings yet
- Istorie StafilococDocument19 pagesIstorie StafilocociuliansavoiuNo ratings yet
- Ocular Parasitic InfectionDocument35 pagesOcular Parasitic InfectionAshwiniNo ratings yet
- Leuservirus PresentationDocument6 pagesLeuservirus Presentationjamielevitt40No ratings yet
- ColistinDocument12 pagesColistinJoaoMarioFloresFernandezNo ratings yet
- RITM ORG CHART - As of May 2017Document6 pagesRITM ORG CHART - As of May 2017Daryl De VeraNo ratings yet
- Riverwalk Medical Clinic Influenza Information SheetDocument6 pagesRiverwalk Medical Clinic Influenza Information Sheetcycy143No ratings yet
- A Note On Mixed Coccidian and Capillaria Infection in PigeonsDocument4 pagesA Note On Mixed Coccidian and Capillaria Infection in PigeonsAnonymous tBJwSUSjNo ratings yet
- 16 Chapter19 Enterobacteriaceae 121004141132 Phpapp01Document105 pages16 Chapter19 Enterobacteriaceae 121004141132 Phpapp01Yelsin Denis Fabian AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 LP (3RD Quarter-4health)Document6 pagesGrade 8 LP (3RD Quarter-4health)Shamaica SurigaoNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument8 pagesMalarianurulzafNo ratings yet
- Beviljademedel PDFDocument7 pagesBeviljademedel PDFmarie_d_hedlundNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of CVSDocument44 pagesMicrobiology of CVSsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Practical Meat Inspection Presentation-2022Document2 pagesPractical Meat Inspection Presentation-2022Mich KidNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document11 pagesCase 1Gwendolyn Talahiban LusaraNo ratings yet
- CDT Aditya Dhala. Od-19-Sd-A-304-325. The Role of NCC in Covid-19Document3 pagesCDT Aditya Dhala. Od-19-Sd-A-304-325. The Role of NCC in Covid-19Ē Vì LNo ratings yet
- Usefulness of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Testing in Hepatitis B Community-Based ScreeningDocument7 pagesUsefulness of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Testing in Hepatitis B Community-Based ScreeningSerendipity21No ratings yet
- Swine FluDocument8 pagesSwine Flumohammadomerkhan96No ratings yet
- Staphylococcal Food Poisoning PPT ContentDocument4 pagesStaphylococcal Food Poisoning PPT ContentARELLANO, Julie Anne G. BSTM 1DNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Pineapple Core Extract Against MRSADocument5 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Pineapple Core Extract Against MRSABoby FelixNo ratings yet
- Hagan and Brunerx27s Infectious Diseases of DomestDocument2 pagesHagan and Brunerx27s Infectious Diseases of DomestNopparach ManadeeNo ratings yet