Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wylie, Clare
Uploaded by
clarewylieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wylie, Clare
Uploaded by
clarewylieCopyright:
Available Formats
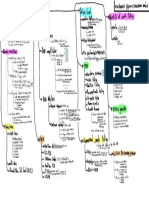
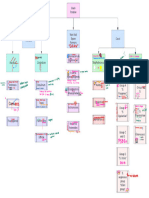
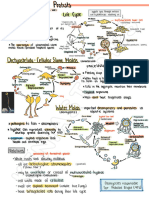
Polio Virus
Ascaris Lumbricoide
Structure
NERVOUS SYSTEM INFECTIONS Structure:
Structure Structure: Nematode
Nematode
Non-enveloped
Non-enveloped Single
3000
3000 amino
amino acids
Single stranded
acids in
stranded RNA
in length
length
RNA with
with positive
positive polarity
polarity
Clare Wylie
Transmission:
Transmission: Ingestion
mature
mature in in dirt
dirt
Ingestion of of egg
egg from
from fecesfeces or or dirt.
dirt. Eggs
Eggs can
can
Transmission:
Transmission:
Oral spread-Fecal
Oral spread-Fecal Pathogenesis and
Pathogenesis and Effects
Effects onon CNSCNS
pread through
pread through water water andand swimming
swimming poolspools during
during outout breaks
breaks One ingested
One ingested the the egg
egg hatches
hatches in in the
the stomach
stomach will will grow
grow within
within
during
during summers
summers the
the gut but also break out into circulation
gut but also break out into circulation to to the
the lungs
lungs toto fully
fully
mature. They will travel back up espouse
mature. They will travel back up espouse where the mature where the mature
Pathogensis
Pathogensis and and Effect
Effect on on CNS
CNS worm is ingested again to live in large intestine.
worm is ingested again to live in large intestine. During this During this
First replicates
First replicates in in the
the epithelia
epithelia cells
cells and
and results
results inin the
the infection
infection stage is
stage is when
when theythey cancan migrate
migrate through
through the the blood
blood stream
stream to to
of tissue
tissue like
like muscles
muscles and and brown
brown fat.
fat. One
One in in 100
100 infections
infections will
will Path of worm in lung tissue; other parts of the body such as the brain. This is not the
of other parts of the body such as the brain. This is not the
lead illustrates the ability of worm to
lead to invasion of Central nervous system and leads to
to invasion of Central nervous system and leads to optimum
optimum place for them to live so it is extremely rare that this
place for them to live so it is extremely rare that this
paralytic poliomyelitis work through tissue happens.
paralytic poliomyelitis happens.
Virus
Virus binds
binds to to receptor
receptor (CD155)-facilitated
(CD155)-facilitated processprocess on on In the few cases that it does and lining
In the few cases that it does and lining of stomach where it of stomach where it
peripheral neurons.
peripheral neurons. This This binding
binding causes
causes a a irreversible
irreversible travels through
travels through circulatory
circulatory system.
system.
confirmation changes
confirmation changes in in the
the virus
virus and
and endocytosis.
endocytosis. The The Movement from
Movement from thethe hydrostatic
hydrostatic skeleton
skeleton
release
release thethe genome
genome into into the
the host
host cell
cell and
and isis taken
taken up up by
by Difficult
Difficult to diagnosis because it
to diagnosis because it may
may not not appear
appear inin CT
CT or
or MRI.
MRI. InIn
endocytosis. It travels up the axons to
endocytosis. It travels up the axons to reach the CNS. reach the CNS. addition,
addition, draining the brain or tests for
draining the brain or tests for bacteria
bacteria return
return positive
positive
Gets into CSN through peripherally nervous
Gets into CSN through peripherally nervous system and system and bacteria test due to the fact that it allows for
bacteria test due to the fact that it allows for bacteria to follow bacteria to follow
traveling along
traveling along the the neural
neural pathway
pathway to to CNS.
CNS. WillWill cause
cause Routes of invasion to the CNS the worm
the worm in in transit
transit to to the
the brain.
brain. Therefore,
Therefore, treatment
treatment is is
paralysis to
paralysis to the
the motor
motor neurons
neurons itit infects
infects first.
first. Causes
Causes damage
damage directed to
directed to inefficient
inefficient models
models like like antibiotics.
antibiotics.
to
to any cell it has to lysis the cell when it leaves. The damage
any cell it has to lysis the cell when it leaves. The damage
in
in the peripheral motor pathways and spinal pathways cause
the peripheral motor pathways and spinal pathways cause
irreversible
irreversible damage
damage and and paralysis.
paralysis. IfIf the
the infection
infection travels
travels up
up to
to
the brain
the brain stem
stem itit can can paralyze
paralyze thethe medulla
medulla in in when
when a a infected
infected The Nervous System
host is
host is unable
unable to to breath.
breath. This
This is
is a
a major
major cause
cause of of death.
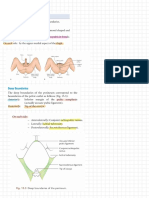
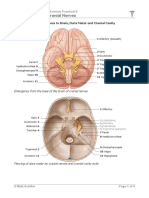
death. The nervous system is the circuit board of our bodies that controls all the functions.
It consists of the central and peripheral systems. The central system consists of
the spinal cord and the brain is highly protected from toxins and pathogens with the
H. Influenza Type B (HIB)
blood-brain barrier and skull. The peripheral system consisting of all the nerves
that are outside the spinal cord and brain connect to the other parts of the Structure:
body are
Structure: Gram
Gram Negative
Negative Coccobacillus
Coccobacillus
Type
Type B B indicates
indicates that
that the
the serotypes
serotypes encapsulated
encapsulated strainstrain
left unprotected.
Most
Most HIB HIB lack
lack aa capsule.
capsule. TheThe capsulated
capsulated form
form isis much
much more
more virulent
virulent
Toxoplasma Gondii Infection of the nervous system causes threats to control over body, psychological
functioning, and life. Penetration to the CNS poses greatest threat because
because
because evades clearance from the immune system while
of
bloodstream.
bloodstream.
evades
the
clearance from the immune system while in
in the
the
delicate nerves and it is difficult for immune cells to clear infection. The follow are The encapsulated form
diseases caused by the pathogens represented here that affect the nervous Transmission:
Transmission: Person Person to to person
person through
through aerosol
aerosol droplets
droplets on the left is more
Structure: system. Can
Can cause
cause deadly
deadly meningitis
meningitis or or pneumonia
pneumonia in in children
children under
under the
the age
age of
virulent 5
ofand
5 the main
Structure: Protozoa-
Protozoa- there
there are
are three
three forms
forms depending
depending on on stage
stage Present in normal flora of mucosal membrane in nasalpharynx of most
in
in life
life cycle.
cycle. Paralysis- caused to the destruction to spinal cord or motor neurons Present in normal flora of mucosal membrane in nasalpharynx of most
type that causes
Transmission Routes Routes people even if they are not given
people even if they are not given vaccine. vaccine. meningitis
Transmission Meningitis- Infection of arachniod membrane, subarachnoid space, and
-Raw meat
-Raw meat or or inadequately
inadequately cookedcooked thatthat is
is infected.
infected.
cerebrospinal fluid. The infection can cause death through destruction of brain
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis and and effects
effects to to CSN
CSN
-Ingest oocytes
-Ingest oocytes by by being
being around
around cats
cats feces
feces
-Mothers to unborn fetus tissue from endotoxins, sepsis, gram-negative shock, inflammation or damage There
There is is aatolack
lack of
of understanding
understanding of of how
how HIB
HIB enters
enters thethe blood
blood stream.
stream.
-Mothers to unborn fetus Some
brain, vascular, and cranial nerve tissues from immune response caused Someby hypothesis
hypothesis it it directly
directly though
though epithelia
epithelia tissue
tissue andand capillary
capillary
Pathogenesis and and Effects
Effects on on Nervous
Nervous systemsystem Sporulated ooysts found in lysosomal enzymes and free radicals. endothelium
endothelium in a cut or abrasion. The capsulated HIB are much less
in a cut or abrasion. The capsulated HIB are much less
Pathogenesis likely to
The Toxoplasma
The Toxoplasma gondiigondii traverse
traverse thethe intestinal
intestinal oror placental
placental transmission Brain Abscesses- commonly occur from bacterial or infect the brain. The to be
be engulfed
likelyabscess engulfed by by cells
cells than
than non-capsulated
non-capsulated form form due
due to
to the
the lower
lower
epithelium as as aa free
free parasite
parasite by by paraceullular
paraceullular transmigration.
transmigration. number
number of
of surface
surface proteins
proteins available
available to
to bind.
bind. Still
Still the
the capsulated
capsulated form
form is
is
epithelium is a mass filled with immune cells, puss, and infecting cells. Dangerousmore duevirulent
to when itit gets
gets into
into the
the blood
blood stream.
stream.
They
They cancan enter
enter macrophages
macrophages or or dendrite
dendrite cells
cells through
through toll-like
toll-like more virulent when
increased pressure and blocking blood flow causing damage to brain. When in the blood, HIB doubles rapidly. Doubling
When in the blood, HIB doubles rapidly. Doubling time is around 50 time is around 50
receptors.
receptors. They use these cells to moves throughout the
They use these cells to moves throughout the body.
body.
Then theythey have
have a a high
high affinity
affinity for
for neurons
neurons as as well
well as
as ocular
ocular minutes.
minutes. Research
Research suggests
suggests thatthat one
one to
to two
two bacteria
bacteria in
in the
the blood
blood stream
stream
Then can
tissue. Cysts
tissue. Cysts with
with larvae
larvae areare formed
formed in in these
these cells
cells can bebe enough
enough to to cause
cause infection
infection ofof CNS.
CNS. TheThe number
number and and duration
duration that
that
Latent forms:
forms: usually
usually disrupters
disrupters of of cysts
cysts and
and proliferation
proliferation of
of the
the bacteria
bacteria is is in
in the
the blood
blood stream
stream is is the
the mediating
mediating factor
factor inin the
the bacteria’s
bacteria’s
Latent entry
tachzoites
tachzoites causecause infection
infection into
into the
the CSN.
CSN.
Works Cited Carruthers, Vern B., and Yasuhiro Suzuki. "Effects of Toxoplasma Gondii entry into
into the
the CNS.
CNS.
Chronic Infection on the Brain." Schizophrenia Bulletin 33.3 (2007): 745-51. Print. Dugdale, The
The CNS
CNS infection
infection is is believed
believed to to occur
occur in
in the choroid
the choroid plexus,
plexus, where
where
Chronic infections of the protozoan leads to tissue remodeling in
infections of the protozoan leads to tissue remodeling in blood
the brain
the brain and
and a a continuous
continuous requirement.
requirement. Tissues
Tissues around
around the
the
David C. "Brain Abscess: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia." National Library of
blood is filtered to
is filtered to become
become cerebrospinal
cerebrospinal fluid,
fluid, is
is the
the site
site of
of entry
entry into
into the
the
Medicine - National Institutes of Health. ADAM, 15 Sept. 2010. Web. 30 May 2011. CNS.
area send
area send outout signals
signals to to inhibit
inhibit or
or attracting
attracting both
both T-cells
T-cells coming
coming <http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000783.htm>. Robin T Clark, J CNS.
in and
and out.
out. Causes
Causes associated
associated with with Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and and mental
mental Philip Nance, Shahani Noor and Emma H Wilson (2011) T-cellproduction of matrix
This
This causes
causes meningitis
meningitis andand many
many deaths
deaths inin children
children under
under thethe age
age of
of
in five.
retardation,
retardation, delusions,
delusions, hydrocephaly
hydrocephaly or or microcephyaly.
microcephyaly. Causes
Causes
metalloproteinases and inhibition of parasite clearanceby TIMP-1 during chronic five. There
There is is aa vaccine
vaccine but
but itit is
is very
very expensive
expensive and and difficult
difficult to
to distribute.
distribute.
behavior change in animal and human hosts. For example, Toxoplasma infection in the brain. ASN NEURO
behavior change in animal and human hosts. For example, (1):art:e00049.doi:10.1042/AN20100027Ren, Ruibao, and Vincent Racaniello.
causes rats
causes rats toto be
be fearless
fearless of of cats.
cats. ItIt is
is related
related toto immune
immune "Poliovirus Spreads from Muscle to the CentralNervous System by Neural
response, brain
response, brain development,
development, and and response
response to to other
other infectious
infectious Pathways." Journal of Infectious Diseases 166.4 (1992): p747-752. Web. 26 May
agent.
agent. 2011. <http://www.jstor.org/stable30112969 .>. "Poliomyelitis; Fact Sheet." World
Health Organiziation . WHO, Nov 2010. Web. 26May 2011.
<http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs114/enindex.html>. Tatter, Stephen
B., and Jonathan W. Hopkins. "Cerebral Manifestations of Ascaris Lumbricoides."
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1997). Print. United States of America. CDC.
Division of Parasitic Disease. Preventing Congenital Toxoplasmosis. Ed. James M.
Hughes and Daniel G. Colley. Print.
You might also like
- @anesthesia - Books 2015 Basic Physiology For Anaesthetists PDFDocument455 pages@anesthesia - Books 2015 Basic Physiology For Anaesthetists PDFovi67% (3)
- SAB HLTAAP001 Recognise Healthy Body SystemsDocument67 pagesSAB HLTAAP001 Recognise Healthy Body SystemsBbas T.95% (20)
- Black Friday Sheet MusicDocument8 pagesBlack Friday Sheet MusicJemma Louise McClelland0% (1)
- Her EmbraceDocument10 pagesHer EmbraceKellen Green100% (2)
- Donizetti - Una Furtiva Lagrima, PartituraDocument5 pagesDonizetti - Una Furtiva Lagrima, PartituraSidney Dutra100% (1)
- 2.0 Exercise PhysiologyDocument54 pages2.0 Exercise PhysiologyPeter WalidNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science VI-Nervous SystemTrishia Mandapat75% (4)
- Science 6 BYMEDocument30 pagesScience 6 BYMElolavillanueva81% (16)
- Wylie, ClareDocument1 pageWylie, ClareMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Bio Notw NewDocument19 pagesCell and Molecular Bio Notw NewPASSORN SAE JEWNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesParasitology Lecture NotesRica DezaNo ratings yet
- Forgan In: FrankDocument1 pageForgan In: FrankJANNAH MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - EukaryoticDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 5 - EukaryoticYuume YuuNo ratings yet
- Apiculture NotesDocument2 pagesApiculture Notesaniketrathod2905No ratings yet
- L1 - Gene ExpressionDocument5 pagesL1 - Gene Expressiontowalovesports920No ratings yet
- Oral Sur 3 FinalDocument20 pagesOral Sur 3 Finalnapat kidsanakaraketNo ratings yet
- Reklamobil-Mobile Ad Industry 2009 by MobileraDocument1 pageReklamobil-Mobile Ad Industry 2009 by Mobileraasliguel_aktasNo ratings yet
- 21900511 - 이성민 - Chapter 3 Reading SummaryDocument1 page21900511 - 이성민 - Chapter 3 Reading Summary이성민학부생No ratings yet
- entitie: NeverDocument1 pageentitie: NeverMr. ACDCNo ratings yet
- Clin - para LA3 MORENODocument9 pagesClin - para LA3 MORENOmoreno.keexiajoyNo ratings yet
- สรุปตาม GuidelineDocument1 pageสรุปตาม GuidelineMawin PraprutdeeNo ratings yet
- Beam 2.10.23Document1 pageBeam 2.10.23Sumana SorathiwaNo ratings yet
- Dust in The Wind For 2 CellosDocument3 pagesDust in The Wind For 2 CellosAlecs SantanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Short Notes 2Document6 pagesBiology Short Notes 2Humayun KhanNo ratings yet
- Ectonil Pour On 61Document4 pagesEctonil Pour On 61felipe melendezNo ratings yet
- Kidneys - FactRecallDocument2 pagesKidneys - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- DahoDocument29 pagesDahofodiy49587No ratings yet
- Amplifying DNA Fragments - FactRecallDocument2 pagesAmplifying DNA Fragments - FactRecallsabinaNo ratings yet
- EXPBIOMED - Module 4 FinalnotesDocument9 pagesEXPBIOMED - Module 4 FinalnotesSophia KIMNo ratings yet
- Haventic: Setting Air in MotionDocument9 pagesHaventic: Setting Air in MotiongepetosdNo ratings yet
- Abcam Adhesion and MethastasisDocument1 pageAbcam Adhesion and MethastasisJosé Jiménez VillegasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument1 pageAnatomy NotesJoe hoeNo ratings yet
- 0412 Katia Shrug InstructionsDocument1 page0412 Katia Shrug InstructionsJudy ZedalisNo ratings yet
- Model Color: Blending Oils and Enamels Highlighting With AcrylicsDocument2 pagesModel Color: Blending Oils and Enamels Highlighting With AcrylicsKeith MoNo ratings yet
- 全身動脈圖表整理Document1 page全身動脈圖表整理irenesong922840053No ratings yet
- Forbrain'S Flyer 8 Pages: Use Your Voice To Boost Your BrainDocument2 pagesForbrain'S Flyer 8 Pages: Use Your Voice To Boost Your BrainDoremiMarinosNo ratings yet
- Tema 6 - Derivación DiscretaDocument5 pagesTema 6 - Derivación DiscretaLuyi WangNo ratings yet
- PeriniumDocument11 pagesPeriniumTahaNo ratings yet
- ECE BAS301 22 (Responses)Document2 pagesECE BAS301 22 (Responses)sejal singhNo ratings yet
- Desamor: Jesús Salamanca Martín A María de Los Santos, Mi EsposaDocument3 pagesDesamor: Jesús Salamanca Martín A María de Los Santos, Mi EsposaDaniNo ratings yet
- Vision PhysiologyDocument1 pageVision PhysiologyOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Frehner Schmid PellierDocument1 pageFrehner Schmid PellierFasha Nurkala KalidasaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning 5Document1 pageStrategic Planning 5Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- General Condtions Fidic 1999Document1 pageGeneral Condtions Fidic 1999ISAAC KIPSEREMNo ratings yet
- TOON Timetable 20230514 36db18aaDocument2 pagesTOON Timetable 20230514 36db18aaMr ChipsNo ratings yet
- Routes of Administration PDFDocument1 pageRoutes of Administration PDFnazbeen.ahmadiNo ratings yet
- 11 Network - Poster - Pbde CabelloDocument1 page11 Network - Poster - Pbde CabelloSabrina MammanaNo ratings yet
- Is This MeDocument3 pagesIs This MeDarwin BordonNo ratings yet
- AspirationsDocument10 pagesAspirationsdr satnam kaurNo ratings yet
- Model ColorDocument2 pagesModel ColorAlexander ShereshovetsNo ratings yet
- (1846) Henry W. Haynes (HWH) Athenaeum 1846Document1 page(1846) Henry W. Haynes (HWH) Athenaeum 1846Spencer S. DilleyNo ratings yet
- Bildschirmfoto 2022-05-08 Um 11.39.35Document1 pageBildschirmfoto 2022-05-08 Um 11.39.35Giorgi AlimbarashviliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DNA ReplicationDocument1 pageChapter 2 DNA ReplicationYuume YuuNo ratings yet
- Organisms: UsingDocument6 pagesOrganisms: UsingsponchywanNo ratings yet
- Gram PositiveDocument1 pageGram PositiveJANNAH MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Existing MATA NetworkDocument1 pageExisting MATA Networkmcorbet6231No ratings yet
- Wizzair Magazine Mediakit 2022Document14 pagesWizzair Magazine Mediakit 2022RobertVasilescuNo ratings yet
- Mandibular and Maxilla FractureDocument1 pageMandibular and Maxilla Fracturenapat kidsanakaraketNo ratings yet
- Famplanenglishd 28533Document2 pagesFamplanenglishd 28533Sawera ChNo ratings yet
- (Zoology) FINAL EXAM (THEORY) BOT-705, Spring (Responses) - Form Responses 1Document1 page(Zoology) FINAL EXAM (THEORY) BOT-705, Spring (Responses) - Form Responses 1Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- CH 28 - Absorptive ProtistsDocument7 pagesCH 28 - Absorptive ProtistsElle QuizonNo ratings yet
- Rust Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRust Cheat SheetLắng DũngNo ratings yet
- 00192-Response LetterDocument3 pages00192-Response LetterlegalmattersNo ratings yet
- Development Psychology 2Document2 pagesDevelopment Psychology 2lovely sowmiNo ratings yet
- It's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentFrom EverandIt's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemMatt Stone100% (1)
- Human Anatomy Human Anatomy Human AnatomyDocument21 pagesHuman Anatomy Human Anatomy Human AnatomyYuvaNo ratings yet
- Dermatome MapsDocument8 pagesDermatome MapsPedro BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday Feb 29Document4 pagesCatch Up Friday Feb 29leicatapangNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesDenis QosjaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Review Answer KeyDocument18 pagesNervous System Review Answer Keydanieljohnarboleda67% (3)
- Nervous System LecDocument26 pagesNervous System LecLuningning Nobleza100% (3)
- Nervous SystemDocument46 pagesNervous SystemsureshdassNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesNervous SystemHugo ChangNo ratings yet
- Ebook Clinical Neuroanatomy PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Clinical Neuroanatomy PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.wheat692100% (29)
- 3rd Quarter Exam G10Document2 pages3rd Quarter Exam G10Jane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of ANS Lecture 1 by Dr. Mudassar Ali RoomiDocument19 pagesPhysiology of ANS Lecture 1 by Dr. Mudassar Ali RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- PCP - Week 2 - QsDocument4 pagesPCP - Week 2 - Qsapi-502171898100% (1)
- Nervous Tissue Modified 2020Document10 pagesNervous Tissue Modified 2020محمد ابن نوضىNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemAnn SerratoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemDocument105 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous SystemAllisya HaneeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- MUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Document22 pagesMUHS BPTH I Year Amended 180609Kumar G PalaniNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument1 pageCranial Nerves品錞RenéeNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Text Book ReadingDocument5 pagesAnestesi Text Book Readingli2delNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Ein 3Document42 pagesMeningitis Ein 3Rifqi FuadiNo ratings yet
- Vanders Chapter 6Document53 pagesVanders Chapter 6gablimlikescheeseNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument35 pagesReflexesNadia AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument2 pagesNerve CellEuro Anthony SayonNo ratings yet
- Forearm and Hand - FRCEM SuccessDocument289 pagesForearm and Hand - FRCEM SuccessskNo ratings yet