Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verbal & Non-Verbal Communication
Verbal & Non-Verbal Communication
Uploaded by
Hazel CababatOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verbal & Non-Verbal Communication
Verbal & Non-Verbal Communication
Uploaded by
Hazel CababatCopyright:
Available Formats
SELF LEANING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
VERBAL & NON-VERBAL
COMMUNICATION
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
CONTENT
Objectives
Introduction To Verbal & Non Verbal Communication
Major Areas Of Non Verbal Behaviour
Video Links
Casestudy
Learnings
Test Yourself
2
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
OBJECTIVES
Understand the Importance of Nonverbal Communication
State a definition of Nonverbal Communication and
identify different types
Describe the purpose Nonverbal Communication serves in
the communication process
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
VERBAL COMMUNICATION
Verbal communication means a communication that takes
place by means of a language or words.
It includes the following contents.
a. Oral communication (Speaking & listening)
b. Written communication (writing & reading)
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Speaking:-
In order to send message in business, speaking plays
a vital role.
Writing:-
It is used when a complex message is sent.
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Listening:-
People in business spend more time in obtaining
information then transmitting it. Listening is the most
important way to receive information.
Reading:-
Reading involves understanding and interpreting the
material.
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION
The study of non-verbal communication examines how
messages are communicated through physical behavior,
vocal cues and spatial relationships.
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
The total impact of a message breaks down like this:
7 percent verbal (words)
38 percent vocal (volume, pitch, rhythm, etc)
55 percent body movements
(mostly facial expressions)
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION IN
ORGANIZATION
Environment
Body placement
Posture
Gestures
Facial expressions and movement
Clothing, dress, appearance
9
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Major areas of nonverbal behaviors are:
Eye contact
Facial expressions
Gestures
10
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Posture and body orientation
Proximity
Para linguistics
11
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
EYE CONTACT
The eyes can give clues to a person’s thoughts.
When someone is excited, his pupils dilate to four times
the normal size.
An angry or negative mood causes the pupils to contract.
12
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
EYE CONTACT
Direct eye-contact conveys interest, warmth, credibility
and concern.
Shifty eyes suggest dishonesty.
Downward gaze may be a sign of submissiveness or
inferiority
13
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
FACIAL EXPRESSIONS
14
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
FACIAL EXPRESSIONS
There are six categories of facial expressions:
Happiness
Sadness
Anger
Disgust
Surprise
Fear
15
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Happiness- “Whoever is happy will make others happy
too.” -Mark Twain
Sadness- “Sadness dulls the heart more than the grossest
sin.”
Anger- “Anger is one letter short of danger”
16
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Disgust- A disgusting expression on the face is
considered negative and should be avoided in formal
gatherings.
Surprise- The eye-brows and the eyes are most affected
in an expression of surprise.
Fear- There is nothing to fear, but fear itself.
17
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
GESTURES
Gestures communicate as effectively as words,
sometimes even better.
Gestures support the verbal communication.
They sometimes detract from what you say.
18
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
There are some negative gestures which should be
avoided:
Pointing at people- It is perceived as accusatory.
Fiddling with your items-It gives the impression that
you are nervous.
Dragging the feet-It implies lethargy.
Head Down- It suggests timidity.
Drooping shoulders- It implies weariness and lethargy.
19
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Weak handshake-It implies meek and ineffectual
personality.
Shifty eyes- It suggests nervousness.
Arms crossed on the chest- It is a defensive gesture.
Hands in pockets- Shows disrespect, and that you have
something to hide.
Covering your mouth- It suggests you are lying.
Shaking feet or legs- It shows indifference and
20
disinterest.
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
AVOID THESE HAND GESTURES
USE THESE HAND GESTURES
21
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
POSTURE
Body posture can be open or closed.
Interested people pay attention and lean forward.
Leaning backwards demonstrates aloofness or rejection.
A head held straight up signals a neutral attitude.
A head down is negative and judgmental.
A head tilted to the side indicates interest.
22
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Some Negative Postures should be avoided:
Rigid Body Posture-Anxious/ Uptight
Hunched Shoulders –Lacks interest/ Feeling inferior
Crossed Arms-Protecting the body/ Negative Thoughts
23
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
VERBAL & NON VERBAL
COMMUNICATION
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I9i5_xwRE_U
39
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
NON VERBAL COMMUNICATION
CASE STUDY
At an early stage project meeting Mary, the project team leader,
presented her suggested project timetable to meet the project goals. During
the presentation she noticed that two team members were showing non-
verbal signs of disapproval. Simon was frowning and shaking his head and
Justin had leant back in his chair and folded his arms. Mary stopped what
she was saying, turned to Simon and Justin and asked ‘I sense you are not
supportive of what I’m saying. Can I clarify anything for you?’ Simon
replied ‘You are right. I think the project timetable is unachievable.’ Mary
responded by directing a question to the whole group ‘How do the rest of
you feel about the timetable I’m suggesting?’ 40
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
By observing these valuable non-verbal cues Mary was able to
open up communication amongst the team and find an early
resolution to this problem. Had she ignored or not been aware of the
cues, she could well have encountered serious problems with
meeting the project timetable and ultimate completion. Additionally,
she might not have received the full support of two valuable team
members.
41
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
LEARNINGS
Facilitates to pay attention to multiple mediums of
communication.
Facilitates to develop proficiency in understanding gesture
clusters.
Helps in understanding that our body has multiple channels
that can be successfully used to communicate thoughts
effectively.
42
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
TEST YOURSELF:
When communicating with others, I pay attention to
non-verbal signals - body language, facial expressions
and gestures.
a. Always or Nearly Always
b. Often
c. Some-times
d. Rarely Never or Hardly Ever
43
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
TEST yourself:
I nod my head and use other gestures and facial
expressions to show that I’m interested in what is
being said.
Always or Nearly Always
Often
Some-times
Rarely Never or Hardly Ever
44
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
Test yourself:
I offer verbal signals while listening, things like, ‘Go
on… ’ or ‘Uh huh’ to encourage the speaker to
continue.
Always or Nearly Always
Often
Some-times
Rarely Never or Hardly Ever
45
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
SELF LEARNING MODULE 1 CHAPTER 5
46
Teamglobal©Kautilya Learning Academy of Professionals
You might also like
- TOLD Checklist Strategy GuideDocument43 pagesTOLD Checklist Strategy GuideTOLDWorkshop100% (2)
- Clay ScriptDocument13 pagesClay Scriptapi-394679663No ratings yet
- International Business Comm IcmDocument179 pagesInternational Business Comm IcmJoram Wambugu50% (2)
- Developmental Milestones of Symbolic or Pretend PlayDocument1 pageDevelopmental Milestones of Symbolic or Pretend PlaySorina VlasceanuNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Completed Scheme of WorkDocument4 pagesUnit 10 Completed Scheme of WorkBrunno BorimNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles: DR Anish KotechaDocument5 pagesLearning Styles: DR Anish KotechaNicolas ObandoNo ratings yet
- Inside Teaching Tim Bowen and Jonathan Marks Heinemann English Language Teaching Oxford 1994 PDFDocument16 pagesInside Teaching Tim Bowen and Jonathan Marks Heinemann English Language Teaching Oxford 1994 PDFdegulasepaNo ratings yet
- IPS910 SAP Public Sector ESDocument500 pagesIPS910 SAP Public Sector ESMariano100% (1)
- 7 Cs of CommunicationDocument27 pages7 Cs of CommunicationHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Document12 pagesOral Comm Q2 Wk7Kearl MandaoNo ratings yet
- Asinas SDPDocument27 pagesAsinas SDPANTONINO AGUILAR JR.No ratings yet
- MCD Work Experience UK EditDocument37 pagesMCD Work Experience UK EditShivuNo ratings yet
- Presentation Skills: Shivali Kamal Mba+Pgpm SEM-1Document8 pagesPresentation Skills: Shivali Kamal Mba+Pgpm SEM-1shivali_kamal4622No ratings yet
- SDP Constantino WORKBOOK PDFDocument29 pagesSDP Constantino WORKBOOK PDFMaxine Constantino100% (1)
- Systematic Language LearningDocument45 pagesSystematic Language LearningIuliana SavinNo ratings yet
- NEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Document8 pagesNEW - REVISED - Oral Comm Q2 Wk7Marilou Iamztol RecamaraNo ratings yet
- Planning Your Internal: Career DesignDocument19 pagesPlanning Your Internal: Career DesignAhmad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Juzallie S. Sioco. - Colloids PDFDocument11 pagesScience 6 - Juzallie S. Sioco. - Colloids PDFJuzallie SiocoNo ratings yet
- The Power of Body Language SyllabusDocument7 pagesThe Power of Body Language SyllabusRapid GamerNo ratings yet
- English Intergrated Language Book 1Document77 pagesEnglish Intergrated Language Book 1thulaganyomachaka01No ratings yet
- Unit 19: Teaching Special GroupsDocument22 pagesUnit 19: Teaching Special GroupsDongjin LeeNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Com - Eng Days 7 - 8Document41 pagesSemester 1 Com - Eng Days 7 - 8Royden DRozarioNo ratings yet
- Oral PresentationDocument10 pagesOral PresentationNoor RefaieNo ratings yet
- Personal Development PlanDocument17 pagesPersonal Development PlanzxymphNo ratings yet
- Focus Persistence ResilienceDocument69 pagesFocus Persistence Resiliencedgavrile100% (1)
- My First-EditedDocument5 pagesMy First-EditedFedir HilchukNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Presentations: Mark PowellDocument7 pagesDynamic Presentations: Mark PowellFedir HilchukNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Theory 2024Document23 pagesModule 1 - Theory 2024Victoria Goñi LarruyNo ratings yet
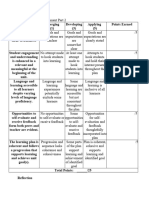
- Edu603 U7 Assignment Part 2 Self Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesEdu603 U7 Assignment Part 2 Self Assessment Rubricapi-736693318No ratings yet
- Core-1 Participant Guide - ENDocument108 pagesCore-1 Participant Guide - ENvishnus22No ratings yet
- Wb01 Etimad m1 Leading From Within Workbook Live OnlineDocument42 pagesWb01 Etimad m1 Leading From Within Workbook Live OnlineLam88rNo ratings yet
- 4.sunum - 1Document21 pages4.sunum - 1aheahaehaeyarrakNo ratings yet
- SDP Students WorkbookDocument28 pagesSDP Students WorkbookRuth MarientesNo ratings yet
- Hawassa University College of Social Sciences: August 2022Document3 pagesHawassa University College of Social Sciences: August 2022Eyuel Nebiyu100% (1)
- NP-LBEF002 Personality DevelopmentDocument7 pagesNP-LBEF002 Personality Developmentnewarsahil34No ratings yet
- A P O P D: Rsentation N Ersonality EvelopmentDocument37 pagesA P O P D: Rsentation N Ersonality EvelopmentTarun DhirNo ratings yet
- 6 Steps To Prepare For Your InterviewDocument1 page6 Steps To Prepare For Your InterviewAnAn LeeNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Purposive Communication Report - Final - r01Document12 pagesGroup 5 - Purposive Communication Report - Final - r01Ramdolfh Kyle ZafraNo ratings yet
- Part - II Communication Skills & Personality DevelopmentDocument10 pagesPart - II Communication Skills & Personality DevelopmentPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- EDENG DOMAINS-of-LITERACY-READINGDocument9 pagesEDENG DOMAINS-of-LITERACY-READINGMelanie CaguinemanNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Q2W4Document18 pagesOral Communication in Context Q2W4GRACE ANNE SEVILLA100% (1)
- Soft Skills PDFDocument31 pagesSoft Skills PDFMamillapalli ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills - IIDocument16 pagesCommunication Skills - IIAdithya s kNo ratings yet
- EngG9W1 BWDocument14 pagesEngG9W1 BWSherlyn Mae BasalatanNo ratings yet
- Soft Skills Training Activities PDFDocument31 pagesSoft Skills Training Activities PDFUsha SinghNo ratings yet
- EDU122 - Assessment 1 (Case Study) (1) Learning and CognitionDocument7 pagesEDU122 - Assessment 1 (Case Study) (1) Learning and CognitionSavannah SchultzNo ratings yet
- Video Assessment Ei4205Document5 pagesVideo Assessment Ei4205Guillermo VasquezNo ratings yet
- A Pathway For Acquiring Soft Skills: SyllabusDocument15 pagesA Pathway For Acquiring Soft Skills: SyllabusK SrivarunNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Preview PDFDocument4 pagesCommunication Skills Preview PDFNaniNo ratings yet
- Educ.10 RubricsDocument4 pagesEduc.10 Rubricsmelody longakitNo ratings yet
- Embodied Soft Skills Training - HandbookDocument108 pagesEmbodied Soft Skills Training - HandbookErmiyasNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Lecture 3 - Visual & Hearing ImpairmentDocument87 pagesTopic 5 Lecture 3 - Visual & Hearing ImpairmentLogavani ThamilmaranNo ratings yet
- Session Guide CGP Module 5 Walkthrough Wo VideoDocument35 pagesSession Guide CGP Module 5 Walkthrough Wo VideoDeona Faye PantasNo ratings yet
- 5 Conversation SkillsDocument27 pages5 Conversation SkillsBryan Domingo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SDP Students WorkbookDocument31 pagesSDP Students WorkbookMonkey D. LuffyNo ratings yet
- Reading 8° III TrimestreDocument6 pagesReading 8° III TrimestreJerryka Gonzalez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- SPEAKING - Bhavanraj KalsiDocument4 pagesSPEAKING - Bhavanraj Kalsijetalal swamikashmirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-To-Order-One's LifeDocument9 pagesChapter 5-To-Order-One's LifeBethNo ratings yet
- Attitude and Ethics.Document20 pagesAttitude and Ethics.rabnawazlodhiNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking: Vimalkumar, Chief Manager & Faculty, State Bank Academy, GurgaonDocument31 pagesPublic Speaking: Vimalkumar, Chief Manager & Faculty, State Bank Academy, GurgaonVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- My Big Ideas Part BDocument17 pagesMy Big Ideas Part BHannah MandrykNo ratings yet
- STAYING POSITIVE - Bhavanraj KalsiDocument4 pagesSTAYING POSITIVE - Bhavanraj Kalsijetalal swamikashmirNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 Series DC Circuits EE-211 - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesLaboratory 1 Series DC Circuits EE-211 - Basic Electrical EngineeringHazel CababatNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 Series DC Circuits EE-211 - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesLaboratory 1 Series DC Circuits EE-211 - Basic Electrical EngineeringHazel CababatNo ratings yet
- AE 112-AE 112-: Partnership Operations)Document32 pagesAE 112-AE 112-: Partnership Operations)Hazel CababatNo ratings yet
- Ge 7 Modules FinalsDocument20 pagesGe 7 Modules FinalsHazel CababatNo ratings yet
- The Culture of ProfessionalismDocument369 pagesThe Culture of Professionalismracan19No ratings yet
- Markedness - Chapter 4 - Book - The Blackwell Companion To PhonologyDocument28 pagesMarkedness - Chapter 4 - Book - The Blackwell Companion To PhonologySamah HassanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Index - 2015: Sl. No. Government Order/ Registrar'Circular No. and Date Subject Page NoDocument9 pagesDetailed Index - 2015: Sl. No. Government Order/ Registrar'Circular No. and Date Subject Page NokalkibookNo ratings yet
- DFD Caverns PromoDocument10 pagesDFD Caverns PromoPhilippe LouisNo ratings yet
- PROJECT TITLE Physical FacilitiesDocument1 pagePROJECT TITLE Physical FacilitiesEmily Jamio100% (1)
- BREB Short Suggestion - 240331 - 174750Document7 pagesBREB Short Suggestion - 240331 - 174750Sushanta BiswasNo ratings yet
- Case Digest Case 65 Mariano Rodriguez vs. Porfirio BelgicaDocument5 pagesCase Digest Case 65 Mariano Rodriguez vs. Porfirio BelgicaSantiagoJr S XiaoNo ratings yet
- Application Letter CSCDocument2 pagesApplication Letter CSCtomalobitoNo ratings yet
- How To Get Enugu State University Direct Entry Form, The Requirements and All You Need To KnowDocument6 pagesHow To Get Enugu State University Direct Entry Form, The Requirements and All You Need To KnowGold 2No ratings yet
- Casnum Post RNO CannamDocument277 pagesCasnum Post RNO CannamGulfishan MirzaNo ratings yet
- IS and CGS ReportDocument6 pagesIS and CGS Reportロザリーロザレス ロザリー・マキルNo ratings yet
- SOCDocument4 pagesSOCJvnRodz P GmlmNo ratings yet
- Chinnanchiru Kiliye.. Celebrating ParenthoodDocument3 pagesChinnanchiru Kiliye.. Celebrating ParenthoodxiaoboshiNo ratings yet
- Fargo Hdp6600 PrinterDocument4 pagesFargo Hdp6600 Printergroovey9040No ratings yet
- A Distinguished Warrior's Burial From DmanisiDocument2 pagesA Distinguished Warrior's Burial From DmanisiGeorgian National MuseumNo ratings yet
- Vtu 6TH Sem Cse Computer Networks 2 Notes 10CS64Document72 pagesVtu 6TH Sem Cse Computer Networks 2 Notes 10CS64EKTHATIGER633590100% (8)
- DLL G6 Q2 WEEK 5 ALL SUBJECTS Mam Inkay PeraltaDocument60 pagesDLL G6 Q2 WEEK 5 ALL SUBJECTS Mam Inkay PeraltaClaire Ann Dao-wan Bandico100% (1)
- Ola Cabs & Electric Scooter - Bhavish AggarwalDocument7 pagesOla Cabs & Electric Scooter - Bhavish AggarwalAyushi ThakurNo ratings yet
- BIOC15 Class 20 NotesDocument9 pagesBIOC15 Class 20 NotesCindy HouNo ratings yet
- Third Summative TestDocument12 pagesThird Summative TestLeah Michelle D. RiveraNo ratings yet
- BS Iso TR 08363-1997 (1999)Document16 pagesBS Iso TR 08363-1997 (1999)Олег СоловьевNo ratings yet
- Las - Ict 7 - Special Programs - Q4 - Week 4Document12 pagesLas - Ict 7 - Special Programs - Q4 - Week 4George Mar Bien AriolaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Globalization On Religious IssuesDocument20 pagesThe Influence of Globalization On Religious IssuesRhea Joy TabilidNo ratings yet
- MSU Brochure 2019Document21 pagesMSU Brochure 2019emonwreNo ratings yet
- Self Declaration Shop PDFDocument2 pagesSelf Declaration Shop PDFSudhir Kotkar0% (2)
- Sign Up 1 New Ed 2021 TBDocument100 pagesSign Up 1 New Ed 2021 TBGabriela RizzoNo ratings yet