Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton' S Laws: ©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Uploaded by
Hind Aldahmani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views44 pagesOriginal Title
Newton's Laws
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views44 pagesNewton' S Laws: ©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Uploaded by
Hind AldahmaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 44
Newton’ s Laws
Chapter 4
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
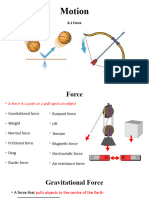
Force
• Contact Force – everyday forces, used to
move objects.
• Action-at-a-distance Force – a force that
is exerted on another object without
contact.
• Combination of several forces acting on a
single object (principle of superposition),
known as the vector sum of all the forces =
NET FORCE
-forces have magnitude and direction
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
4 Fundamental Forces in Nature
Gravitational Force Electromagnetic Force
Weak Nuclear Force Strong Nuclear Force
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Contact Forces
• Normal force (FN) – support force from
contact with a surface
• Frictional force (f) – forces that opposes
the tendency to slide across a surface
• Spring Forces (Fs) – force a spring
exerted when stretched or compressed.
• Strings (T) – Strings will exert a tension
force against the applied force
• Applied force (F) – Any force applied by
someone or something that does not fall
into the category above.
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Weight vs Mass
• Weight and mass are NOT Equal
• Gravitational force (Fg) – force caused
by the acceleration due to gravity.
(Weight is the magnitude of this force,
the sign will indicate the direction of
the Fg
• All objects in Earth’ s gravitational
field experience the same acceleration.
Field is always directed towards the
center of the Earth.
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Mass = amount of matter in an object, a measure of an objects
inertia (units: kg)
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Net Force
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Free Body Diagrams
• A drawing of all the forces acting on
an object, free from its
surroundings.
• Draw the object, draw the force
vectors (magnitude and direction),
label all drawn forces, combine all
forces in the same plane (x, y, or z)
to determine the net force
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Inertia
• Newton’ s First Law: Objects at
rest/motion will remain at
rest/motion, unless an outside net
force acts on it.
• Inertial Frame of Reference: a frame
of reference in which the laws of
motion are held true (constant
velocity)
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Forces and
Acceleration
• Force - a push or pull on an
object.
• when you push on something with a
NET force, its velocity will
change (accelerate)
• Force Law 1: Fconst = aconst (always
in the same direction)
• small force = small accel
• LARGE FORCE = LARGE ACCEL
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Newton’ s 2nd Law
• Acceleration of an object is directly
proportional to the net force, and
inversely proportional to the mass of
the object.
• a = F / m
• Units: 1 Newton = 1 kg x 1 m/s2
1 pound = 1 slug x 1
ft/s2
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
• Apparent Weight = magnitude of the
gravitational force as read by a
scale (spring)
• Weightlessness = when apparent weight
equals zero (free falling)
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Since forces can act in 3-dimensions,
the object can accelerate in 3-
dimensions. Just keep your vector
components separate and solve for
each.
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
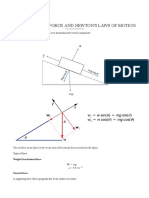
Inclined Plane:
Objects on an
inclined plane must
be treated with a
tilted x-y plane.
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Newton’ s 3 Law rd
Challenge
• Trial 1: Person 1 = do not pull,
Person 2 = pull to 15 N
• What does each scale read?
• Trial 2: Person 1 = pull to 10 N,
Person 2 = do not pull
• What does each scale read?
• Trial 3: Person 1 = pull to 8 N,
Person 2 = pull to 14 N
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Newton’ s 3rd Law
• For every force, there is an equal
and opposite force.
• FBA = - FAB
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Action – Reaction
Forces
• Walk out of the room
• Swim forward
• Rocket propelled into the air, or
through space
• Tire on the road
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Batman Begins
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
Superhero:
Acceleration due to gravity
of Planet Krypton
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
©2008 by W.H. Freeman and Company
You might also like
- Aplications of Newton's LawsDocument54 pagesAplications of Newton's LawsHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Aplications of Newton's LawsDocument54 pagesAplications of Newton's LawsHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Forces: Newton's Laws of Motion Static and Kinetic FrictionDocument9 pagesForces: Newton's Laws of Motion Static and Kinetic FrictionDinum PereraNo ratings yet
- General Physics Ch2.2Document6 pagesGeneral Physics Ch2.2nahomNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion: Sections 3.1-3.6Document52 pagesForce and Motion: Sections 3.1-3.6Ahmad Shex MhamadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Motion and Forces 2023 To 2024 VersionDocument37 pagesUnit 2. Motion and Forces 2023 To 2024 VersionMr. CNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Week 4Document34 pagesChapter Four: Week 4kenyuutaNo ratings yet
- 4-Laws of Motion - 05Document66 pages4-Laws of Motion - 05Ali100% (1)
- Force and Motion - Cause and EffectDocument52 pagesForce and Motion - Cause and EffectZari Sofia LevisteNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Free-Body Diagrams PDFDocument33 pagesFree-Body Diagrams PDFRITUPARNA BISWASNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Kinematics and Dynamics of ParticlesDocument129 pagesChapter Two: Kinematics and Dynamics of ParticlesEphrem ChernetNo ratings yet
- Mock TeachingDocument30 pagesMock TeachingRN Builder IpohNo ratings yet
- 04 Lecture OutlineDocument32 pages04 Lecture Outlinewoboc79249No ratings yet
- FORCEDocument14 pagesFORCEthepogi2005No ratings yet
- PHY 102 Lecture Particle DynamicxDocument22 pagesPHY 102 Lecture Particle Dynamicxwww.gulraizsaadiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Engineering MechanicsMaria RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document29 pagesLecture 5أبوصهيبالتاجوريNo ratings yet
- Physics Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesPhysics Reviewer PDFJam Uly Gasty100% (1)
- Newtons Laws of Motion GCDocument18 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion GCfrancine allen bobonNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDocument27 pages3rd Week - Forces and Newton LawsDoddy HardhienataNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Newtons Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesLecture 4 Newtons Laws of MotionDonnette Commissiong JamesNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of MotionDocument50 pagesNewtons Laws of MotionJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- 4 2 Forces WebDocument19 pages4 2 Forces Webapi-261462856No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument41 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionAbdullah alifNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument21 pagesForce and MotionLalaine MamaedNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Laws of MotionDocument49 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motionbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- F2 SC 8.1 ForceDocument22 pagesF2 SC 8.1 Forcekaozhiqi0717No ratings yet
- Physics 1 Mechanics: Rahadian N, S.Si. M.SiDocument23 pagesPhysics 1 Mechanics: Rahadian N, S.Si. M.SiDimas Asmoro AjiNo ratings yet
- DYNAMICSDocument6 pagesDYNAMICSFatima NadeemNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics Note 1.Document6 pagesGrade 12 Physics Note 1.babaNo ratings yet
- Physics-Notes 02Document7 pagesPhysics-Notes 02JanusNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument29 pagesPhysicsB VIDATTE VILLANIEVANo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument56 pagesForcesMais MarwanNo ratings yet
- 4 NewtonLawsDocument25 pages4 NewtonLawsAyham SmadiNo ratings yet
- Forces: Free Body DiagramsDocument45 pagesForces: Free Body DiagramsAsad SamiNo ratings yet
- Law of MotionDocument76 pagesLaw of MotionLove With Books 2470% (1)
- Chapter 5Document91 pagesChapter 5Fabian ViasusNo ratings yet
- Physics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawsDocument40 pagesPhysics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawssosatukiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Newtons Law of MotionDocument40 pagesChapter 4 - Newtons Law of MotionncmzcnmzzNo ratings yet
- DLR-Fizik Konu AnlatımıDocument18 pagesDLR-Fizik Konu Anlatımıugurhan96No ratings yet
- Physics Lec 06 NewtonDocument19 pagesPhysics Lec 06 NewtonAnthony Wijaya, S.Pd., M.Si.No ratings yet
- Force: by Sandeep VermaDocument18 pagesForce: by Sandeep Vermasandeep vermaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument44 pagesThe Laws of MotionPHAKVISETH PEMNo ratings yet
- 288559883-Gr 12 Physics - Definitions and LawsDocument15 pages288559883-Gr 12 Physics - Definitions and Lawstaahirgaffor1No ratings yet
- Lecture 1.4 - Week 3 Monday - KineticsDocument27 pagesLecture 1.4 - Week 3 Monday - KineticsAmala CuganesanNo ratings yet
- Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument38 pagesForces and Newton's Laws of MotionfarismohNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2:forceDocument74 pagesChapter 2:forceTing CheongNo ratings yet
- Phy Outline Ch04Document49 pagesPhy Outline Ch04knight.alfardanNo ratings yet
- Mech 2 Lo.1Document37 pagesMech 2 Lo.1Mohamed KilanyNo ratings yet
- 5 - Forces, Density and PressureDocument36 pages5 - Forces, Density and PressureKamran KhursheedNo ratings yet
- Chap3 Newton LawsDocument65 pagesChap3 Newton LawsAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Session 16 - Newton's LawsDocument35 pagesSession 16 - Newton's LawsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ap 1 DynamicsDocument10 pagesAp 1 DynamicsCai MingleiNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument44 pagesThe Laws of Motionmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionDocument27 pagesLecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionAnonymous IlzpPFINo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Newton's Law (v2)Document55 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Newton's Law (v2)Salina MohmadNo ratings yet
- WEEK-6: Ap Unit-2 Textbook Chapter-3 ForcesDocument22 pagesWEEK-6: Ap Unit-2 Textbook Chapter-3 ForcesHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Unit 2 Class 4Document21 pagesWeek 6 Unit 2 Class 4Hind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- WEEK-6: Text Book Chapter-3 ForcesDocument31 pagesWEEK-6: Text Book Chapter-3 ForcesHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument30 pagesCircular MotionHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Unit 2 Class 4Document21 pagesWeek 6 Unit 2 Class 4Hind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Ap Physics C: MechanicsDocument10 pagesKinematics: Ap Physics C: MechanicsHind AldahmaniNo ratings yet
- P5 Mathematics Exam Package Sample FileDocument33 pagesP5 Mathematics Exam Package Sample FileGandhiNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics 1235 Marks Study Material English Medium PDFDocument138 pages11th Physics 1235 Marks Study Material English Medium PDFMohana UMNo ratings yet
- Sprial Book - Feb 2023Document4 pagesSprial Book - Feb 2023Yuvansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Yarn Count Measurement SystemDocument6 pagesYarn Count Measurement SystemMuhammad Jafor IqbalNo ratings yet
- Question 5 I, II CIE November 2019 (v1) MathsDocument1 pageQuestion 5 I, II CIE November 2019 (v1) MathsSC CHIMNo ratings yet
- Tuto 81 Vol of Rev ShellDocument2 pagesTuto 81 Vol of Rev ShellAZRI FIRDAUS이광수No ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument1 pageUnit ConversionTimothy Gregoire Jr.No ratings yet
- Rigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorDocument9 pagesRigid Bodies, Statics, Mechanics Notes From A-Level MathsTutorA-level Maths Tutor100% (3)
- Force and Motion Review With AnswersDocument6 pagesForce and Motion Review With AnswersDayz LopezNo ratings yet
- Newton SummativeDocument5 pagesNewton SummativeJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDocument3 pagesPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzNo ratings yet
- Mix Gradation of Aggregates: Weights For Compacted SpecimensDocument11 pagesMix Gradation of Aggregates: Weights For Compacted SpecimensFiras BarrajNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Frames of Reference, Forces and Newton's Laws of MotionJacko LenoNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Practice ExerciseDocument37 pagesMensuration Practice ExerciseManjunath K LNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsSambandha SilwalNo ratings yet
- Noxon BSP Threaded FitiingsDocument24 pagesNoxon BSP Threaded FitiingsZoran DanilovNo ratings yet
- Konversi SatuanDocument6 pagesKonversi SatuanUtaph Ozwald SynysterNo ratings yet
- Archimedes Principles eDocument7 pagesArchimedes Principles erenedavid0% (2)
- QS1Document154 pagesQS1Bhagyaraj KoppishettyNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculation Conversions TleDocument1 pageDosage Calculation Conversions TleBlesie MoradaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsDocument10 pagesAP Physics 1 Algebra Based Unit 2 DynamicsNikhita RajeshNo ratings yet
- Q4W4 Math DLLDocument9 pagesQ4W4 Math DLLMaria Cristina AguantaNo ratings yet
- Motion Under GravityDocument5 pagesMotion Under GravityRizul thakur100% (1)
- How To Calibrate Level TrollDocument3 pagesHow To Calibrate Level TrollGirishkumar B Prajapati100% (9)
- MCQ CH Gravitation 9Document8 pagesMCQ CH Gravitation 9lembdaNo ratings yet
- Soal Latihan Ujian IUP UGMDocument14 pagesSoal Latihan Ujian IUP UGMsarah fadhilah100% (1)
- Handout # 3 MEASUREMENT OF HORIZONTAL DISTANCESDocument8 pagesHandout # 3 MEASUREMENT OF HORIZONTAL DISTANCESCCCCCCCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Dynamics: Force and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Net F Ma (63.0 KG) (4.20 M/s ) 265 NDocument15 pagesChapter 4: Dynamics: Force and Newton'S Laws of Motion: Net F Ma (63.0 KG) (4.20 M/s ) 265 NCedric KouakouNo ratings yet
- ConversionDocument1 pageConversionGOMEZ, AICHAELSON C.No ratings yet